Arrowroot vs. Cassava — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Arrowroot is higher in minerals and vitamins. It is also lower in calories, carbs, and saturated fat.
On the other hand, cassava has lower sodium than arrowroot.
Introduction
We will compare cassava and arrowroot regarding nutrition and health impact.
What's The Actual Difference?
Arrowroot, also known as maranta, is a large perennial herb in the Marantaceae family. Cassava, also known as yuca or manioc, is native to South America and belongs to the Euphorbiaceae family. Cassava is a perennial plant, but it is grown as an annual crop. Cassava root has an earthy, slightly sweet, nutty flavor with a hint of bitterness. It benefits from being cooked with strong-flavored ingredients because it is mild. Arrowroot has almost no flavor and is allergy-friendly, making it an excellent choice for those who avoid corn, potatoes, or gluten.
Nutrition
The food varieties used in this article are raw cassava and raw arrowroot. At the bottom of this page, nutrition infographics visually show their differences.
Vitamins
Arrowroot has higher vitamin content than cassava. It contains more folate, Vitamin A, E, B1, B2, B3, B5, and B6.
100g of arrowroot can fully cover your daily folate need.
On the other hand, cassava has nine times more Vitamin C.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+64.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+22.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+98.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+172.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+202.3%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+1151.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+984.2%
Minerals
Arrowroot has more minerals than cassava. It provides seven times more iron and two times more magnesium.
It also has more zinc, phosphorus, potassium, and copper than cassava.
On the other hand, cassava has more calcium and less sodium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+19%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+67.5%
Contains
more
IronIron
+722.2%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+21%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+85.3%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+263%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+166.7%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-46.2%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+120.7%
Calories
The number of calories of cassava is almost three times higher than that of arrowroot. Cassava contains 160 calories per 100g, whereas arrowroot contains only 65 calories per 100g.
Carbs
Cassava has 38 g of carbs, whereas arrowroot has 13.39g.
Fiber
Arrowroot has 1.3g of fiber per 100g, while cassava has 1.8g.
Glycemic Index
Arrowroot has a lower GI than cassava. The glycemic index of arrowroot is 58, while cassava has GI equal to 94.
Health Impact
Gluten-free
Cassava and arrowroot are gluten-free by nature. Their powder can be used in place of wheat flour. Arrowroot's resistant starch benefits gluten-free products by improving texture, crispness, and flavor [1].
Gut Health
Both contain resistant starch, a type that bypasses digestion and has properties similar to soluble fiber.
The beneficial bacteria in your gut are fed by resistant starch, which may help reduce inflammation and promote digestive health [2].
Side Effects
Toxicity
Cassavas have the potential to produce solanine, a toxic glycoalkaloid. These plants can produce solanine, especially when exposed to sunlight or other unfavorable conditions. Diarrhea, vomiting, fever, and abdominal pains are all poisoning symptoms [3].
Infographic
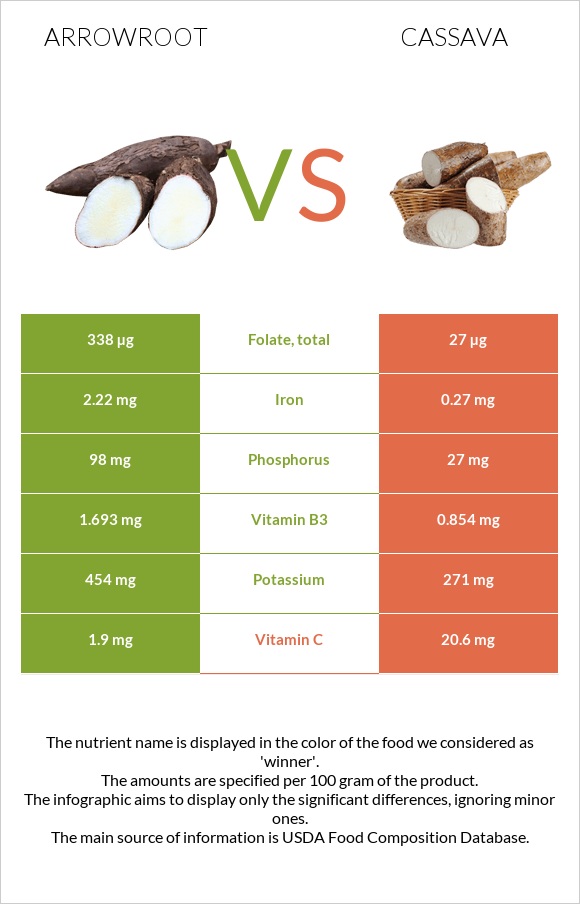
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Folate | 338µg | 27µg | 78% |
| Iron | 2.22mg | 0.27mg | 24% |
| Vitamin C | 1.9mg | 20.6mg | 21% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.266mg | 0.088mg | 14% |
| Phosphorus | 98mg | 27mg | 10% |
| Manganese | 0.174mg | 0.384mg | 9% |
| Carbs | 13.39g | 38.06g | 8% |
| Protein | 4.24g | 1.36g | 6% |
| Calories | 65kcal | 160kcal | 5% |
| Potassium | 454mg | 271mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.143mg | 0.087mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B3 | 1.693mg | 0.854mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.292mg | 0.107mg | 4% |
| Choline | 23.7mg | 4% | |
| Zinc | 0.63mg | 0.34mg | 3% |
| Fiber | 1.3g | 1.8g | 2% |
| Copper | 0.121mg | 0.1mg | 2% |
| Vitamin K | 1.9µg | 2% | |
| Magnesium | 25mg | 21mg | 1% |
| Calcium | 6mg | 16mg | 1% |
| Sodium | 26mg | 14mg | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 0.19mg | 1% | |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.059mg | 0.048mg | 1% |
| Fats | 0.2g | 0.28g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 12.09g | 36.26g | N/A |
| Sugar | 1.7g | N/A | |
| Vitamin A | 1µg | 1µg | 0% |
| Selenium | 0.7µg | 0.7µg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.039g | 0.074g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.004g | 0.075g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.092g | 0.048g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.019mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.028mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.027mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.039mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.044mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.011mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.026mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.035mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.02mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +211.8% |
| Contains more WaterWater | +35.3% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +129% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +40% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +184.2% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -47.3% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +91.7% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +1775% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Arrowroot - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168490/nutrients
- Cassava - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169985/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.



