Beef sirloin vs. Beef tenderloin — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Beef tenderloin is a tender cut with a milder flavor. It is higher in calories and fats, including saturated fats. Beef tenderloin is also richer in iron and vitamins B2, B5, and B12.
In comparison, beef sirloin contains higher amounts of protein, copper, phosphorus, zinc, potassium, and vitamins B3 and B6.
Introduction
This article is a comparison between two cuts of beef meat; beef tenderloin and beef sirloin. They are popular beef cuts, but a difference exists between them. The difference is mainly regarding the tenderness, flavor, and price.
Beef tenderloin is the most tender cut of beef. It comes from the loin section, a long narrow cylindrical muscle. It is also known as filet mignon.
In comparison, sirloin is not as tender and comes from the back loin area of the beef. It is a tougher meat compared to tenderloin.
Regarding its flavor profile, beef tenderloin has a mild and delicate flavor. In comparison, beef sirloin has a robust and beefy flavor.
The culinary usage of each can be different. Tenderloin, being tender, is mostly used for grilling, whereas sirloin can be used for grilling and stew cooking.
Beef tenderloin is the most expensive cut of beef because of its delicacy and high demand. Sirloin is a cheaper cut, and it is also used for grilling.
In short, beef tenderloin is the most tender cut and has a mild and delicate flavor. However, it is more expensive. On the other hand, beef sirloin is a bigger cut and not as tender as tenderloin. Sirloin has a robust and beefy flavor.
Nutritional content comparison
This section will compare 100g of each in cooked forms.
It is very important to consider meat hydration here. Beef tenderloin is 48% water, and sirloin is 63% water.
The fact that tenderloin has looser muscle fibers (thus its tenderness), it loses more water during the grilling process.
Calories
Beef tenderloin is higher in calories by 1.8 times compared to beef sirloin. Beef tenderloin contains 324 calories. In comparison, beef sirloin contains 177 calories.
Carbs
Their carb content is insignificant.
Fats
In this article, we are considering 1/8th trimmed tenderloin, and the sirloin is full trim. Thus, tenderloin is higher in fats compared to sirloin.
Tenderloin contains 25g of fat distributed equally between saturated and monounsaturated fats. In comparison, sirloin is much lower in fats. It contains 5g of fat.
The following diagram is their distribution diagram.
@fattype
Protein
The difference between amounts of protein is very significant; however, beef sirloin is richer in protein compared to tenderloin. Sirloin contains 30g of protein, whereas tenderloin contains 24g.
Below we can visualize their macro distributions.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+28.9%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+31.4%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+389.1%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+430.5%
Minerals
Beef tenderloin is richer in iron. In comparison, beef sirloin is richer in zinc, copper, phosphorus, and potassium.
Below are their mineral distributions.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+22.7%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+144.4%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+23.9%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+41.4%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+24.6%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+69.9%
Contains
more
IronIron
+62%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+44.7%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-13.6%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+27.3%
Vitamins
Tenderloin is richer in vitamins B2, B5, and B12. In comparison, sirloin is richer in vitamins B3 and B6.
Below are their vitamin distributions.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+200%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+142.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+172.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+25%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+59.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+67.3%
Health impacts
Well, focus on the differences here, and we can highlight some health impacts regarding this difference.
As seen in this article, a fully trimmed beef cut is a better option than a fatty one. Tenderloin is higher in fats and specifically saturated fats, compared to sirloin. This increases the risks of cardiovascular diseases. (1)
Sirloin affects satiety aswell. Since it is richer in protein, it has higher satiety durations than tenderloin. This can have several benefits in overeating cases, and if you want to focus on a weight loss program, sirloin can be a better option. (2)
Tenderloin is richer in iron and vitamin B12. Since iron deficiency anemia is the most common type of anemia, and vitamin B12 is another type of anemia. We must focus on consuming bioavailable forms of iron to prevent iron deficiency anemia and, in addition, consume vitamin B12-rich foods to prevent vitamin B12 anemia (3)(4).
Regarding their mineral profiles, sirloin is richer in zinc, copper, phosphorus, and magnesium, essential in several physiological and metabolic pathways.
