Winter melon nutrition: calories, carbs, GI, protein, fiber, fats

Introduction
Winter melon is a well-known vegetable/fruit consumed chiefly in Asian countries (1). While it is a fruit from a botanical point of view, it is sometimes used and consumed as a vegetable.
Winter melon is native to Japan and is grown in hot countries. Also known as a wax gourd, winter melon has a lot of health benefits and has various medical uses worldwide. The gourd has been known for its pharmaceutical attributes and therapeutic and healing properties (2).
It has low amounts of anti-nutrients and a decent amount of nutrients, making it a wholesome food to consume (3).
Further research is needed to prove its pharmacological effects on humans.
In this article, an in-depth nutrition analysis of the winter gourd will be conducted, along with a discussion of its health benefits and risks.
Table of contents
- General Information
- Varieties
- Nutrition
- Weight Loss and Diets
- Health Impact
- Health Benefits
- Cardiovascular
- Diabetes
- Cancer
- Mental Health and Brain Health
- Pregnancy
- Immune Health
- Sexual Health
- Analgesic and Antiedemic Effects
- Digestive Health
- Kidney Health
- Aging
- Downsides and Risks
- Cooking and Use
- Storage, Keeping, and Conservation
- History
- Production and Consumption
- Price
- References
General Information
Classification
Wax gourd is scientifically called Benincasa hispida (1). It belongs to the Cucurbitaceae family, the same family as cucumber, melon, squash, gourd, and zucchini (4).
The cucurbit family is genetically diverse and grows in drought-prone regions (5). Cucurbits belong to a family of plants known for their numerous health benefits. The gourd family is rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and phytonutrients (6).
Winter melon has many other English names, such as white gourd, ash gourd, wax gourd, white pumpkin, tallow gourd, gourd melon, and Chinese watermelon (2). Other names include kundur fruit, chalkumra, Chinese preserving melon, and ash pumpkin (7).
The label “winter” comes from the fact that it can be stored in summer and eaten in winter.
Taste and Appearance
The wax gourd has a mild and sweet taste that is almost bland. This makes it a great medium to absorb whatever flavor it is put in. It is used as a vegetable in Asian countries. However, unlike its relatives, like cucumber, it cannot be eaten raw. It has to be cooked.
The immature fruits have little hairs, while the mature ones lose their fuzz and develop a waxy layer, hence its name - wax gourd (7). The winter melon may resemble a combination of cucumber, pumpkin, and zucchini. This is because it is a relative of these plants. The gourd has an oblong shape. It has white flesh and a cavity in the center with a mushy substance and seeds.
Varieties
There are many winter melon varieties, including honeydew melon, casaba, Santa Claus type, etc. (8). Two cultivars of winter melon are grown in Malaysia (9).
A study identified 16 different cultivars of winter melon according to different shapes, sizes, and skin colors (10).
