Couscous vs. Quinoa — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Couscous is classified as a refined or processed grain, whereas quinoa is a whole grain. Couscous is made from wheat and, therefore, contains gluten, unlike quinoa.
Couscous is higher in carbohydrates mainly due to net carbs, containing about 3g more of it per 100g serving. At the same time, quinoa is two times richer in dietary fiber.
Quinoa is richer in fats and protein. It is also the absolute winner in the vitamin and mineral categories, providing eight times more magnesium and manganese, seven times more phosphorus, five more vitamin E and copper, and four times more vitamin B9 or folate, zinc, and iron.
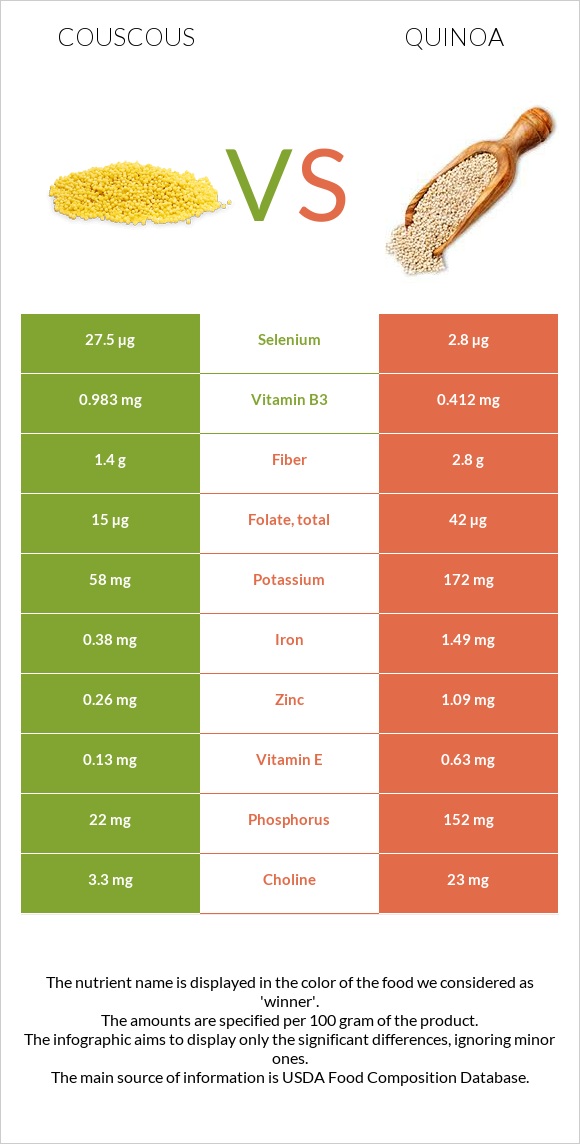
That being said, couscous contains 10 times more selenium.
All in all, while these two grains contain similar calories and macronutrients, quinoa is nutritionally denser and may have a more beneficial health impact.
Introduction
Quinoa and couscous are grain foods that have gained more popularity in recent years as healthy and nutritious additions to any diet. In this article, we will compare the two with the main focus on nutrition and health impacts.
Classification and Origin
Couscous is a staple food in North African countries such as Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia. Quinoa is native to the Andean region of South America, particularly Peru, and was a staple food of the Inca civilization.
Couscous is a type of grain made from semolina flour, which is coarse wheat flour. Quinoa, on the other hand, is not a true grain but is classified as a pseudo-cereal. It is a seed that comes from a flowering plant in the amaranth family. It is often used as a gluten-free substitute for rice or couscous.
Couscous is classified as a refined or processed grain, whereas quinoa is a whole grain.
Appearance, Taste, and Use
Couscous has a small, round, and granular appearance that resembles tiny beads. It is usually pale yellow and has a slightly nutty flavor.
Quinoa has a similar size and shape to couscous, but its appearance is different. Quinoa seeds have a flat, oval shape with smooth edges. They can come in various colors, including white, red, and black.
Couscous is typically steamed or boiled in water, whereas quinoa is cooked similarly to rice. However, quinoa has a longer cooking time than couscous.
Couscous is smaller and more granular in texture compared to quinoa, which has a softer and fluffier texture.
Nutrition
The nutritional information in this article is presented for 100g servings of cooked quinoa and couscous.
One average serving size of these grains per person is considered to be one cup of cooked grains weighing around 157g for couscous and 185g for quinoa.
Macronutrients and Calories
The two grains are very similar in macronutrient composition, being comprised of around 72% water and a little over 20% carbohydrates.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+16.1%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+1100%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+196.2%
Calories
A 100g serving of quinoa provides only eight more calories than couscous. Quinoa and couscous contain 120 and 112 calories, respectively.
Quinoa and couscous are medium-calorie foods.
Carbohydrates
Couscous is higher in carbohydrates mainly due to net carbs, containing about 3g more of it per 100g serving. At the same time, quinoa is two times richer in dietary fiber.
The same 100g serving of couscous has 23.2g of carbohydrates, whereas quinoa contains 21.3g.
Quinoa is an excellent source of dietary fiber, falling in the top 28% of foods as a source of this nutrient.
Most of the net carbs found in quinoa are made up of starch.
Protein
Quinoa is also somewhat higher in protein. Quinoa contains 0.6g more protein per 100g serving. In this serving size, it has 4.4g of protein compared to couscous with 3.8g.
