Tahini vs. Almond butter - Health and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Tahini is higher in carbs, saturated fats, polyunsaturated fats, zinc, copper, selenium, iron, phosphorus, sodium, and B complex vitamins. In comparison, almond butter is higher in proteins, monounsaturated fats, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, and vitamins B2 and E. They offer numerous health benefits and can be added to our diets in moderation.
Introduction
This article compares two types of spreadable foods: tahini and almond butter.
The first difference is that tahini comes from sesame seeds, whereas almond butter, as the name states, comes from almonds.
Both have many differences in nutritional content, health impacts, and general differences.
Nutrition
Regarding their nutritional contents, let’s compare 100g of tahini to almond butter.
Tahini and almond butter are nutrient-packed foods with remarkable nutritional profiles.
Calories
Almond butter is higher in calories than tahini.
Almond butter contains 614 calories, whereas tahini contains 595 calories.
Carbs
Tahini is higher in carbs than almond butter. Tahini contains 21.2g of carbs, whereas almond butter contains 18.8g of carbs.
Fiber
Even though almond butter is lower in carbs, it is higher in fiber. They both contain a decent amount of fibers. Almond butter contains 10.3g of fiber, whereas tahini contains 9.3g.
Eating 100g of tahini or almond butter is not advised to get the fiber from it.
Protein
Almond butter is richer in protein than tahini. Tahini contains 17g of protein, whereas almond butter contains 21g.
You can read about peanut butter vs. almond butter in this article.
Fats
The main source of calories and the highest macronutrient in both is fat. However, their amount is close, with almond butter slightly higher, equaling 55.5g, whereas tahini contains 54g.
The main difference comes in the type of fatty acid distributions.
Tahini contains almost double the amount of saturated fats compared to almond butter. In addition, tahini is richer in polyunsaturated fats by a difference of 10 grams.
Almond butter is richer in monounsaturated fats.
The major fat type in tahini is polyunsaturated fats, whereas almond butter is monounsaturated fats.
Minerals
Both these foods are highly dense in minerals.
Tahini is richer in zinc, copper, selenium, iron, and phosphorus and is higher in sodium.
In comparison, almond butter is richer in magnesium, manganese, and potassium.
It is important to mention that both are highly rich in these minerals collectively. For comparison purposes, we are stating which one is richer. You can visualize their mineral distributions in the diagrams below.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+193.7%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+80.7%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-93.9%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+46.4%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+22.8%
Contains
more
IronIron
+156.4%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+72.4%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+40.4%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+44.1%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+1333.3%
Vitamins
Tahini is richer in most B complex vitamins: B1, B3, B5, B6, and folate. In comparison, almond butter is richer in vitamins B2 and E. Almond butter also contains many B complex vitamins.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+9584%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+98.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+2875.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+72.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+117.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+44.7%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+84.9%
Oxalate
Since tahini is made of sesame and almond butter from almonds, let’s consider the oxalate contents of sesame and almond butter.
They are both classified as high oxalate foods.
Sesame is higher and contains 380mg of oxalate, whereas almonds contain 296mg of oxalate.
Health Impacts
Although packed with calories and fats, they have some positive health impacts.
The best way to consume them is in moderation and association with other foods.
For example, hummus is prepared with tahini.
Cardiovascular Health
A clinical trial revealed that tahini consumption is associated with lower blood pressure and pulse rate. Additionally, it may improve vascular endothelial function, which is important in the pathogenesis of arterial hypertension (1,2).
According to the study, almond butter may improve lipid profile, especially by reducing LDL (bad cholesterol) levels and increasing HDL (good cholesterol) levels in the blood (3).
It is worth noting that tahini may have a positive effect on the lipid profile, although its mechanisms are currently unknown. Moreover, tahini contains tocopherol, which may lower the risk of atherosclerosis (4).
Consuming almond butter and tahini in moderation may help maintain a healthy cardiovascular system.
Metabolic Health and Diabetes
Consumption of almond butter is associated with decreased risks of metabolic diseases and diabetes. It is also associated with decreased postprandial glucose levels (5)(6).
You can also read about peanut vs. almond in this text.
Almond butter and tahini contain phytochemicals that have antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and anti-carcinogenic properties.
Downsides
Kidney Stones
High oxalate content increases the risk of kidney stones. Tahini and almond butter are high in oxalate, which increases the risk of oxalate stones. In addition, it is best to pay attention to the amount of calcium and oxalate content consumed by individuals with a history of kidney stones from oxalate (7).
However, a nuance here is that tahini and almond butter are rich in calcium aswell. High-calcium foods bind oxalate and remove it from the gastrointestinal system instead of the kidneys (8).
Weight Gain
Since they are low-volume and highly caloric foods, it’s best to consume them in moderation.
Especially in the case of tahini since it's higher in calories.
Allergy
Nut consumption is associated with allergic reactions, especially when both sesame and almonds are associated with allergic reactions.
General Differences
There are many general differences between almond butter and tahini.