Nutrition
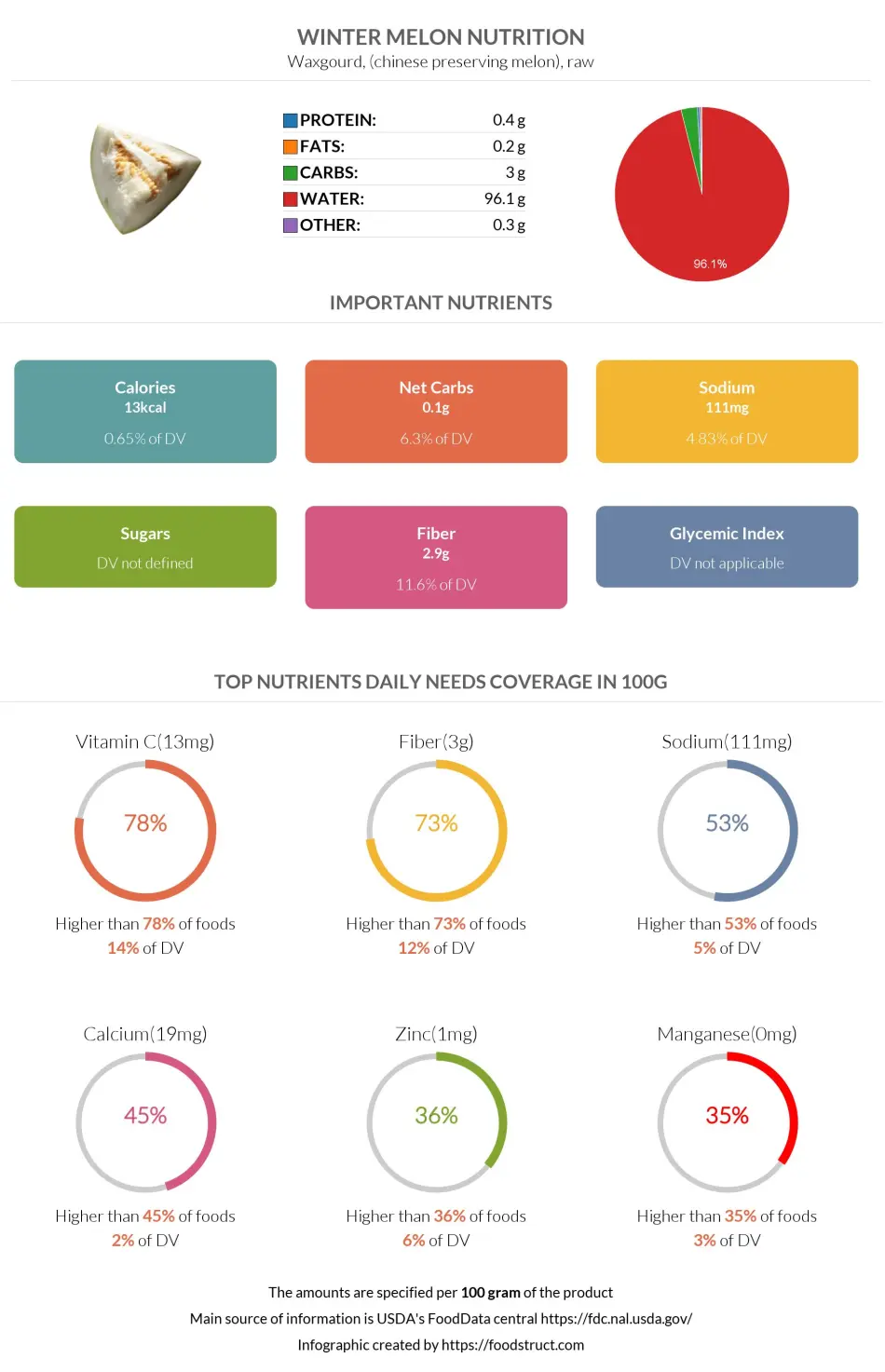
One average serving of winter melon per person is 1 cup of 132 grams. However, the infographics below will be presented for 100g servings of winter melon.
This fruit is composed of 94% water. The remaining 6% is nutrients, predominantly carbohydrates. Winter melon is an excellent source of vitamin C. Similarly, it is relatively rich in fiber, sodium, calcium, and zinc.
Macronutrients chart
Macronutrient Calories
Calories
Winter melon contains 13 calories per 100 grams and 17 calories per average serving size. Thus, it is a very low-calorie food.
Winter melon falls in the top 2% of foods low in calories compared to the other foods in our database.
Carbohydrates
One hundred grams of this food provides 3g of carbohydrates per 100g serving. This carb content consists of 2.9g of dietary fiber and 0.1g of net carbs. This is 542 times lower than net carbs in chocolate. It is, therefore, a low-carbohydrate food.
Winter melons have 1.2 times more fiber than oranges. 100 grams covers 12% of daily fiber needs, falling in the top 27% of foods as a nutrient source.
In a study that compared the crude fiber content of cucurbit family plants, ash gourd contained the highest amount of crude fiber (3).
The food also contains 0g of sugar, which is suitable for people following a low-sugar diet.
Fiber content ratio for Winter melon
Protein
Winter melon does not contain notable amounts of protein, providing less than 1g of protein (0.4g per 100g).
