General tso's chicken vs. Sesame chicken — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
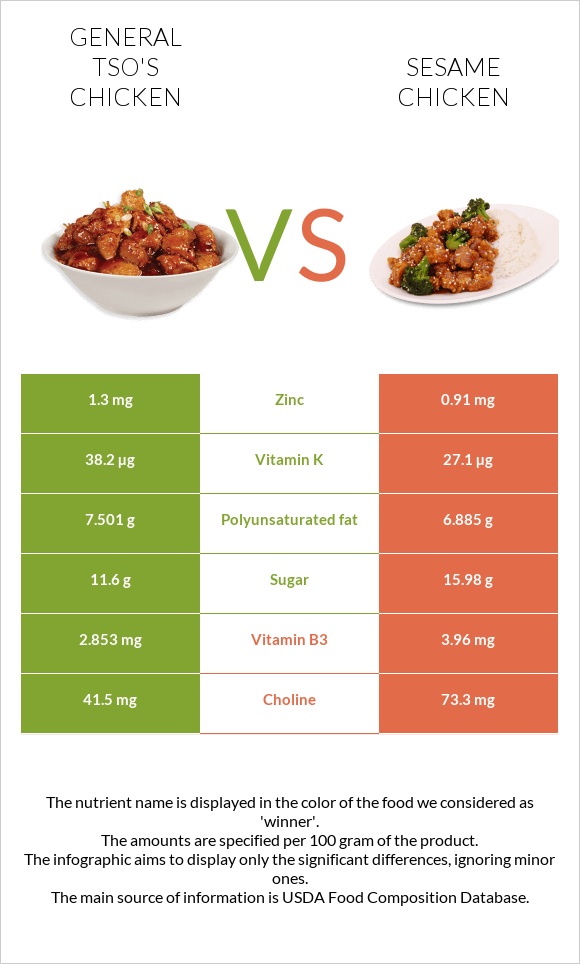
Sesame chicken is more prosperous in vitamin B2, A RAE, B3, and choline. In contrast, General Tso's chicken has higher vitamin K levels and polyunsaturated fat. Specifically, sesame chicken contains significantly more Vitamin A RAE, with 83µg, whereas General Tso's chicken has only 11µg, making it eight times less. Additionally, General Tso's chicken has a lower sugar content than sesame chicken.
Introduction
Sesame and General Tso's chicken are the most often ordered Chinese dishes. People naturally have tastes in food, but how different are these two dishes in terms of their nutritional value and overall health impact? We shall discover the answer to this question in the following article.
What's the Difference?
General Tso's chicken, originating from Hunan cuisine and Chef Peng Chang-kuei, features a spicy and tangy sauce with ingredients like chicken broth, green onions, corn starch, brown sugar water, hoisin sauce, chili peppers, and garlic. This results in a sweet and spicy dish commonly stir-fried with vegetables.
On the other hand, sesame chicken, associated with the Chinese word 'Zongtang,' offers a sweeter alternative. Deep-fried succulent chicken thighs are coated in soy sauce, brown sugar or honey, rice vinegar, toasted sesame oil, and ginger, resulting in a sweet, sour, and spicy glaze. The nuttier flavor, derived from toasted sesame seeds, further distinguishes sesame chicken and contributes to its unique taste.
When deciding between the two dishes, texture and taste play crucial roles. General Tso's caters to those who enjoy a stir-fry with its spicy kick. At the same time, sesame chicken, with its sweeter profile and nutty undertones, is recommended for those seeking crispy fried chicken.
Nutrition
The nutritional information below is presented for Chinese restaurants' sesame chicken and General Tso's chicken dishes. The nutritional information does not include rice or broccoli in the dishes; however, the ingredients and amount of breading and sauce may vary from restaurant to restaurant.
Based on 100-gram servings of these dishes, the infographics provide information. However, one average order of sesame chicken weighs 547g, while one General Tso's chicken order weighs 535g.
Macronutrients and Calories
These dishes have similar macronutrient compositions since chicken is the main ingredient in both, and the coating makes up for any nutritional differences.