In this article, we can read about the negative impacts red meat can cause.
Infographic
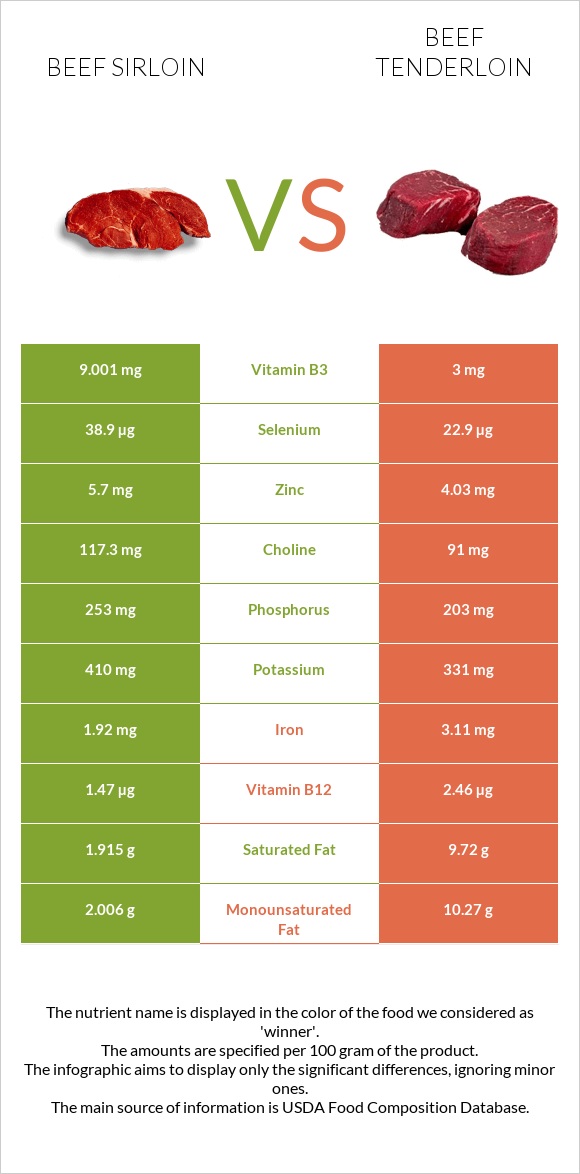
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B12 | 1.47µg | 2.46µg | 41% |
| Vitamin B3 | 9.001mg | 3mg | 38% |
| Saturated fat | 1.915g | 9.72g | 35% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.681mg | 0.25mg | 33% |
| Fats | 5.03g | 24.6g | 30% |
| Selenium | 38.9µg | 22.9µg | 29% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 2.006g | 10.27g | 21% |
| Iron | 1.92mg | 3.11mg | 15% |
| Zinc | 5.7mg | 4.03mg | 15% |
| Protein | 30.8g | 23.9g | 14% |
| Calories | 177kcal | 324kcal | 7% |
| Phosphorus | 253mg | 203mg | 7% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.163mg | 0.26mg | 7% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.607mg | 0.25mg | 7% |
| Choline | 117.3mg | 91mg | 5% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.185g | 1g | 5% |
| Copper | 0.085mg | 0.123mg | 4% |
| Vitamin E | 0.39mg | 3% | |
| Potassium | 410mg | 331mg | 2% |
| Cholesterol | 81mg | 85mg | 1% |
| Magnesium | 27mg | 22mg | 1% |
| Calcium | 22mg | 9mg | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 1.4µg | 1% | |
| Folate | 10µg | 8µg | 1% |
| Sodium | 66mg | 57mg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.011mg | 0.014mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.088mg | 0.09mg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.202mg | 0.268mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 1.23mg | 1.044mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 1.401mg | 1.075mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 2.45mg | 1.889mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 2.603mg | 1.989mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.802mg | 0.612mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 1.217mg | 0.933mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.528mg | 1.163mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.983mg | 0.818mg | 0% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -80.3% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +412% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +440.5% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Beef sirloin - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168636/nutrients
- Beef tenderloin - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169544/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