However, it does contain some free amino acids.
The amino acids are mostly focused in the seeds of this plant and least in the pulp (11).
Winter melon seeds have been shown to have a decent amount of gamma-aminobutyric acid, also known as GABA, an important neurotransmitter indispensable for brain health (12).
Fats
Ash gourd contains an insignificant amount of fats - just 0.1g per 100g.
Naturally, winter melon also contains no cholesterol.
Vitamins
Overall, winter melon is not a great source of vitamins.
Winter melon lacks the fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, K and water-soluble cobalamine or vitamin B12. It contains some vitamins B1, B3, B6, B5, and folate or B9.
It’s primarily rich in vitamin C and vitamin B2.
At the same time, one hundred grams of this food covers 14% of the daily need for vitamin C. However, the amount of vitamin C it contains is 4.1 times less than lemon. Furthermore, 100 grams of winter gourd covers 8% of daily vitamin B2 needs.
Vitamin coverage chart
Minerals
Among all the studied minerals, 100g of this food covers the daily need for iron and zinc the most (5% and 6%, respectively).
This fruit provides moderate levels of calcium and manganese and is low in magnesium, phosphorus, copper, selenium, and potassium.
Winter melon is relatively high in sodium, containing 111mg per 100g serving.
Winter melon lacks choline.
Mineral coverage chart
Phytochemicals
Winter melon provides gallic acid, a potent antioxidant compound, and phenolic acid, known for its various health benefits (18).
Glycemic Index
While an exact value for the glycemic index of winter melon has not been researched, it can assumed to be low due to its very low content of net carbs.
Acidity
The acidity based on PRAL, i.e., potential renal acid load value, is 0.3. The higher the positive value of the PRAL, the more acid the food produces in your body.
Weight Loss and Diets
Winter melon is rich in dietary fiber, helping keep you full for a longer time, thus limiting your food consumption (13).
It is also very low in calories, fats, and sugars. It is an optimal addition to a weight loss diet plan.
| Keto | A 100-gram serving contains 0.1g of net carbs. It is very low in carbs and can be consumed on a keto diet. |
| DASH | The DASH diet is typically used to lower blood pressure. It focuses mainly on fruits and vegetables. One study suggested that winter melon has an ACE-inhibiting effect. This means it has an effect similar to blood pressure-lowering drugs (however, it should not be used as a drug replacement). Therefore, winter melon can be consumed on the DASH diet. |
| Atkins | Winter melon can be consumed on an Atkin’s diet, as a 100-gram serving contains only 3g of carbohydrates. |
| Mediterranean | The Mediterranean diet involves eating plant-based foods and a lot of fruits and vegetables. Hence, ash gourd can be consumed on this diet. |
| Paleo | The paleo diet involves eating whole foods that are not processed, including lots of fruits and vegetables. Winter melon is, therefore, paleo-friendly. |
| Vegan/ Vegetarian/ Pescetarian | Winter melon is suitable for vegans, vegetarians, and pescetarians. It is void of animal products. |
| Gluten-free | Winter melon is gluten-free. |
| Dukan | Winter melon cannot be consumed during the first phase of the Dukan diet (the Attack Phase). |
| Intermittent Fasting | Winter melon cannot be consumed during fasting hours. However, they can naturally be consumed during eating periods. |
| Low Fat & Low-Calorie | Winter melon is very low in fats and low in calories. Therefore, it can be consumed on a low-fat and low-calorie diet. |
| Low Carb | It is very low in carbohydrates (0.1g of net carbs and 3g of carbohydrates per 100g serving). |
| Anti Inflammatory | It is full of anti-inflammatory compounds and can be consumed on an anti-inflammatory diet. |
| BRAT | Winter melon is gentle on the stomach and can be used in a BRAT diet. |
Health Impact
Health Benefits
The fruit has some properties, such as anti-ulcerative, anti-obesity, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, vasodilating, etc. This is mainly due to the bioactive compounds present in this food.