General Tso's chicken consists of 45% water and 55% nutrients, while sesame chicken contains 43% water and 57% nutrients.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+14.8%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+11.1%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+12%
Calories
General Tso's and sesame chicken are both high-calorie foods. A 100-gram serving of each dish provides around 15% of the recommended daily calorie intake.
Sesame chicken provides 293 calories per 100g serving, while General Tso's chicken provides 295 calories in an equal serving. One average order of sesame chicken provides 1603 calories, while one of General Tso's contains 1580 calories.
Protein
Compared to General Tso's chicken, sesame chicken is around 1.5g richer in protein per 100g serving. The protein in General Tso and sesame chicken is high quality. One order of these dishes covers the daily value of all essential amino acids.
General Tso's chicken has more essential amino acids than sesame chicken.
Fats
General Tso's chicken is higher in fat by about 2g per 100g serving, containing 16.36g, while sesame chicken has 14.25g of fat. Regarding cholesterol content, sesame chicken has 59mg, while General Tso's chicken has slightly less, with 53mg.
The amount of unsaturated and saturated fat in both chicken dishes is nearly equal. The fat compositions of these two dishes are similar. Both sesame and General Tso's chicken contain over 50% polyunsaturated fats, followed by monounsaturated and saturated fats. However, a 100g serving covers over 12% of the recommended daily value of saturated fats.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-12.7%
Carbohydrates
Sesame chicken is higher in carbohydrates, by about 2.8g per 100 g serving, due to net carbs such as starch and sucrose. While both dishes are insufficient sources of dietary fiber, General Tso's chicken is slightly richer in fiber. Sesame and General Tsos chicken provide 26.9g and 23.9g of carbohydrates per 100g, respectively.
Starch and sucrose are the predominant carbohydrates in these dishes. There is also glucose and fructose in sesame chicken, whereas there is none in General Tso's chicken.
Carbohydrate type comparison
Contains
more
SucroseSucrose
+12.7%
Contains
more
GlucoseGlucose
+251.6%
Contains
more
FructoseFructose
+294.1%
Vitamins
It's hard to choose a definitive winner in this category as the two dishes are rich in different vitamins.
General Tso's and sesame chicken are excellent sources of B-complex vitamins, containing nearly equal amounts. However, sesame chicken is slightly higher in vitamins B1, A, E, and B3 (niacin), B2, B6, and vitamin B12.
General Tso's chicken is slightly higher in vitamins D, K, B5, C, B9, and folate.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+60%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+100%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+41%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+37.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+654.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+48.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+90.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+38.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+32.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+13.6%
Minerals
These two chicken dishes are similar in their mineral compositions overall. Nonetheless, sesame chicken is slightly richer in magnesium, selenium, and copper, while General Tso's chicken is higher in iron and zinc.
While both dishes are high in salt, General Tso's chicken contains slightly less sodium. The sodium content per 100g serving of sesame and General Tsos chicken is 482mg and 435mg, respectively.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+42.9%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-9.8%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+22.2%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+10.9%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+10.7%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+16%
Glycemic Index
Boiled chicken contains nearly no carbohydrates and has a glycemic index of 0. However, the coating and the deep-frying significantly raise this value.
The glycemic indices of General Tsos and sesame chickens have not yet been calculated. With a glycemic index of 46, they are about the same as chicken nuggets. (1).
Insulin Index
The insulin index values of foods show how eating a particular item raises blood insulin levels. Additionally, no research has been done on General Tsos and sesame chicken's insulin index levels. Compared to roasted chicken, which has an insulin index of 23, chicken nuggets have been shown to have an index of 41 (2, 3). This value is classified as having a low insulin index.
Acidity
Both sesame chicken and General Tso's chicken have acidic properties. Still, sesame chicken has a slightly higher acidity level, with a PRAL of 6.8, compared to General Tso's chicken, which has a PRAL of 6.2.
Health Impact
Sesame and General Tso's chicken may be good sources of protein, vitamins, and minerals, but they are high in saturated fat, net carbs, and sodium, which may negatively impact health. Research has shown that eating a lot of deep-fried food might have a bad influence on one's health overall, raising the risk of heart disease and type 2 diabetes (4, 5). As vegetables such as broccoli and carrots provide fiber, vitamins, and minerals, eating sesame and General Tso's chicken alongside vegetables can be slightly healthier.