Almond butter comes from ground almonds, whereas tahini comes from ground sesame seeds.
Taste and Texture
Tahini has a peculiar and stronger taste than almond butter. Almond butter is milder and can be associated with sweet foods. In comparison, tahini can be associated with sweet and salty foods such as hummus or halva, one being salty and the other sweet.
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34707227/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9616110/
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/07315724.2003.10719293
- https://d1wqtxts1xzle7.cloudfront.net/89942901/tahini--the-magical-condiment-an-indepth-look-at-its-nutritional-and-health-benefits-libre.pdf?1660934174
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2696988/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21276226/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24393738/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30566003/
Infographic
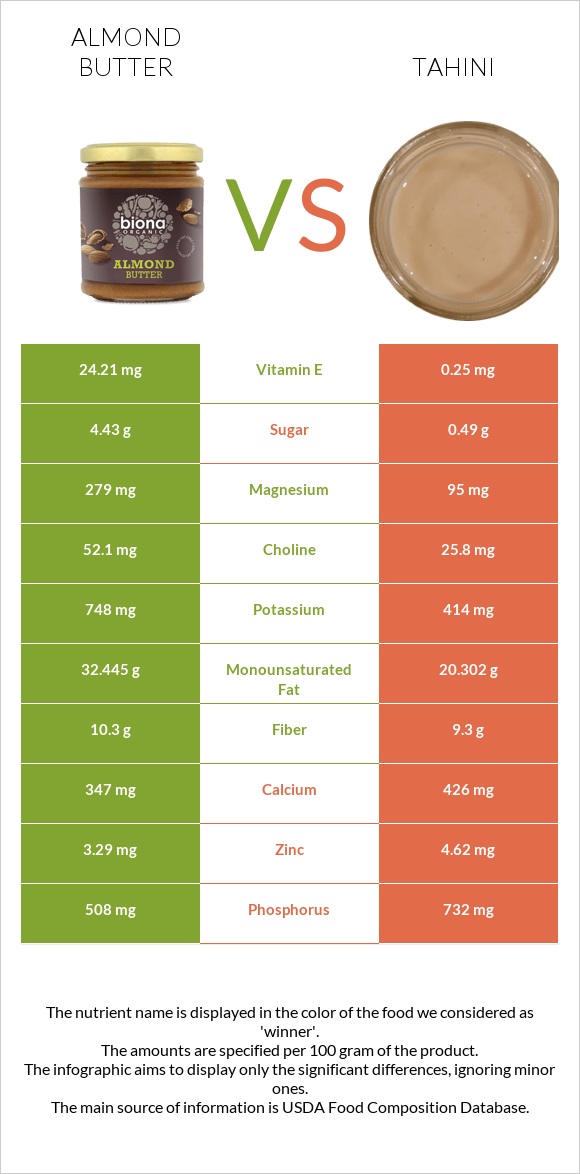
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin E | 24.21mg | 0.25mg | 160% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.041mg | 1.22mg | 98% |
| Copper | 0.934mg | 1.61mg | 75% |
| Iron | 3.49mg | 8.95mg | 68% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 13.613g | 23.564g | 66% |
| Selenium | 2.4µg | 34.4µg | 58% |
| Magnesium | 279mg | 95mg | 44% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.939mg | 0.473mg | 36% |
| Phosphorus | 508mg | 732mg | 32% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 32.445g | 20.302g | 30% |
| Manganese | 2.131mg | 1.456mg | 29% |
| Saturated fat | 4.152g | 7.529g | 15% |
| Vitamin B3 | 3.155mg | 5.45mg | 14% |
| Zinc | 3.29mg | 4.62mg | 12% |
| Folate | 53µg | 98µg | 11% |
| Potassium | 748mg | 414mg | 10% |
| Protein | 20.96g | 17g | 8% |
| Calcium | 347mg | 426mg | 8% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.318mg | 0.693mg | 8% |
| Sodium | 7mg | 115mg | 5% |
| Choline | 52.1mg | 25.8mg | 5% |
| Fiber | 10.3g | 9.3g | 4% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.103mg | 0.149mg | 4% |
| Fats | 55.5g | 53.76g | 3% |
| Calories | 614kcal | 595kcal | 1% |
| Carbs | 18.82g | 21.19g | 1% |
| Net carbs | 8.52g | 11.89g | N/A |
| Sugar | 4.43g | 0.49g | N/A |
| Starch | 0.08g | 0% | |
| Vitamin A | 0µg | 3µg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.159mg | 0.372mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.555mg | 0.706mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.813mg | 0.731mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.483mg | 1.302mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.612mg | 0.545mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.122mg | 0.561mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 1.149mg | 0.901mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.937mg | 0.95mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.55mg | 0.5mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +23.3% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +12.6% |
| Contains more WaterWater | +86% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +62.3% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -44.9% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +59.8% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +73.1% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Almond butter - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168588/nutrients
- Tahini - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170189/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.