Wax gourd seeds, which are often discarded, also have various properties. This needs to be further investigated by the medical community (14).
Cardiovascular
ACE inhibitors (angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors) are substances that dilate blood vessels and thus lower blood pressure. These are regular blood pressure medication constituents that are prescribed by a physician. In one study, wax gourd extract was shown to have angiotensin-converting enzyme-inhibiting activity (it has an ACE-inhibiting effect). Wax gourd, therefore, has cardioprotective capabilities (15).
Winter melon may be used as a cardiotonic as it has been used historically (16). However, further evidence is needed.
Moreover, winter melon contains potassium, which is known to be a vasodilator, dilating blood vessels and aiding in the lowering of blood pressure.
Diabetes
Extract from white pumpkin lowered blood glucose levels in diabetic rats. It was also shown to decrease cholesterol, triglycerides, and LDL (low-density lipoprotein) values ompared to diabetic rats who did not receive the treatment (17).
So, B. Hispida can improve lipid metabolism in diabetic rats (further studies are needed to prove that in humans).
On top of that, ash gourd contains gallic acid, a chemical compound known to reduce the risk of diabetes type 2 (18).
Cancer
Winter gourd has cytotoxic and anticancer effects. Furthermore, it exhibits a dose-dependent anti-inflammatory activity (19).
Winter melon has antioxidant effects as well (20). Antioxidants are known to scavenge free radicals and protect cells from damage.
Moreover, ash gourd fruit was shown to have 5 alpha-reductase inhibiting effects (21). Five alpha-reductase inhibitors block the hormone DHT (dihydrotestosterone) and are used to treat the enlarged prostate gland. The ash gourd fruit was shown to stop the testosterone-induced abnormal growth of prostate cells in rats (21).
Mental Health and Brain Health
In one animal model study, the winter melon extract exhibited an anti-anxiety (anxiolytic) effect (22).
A chemical called γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) was isolated from the ash gourd. This substance has mental health benefits (12). A substance in winter melon has also been used as an ayurvedic treatment for epilepsy (12).
Ash gourd juice extract was shown to have anti-depressive effects (23). Fresh ash gourd juice improved morphine withdrawal symptoms in rats (24).
Moreover, this food is used in Ayurvedic medicine to treat schizophrenia (25).
Pregnancy
Winter melon may be consumed in moderation during pregnancy. However, always consult your physician first. The fiber content in winter melon helps relieve constipation. Additionally, the zinc and vitamin C present in the food help improve the immune system.
Immune Health
Winter melon has antimicrobial effects (26). Moreover, winter melon is rich in vitamin C, which is necessary to create immune cells. The zinc contained in this food also strengthens the immune system.
Sexual Health
Winter melon may be beneficial in treating sexually transmitted diseases. Winter melon seed oil is used to treat syphilis, and the seed ash is used to treat gonorrhea in some countries (27).
Analgesic and Antiedemic Effects
Traditionally, winter gourd has been used as an analgesic (pain-blocking) and in managing fever. Extracts have been shown to have antinociceptive (pain-blocking) and antipyretic (fever-lowering) effects. The analgesic effects may be due to phytonutrients called flavonoids (28).
Two chemicals isolated from the wax gourd, called alnusenol and multiflorenol can inhibit histamine release in the smooth muscles, thus providing an analgesic effect (29).
Ash gourd also has anti-edematous properties, reducing swelling (30).
Digestive Health
Winter melon is 97% water and high in fiber, so it helps improve the digestive process (31).
A study showed the anti-ulcerogenic activity of Benincasa hispida extract, which further substantiates its use in treating ulcers in Ayurvedic medicine. The extract may be further considered as a constituent of ulcer drugs. Winter gourd heals ulcers and neutralizes stomach acids (32).
Winter melon has an antidiarrheal effect, as demonstrated by a research paper (33).
It can act as a vermifuge, too. A vermifuge is an antiparasitic substance that expels parasites from the body (34).
Kidney Health
Benincasa hispida had renoprotective (kidney-protecting effects) in rats with induced kidney failure (35).