Cardiovascular Health
Several mechanisms suggest that frequent consumption of fried food increases the risk of hypertension, coronary heart disease, stroke, heart failure, and coronary mortality, including an increase in blood "bad" cholesterol levels (4, 6). Sesame and General Tso's chicken also contain a high sodium content. Diets high in sodium have also been shown to cause high blood pressure (7).
Diabetes
For those at risk of diabetes, sesame, and General Tso's chicken should be taken strictly in moderation, even if they may have low glycemic and insulin index values. When discussing diabetes risk, the cooking technique could be as important as the meal's contents. Compared to cooking meat at moderate temperatures like boiling, steaming, and stir-frying, cooking meat at high temperatures like deep-frying, grilling, and barbecuing raises the risk of type 2 diabetes (8).
Obesity
Plenty of fried meals can dramatically increase calorie consumption since they contain more calories than non-fried ones. Weight gain may result from this.
Furthermore, research suggests that because trans fats in fried meals can alter hormones that control hunger and fat storage, they may significantly contribute to weight gain (9).
Numerous observational studies have demonstrated a positive correlation between fried food consumption and obesity, regardless of the cause—high trans fat or high-calorie content (10, 11).
Sources
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5852758/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/
- https://ses.library.usyd.edu.au/handle/2123/11945
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33468573/
- https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/news
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4632424/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6770596/
- https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/2018/03/23/how-meat-is-cooked-may-affect-risk-of-type-2-diabetes/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20644558/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33825582/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6196377/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.617mg | 12% | |
| Vitamin K | 38.2µg | 27.1µg | 9% |
| Vitamin A | 11µg | 83µg | 8% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.118mg | 0.225mg | 8% |
| Vitamin B3 | 2.853mg | 3.96mg | 7% |
| Choline | 41.5mg | 73.3mg | 6% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.202mg | 0.267mg | 5% |
| Zinc | 1.3mg | 0.91mg | 4% |
| Selenium | 14.4µg | 16.7µg | 4% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 7.501g | 6.885g | 4% |
| Protein | 12.9g | 14.33g | 3% |
| Fats | 16.36g | 14.25g | 3% |
| Cholesterol | 53mg | 59mg | 2% |
| Sodium | 435mg | 482mg | 2% |
| Saturated fat | 2.76g | 2.41g | 2% |
| Fructose | 0.51g | 2.01g | 2% |
| Vitamin C | 1.6mg | 1mg | 1% |
| Carbs | 23.99g | 26.88g | 1% |
| Magnesium | 18mg | 22mg | 1% |
| Iron | 1.16mg | 1.09mg | 1% |
| Fiber | 0.9g | 0.7g | 1% |
| Copper | 0.046mg | 0.051mg | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 1.21mg | 1.31mg | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 0.2µg | 0.1µg | 1% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.027mg | 0.04mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.22µg | 0.25µg | 1% |
| Folate | 11µg | 8µg | 1% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 3.879g | 3.546g | 1% |
| Calories | 295kcal | 293kcal | 0% |
| Net carbs | 23.09g | 26.18g | N/A |
| Vitamin D | 6 IU | 5 IU | 0% |
| Calcium | 12mg | 12mg | 0% |
| Potassium | 201mg | 204mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 11.6g | 15.98g | N/A |
| Starch | 11.83g | 10.7g | 0% |
| Phosphorus | 127mg | 130mg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.075mg | 0.083mg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0.09g | 0.045g | N/A |
| Tryptophan | 0.142mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.552mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.564mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 1.026mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 1.089mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.332mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.563mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.607mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.333mg | 0% | |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.005g | 0.003g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.005g | 0.005g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.84g | 0.774g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.006g | 0.006g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - Eicosatrienoic acid | 0.001g | 0.001g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.005g | 0.039g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Dihomo-gamma-linoleic acid | 0.01g | 0.009g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.011g | 0.009g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 6.47g | 5.925g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- General tso's chicken - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/167675/nutrients
- Sesame chicken - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168087/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.