In addition, it has been used in ancient Ayurvedic medicine to treat kidney infections (36).
It has been used in Ayurveda in the treatment of kidney stones (urinary calculi) as well (16).
Aging
A study revealed that Benincasa hispida has anti-aging effects on the skin and that a cream made from B. hispida extract can actually help slow down the aging appearance of the skin (37).
Downsides and Risks
A study showed that the consumption of 70% extract of winter melon, up to 1000mg/kg of body weight, is non-toxic and safe in rats. However, further studies are needed to confirm this in humans (38).
Pregnant and lactating women should consult their physicians first before consuming the food.
Cooking and Use
Winter gourd is a versatile ingredient. It can be eaten in many ways: baked, sauteed, candied, jammed, boiled, parboiled, steamed, grilled, and fried. It can be used in soups, smoothies, jams, teas, stews, etc. It can also be eaten raw in salads. The ash gourd is used in India to make petha candies (31).
The seeds can be consumed, too, similar to how sunflower seeds are consumed.
Winter Melon Tea
Winter melon tea is a great soothing tea. It is free of sugar (you can add your preferred sweetener).
To make winter melon tea, simmer the pulp in water for 30 minutes to an hour. Then, sift the tea, and don’t forget to squeeze the remaining tea from the spongy melon chunks.
Winter Melon Juice
Preparing winter melon juice involves peeling the fruit and removing the seeds. This is followed by cutting the pulp into chunks and juicing it using a juicer.
Storage, Keeping, and Conservation
Given that the white pumpkin is in average shape and is not scarred, it can be stored for an extended period (up to a year). This is due to a waxy protective layer that is present around this fruit (12).
History
Winter gourd has been used in many medicinal systems, including the Ayurvedic System, Traditional Chinese Medicine, and Unani Medicine (3).
Wax gourd has been grown all over Asia (39). The ash gourd may have been domesticated in these two regions: Southern China and Southeastern Nepal (10).
Production and Consumption
The ash gourd is grown on a vine. It is relatively more straightforward to grow compared to other plants in the cucurbit family and is to be grown in dry areas (40). Excessive humidity will negatively affect the growth of this plant.
Price
You can find winter melons in India for the price of 0.5$/kg (41).
References
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/301563102
- http://www.ijpsr.info/docs/IJPSR13-04-12-007.pdf
- https://hero.epa.gov/hero/index.cfm/reference/details/reference_id/8163668
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/285889089
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/225777988
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2210523913000160
- https://www.hindawi.com/journals/omcl/2021/6349041/
- Honeydew and Other Winter Melons in the Garden
- https://www.academia.edu/9263823/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/226246482
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/215644067
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0963996910003996
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21676152/
- http://www.pakbs.org/pjbot/PDFs/43(4)/PJB43(4)2029.pdf
- https://www.academia.edu/23257113/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8683187/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1995764511600254
- http://journalarticle.ukm.my/7515/1/09_Z._Fatariah.pdf
- https://www.cabdirect.org/cabdirect/welcome/?target=%2fcabdirect%2fabstract%2f20113060170
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/10496475.2014.940437
- Effect of Benincasa hispida fruits on prostatic in Nandecha Nahata
- International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Phytopharmacological Research
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/285889250
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11077182/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/45268094
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4009219/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/26317575
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19553176/
- Effect of methanolic extract of Benincasa hispida induced bronchospasm
- https://scialert.net/fulltext/?doi=ijp.2010.652.657&org=11
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11694361
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.2042-7158.1994.tb05722.x
- http://www.bioline.org.br/pdf?pt05006
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9612135/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19395782/
- https://www.cabdirect.org/cabdirect/welcome/?target=%2fcabdirect%2fabstract%2f19890357093
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3193683/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0273230020302117
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/288476545
- http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.854.2454&rep=rep1&type=pdf
- https://www.indiamart.com/proddetail/fresh-winter-melon-16408945148.html
Top nutrition facts for Winter melon

| Calories ⓘ Calories for selected serving | 13 kcal |
| Net Carbs ⓘ Net Carbs = Total Carbohydrates – Fiber – Sugar Alcohols | 0 grams |
| Default serving size ⓘ Serving sizes are mostly taken from FDA's Reference Amounts Customarily Consumed (RACCs) | 1 cup, cubes (132 grams) |
| Acidity (Based on PRAL) ⓘ PRAL (Potential renal acid load) is calculated using a formula. On the PRAL scale the higher the positive value, the more is the acidifying effect on the body. The lower the negative value, the higher the alkalinity of the food. 0 is neutral. | 0.3 (acidic) |
| Oxalates ⓘ https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Level-of-some-anti-nutrients-present-in-ash-gourd-fruit_tbl2_337854043 | 3 mg |
Winter melon calories (kcal)
| Calories for different serving sizes of winter melon | Calories | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Calories in 100 grams | 13 | |
| Calories in 1 cup, cubes | 17 | 132 g |
| Calories in 1 waxgourd | 741 | 5700 g |
Mineral chart - relative view
Vitamin chart - relative view
Protein quality breakdown
Fat type information
All nutrients for Winter melon per 100g
| Nutrient | Value | DV% | In TOP % of foods | Comparison |
| Vitamin A | 0µg | 0% | 100% | |
| Calories | 13kcal | 1% | 98% |
3.6 times less than Orange
|
| Protein | 0.4g | 1% | 91% |
7.1 times less than Broccoli
|
| Fats | 0.2g | 0% | 88% |
166.6 times less than Cheese
|
| Vitamin C | 13mg | 14% | 22% |
4.1 times less than Lemon
|
| Net carbs | 0.1g | N/A | 74% |
541.7 times less than Chocolate
|
| Carbs | 3g | 1% | 66% |
9.4 times less than Rice
|
| Cholesterol | 0mg | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Vitamin D | 0µg | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Magnesium | 10mg | 2% | 84% |
14 times less than Almonds
|
| Calcium | 19mg | 2% | 55% |
6.6 times less than Milk
|
| Potassium | 6mg | 0% | 97% |
24.5 times less than Cucumber
|
| Iron | 0.4mg | 5% | 80% |
6.5 times less than Beef broiled
|
| Fiber | 2.9g | 12% | 27% |
1.2 times more than Orange
|
| Copper | 0.02mg | 3% | 91% |
6.2 times less than Shiitake
|
| Zinc | 0.61mg | 6% | 64% |
10.3 times less than Beef broiled
|
| Phosphorus | 19mg | 3% | 89% |
9.6 times less than Chicken meat
|
| Sodium | 111mg | 5% | 47% |
4.4 times less than White bread
|
| Manganese | 0.06mg | 3% | 65% | |
| Selenium | 0.2µg | 0% | 94% | |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.04mg | 3% | 78% |
6.7 times less than Pea raw
|
| Vitamin B2 | 0.11mg | 8% | 66% |
1.2 times less than Avocado
|
| Vitamin B3 | 0.4mg | 3% | 81% |
23.9 times less than Turkey meat
|
| Vitamin B5 | 0.13mg | 3% | 86% |
8.5 times less than Sunflower seeds
|
| Vitamin B6 | 0.04mg | 3% | 85% |
3.4 times less than Oats
|
| Vitamin B12 | 0µg | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Folate | 5µg | 1% | 79% |
12.2 times less than Brussels sprouts
|
| Trans fat | 0g | N/A | 100% |
N/A
|
| Saturated fat | 0.02g | 0% | 92% |
368.4 times less than Beef broiled
|
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.04g | N/A | 86% |
264.8 times less than Avocado
|
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.09g | N/A | 86% |
542.2 times less than Walnut
|
| Tryptophan | 0mg | 0% | 98% |
152.5 times less than Chicken meat
|
| Lysine | 0.01mg | 0% | 98% |
50.2 times less than Tofu
|
| Methionine | 0mg | 0% | 98% |
32 times less than Quinoa
|
Check out similar food or compare with current
NUTRITION FACTS LABEL
Serving Size ______________
Health checks
Winter melon nutrition infographic
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.