Grains are not the best source of protein. A 100g serving of quinoa covers only 10% of the daily needed protein value.
Fats
While both grains contain very little fat, quinoa is 12 times higher in this nutrient. A 100g serving of quinoa contains about 2g of fats, while couscous has insignificant amounts.
The fat compositions of these grains are very similar to each other.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-87.4%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+2300%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+1584.4%
Vitamins
Quinoa wins in the vitamin category, containing about five times more vitamin E, four times more vitamin B2, three times more vitamin B9 or folate, two times more vitamin B6, and overall more vitamins A and B1.
That being said, couscous is two times higher in vitamin B3 and contains vitamin K, which quinoa lacks entirely.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+138.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+384.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+69.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+307.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+141.2%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+180%
Minerals
Quinoa is also significantly richer in most minerals. It is eight times higher in magnesium and manganese, seven times higher in phosphorus, five times higher in copper, four times higher in zinc and iron, three times higher in potassium, and two times higher in calcium.
Quinoa is particularly good as a source of iron, magnesium, copper, and phosphorus.
At the same time, couscous contains ten times more selenium. Unsalted cooked couscous is also somewhat lower in sodium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-28.6%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+882.1%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+700%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+112.5%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+196.6%
Contains
more
IronIron
+292.1%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+368.3%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+319.2%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+590.9%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+651.2%
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index of couscous from Australia rehydrated with water has been measured to be 65. Israeli couscous has a glycemic index of 53 (1).
Based on four studies, the average glycemic index of quinoa is 53 (1).
You can find a detailed article on the glycemic index of couscous on our page.
Thus, couscous and quinoa have similar glycemic index values, falling in the low to medium category.
Insulin Index
The insulin index of foods measures how much and how quickly its consumption raises blood insulin levels.
Couscous has been studied to have a relatively high insulin index value of 84 (2).
There is no research concerning the insulin index value of quinoa yet.
Health Impact
Cardiovascular Health
Research shows that adding quinoa seeds to one’s diet can help decrease cardiovascular disease risk by lowering body weight, waist circumference, fat mass, triglyceride, and total cholesterol levels (3).
Whole grain foods, especially quinoa, have a high dietary fiber content, which increases their potential for disease prevention and lowers the risk of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease (4).
Refined grains, such as couscous, do not increase the risk of heart failure, stroke, or cardiovascular disease (5). However, there is no research demonstrating risk-lowering effects either.
Diabetes
As mentioned above, quinoa and couscous have similar glycemic index values. However, couscous has a high insulin index, meaning its intake leads to a rapid increase in blood insulin levels.
Several quinoa components, such as fiber, protein, and polyphenols, may provide defense against the metabolic side effects of type 2 diabetes and obesity. Quinoa consumption can help reduce fasting blood glucose and triglyceride levels (6).
Refined grains are not linked to a lower risk of type 2 diabetes, but a high intake of whole grains is. Thus, switching to whole grains from processed grains is advised to help lower this risk (7).
Gluten Intolerance
Some cereals and grain products, primarily wheat, rye, spelt, etc., contain the protein known as gluten. Gluten-related illnesses, including Celiac disease and non-celiac gluten sensitivity, are brought on by the consumption of this protein, causing symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, and diarrhea.
Couscous is made from wheat, making gluten one of the main proteins found in this grain. Unlike couscous, quinoa is gluten-free and can be used as a substitute for wheat or couscous for people on a gluten-free diet.
FODMAPs
As a wheat product, couscous is high in FODMAPs and may cause abdominal cramps, bloating, flatulence, and diarrhea.
On the other hand, quinoa is low in them and can be consumed during low FODMAP diets.
Sources.
- https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/114/5/1625/6320814
- https://ses.library.usyd.edu.au/handle/2123/11945
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33037704/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6566984/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36075506/
- https://www.mdpi.com/2673-4540/2/2/7/htm
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24158434/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Selenium | 27.5µg | 2.8µg | 45% |
| Manganese | 0.084mg | 0.631mg | 24% |
| Phosphorus | 22mg | 152mg | 19% |
| Copper | 0.041mg | 0.192mg | 17% |
| Iron | 0.38mg | 1.49mg | 14% |
| Magnesium | 8mg | 64mg | 13% |
| Zinc | 0.26mg | 1.09mg | 8% |
| Starch | 17.63g | 7% | |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.371mg | 7% | |
| Folate | 15µg | 42µg | 7% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.064g | 1.078g | 7% |
| Fiber | 1.4g | 2.8g | 6% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.027mg | 0.11mg | 6% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.051mg | 0.123mg | 6% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.063mg | 0.107mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.983mg | 0.412mg | 4% |
| Choline | 3.3mg | 23mg | 4% |
| Fats | 0.16g | 1.92g | 3% |
| Potassium | 58mg | 172mg | 3% |
| Vitamin E | 0.13mg | 0.63mg | 3% |
| Protein | 3.79g | 4.4g | 1% |
| Carbs | 23.22g | 21.3g | 1% |
| Calcium | 8mg | 17mg | 1% |
| Saturated fat | 0.029g | 0.231g | 1% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.022g | 0.528g | 1% |
| Calories | 112kcal | 120kcal | 0% |
| Net carbs | 21.82g | 18.5g | N/A |
| Sugar | 0.1g | 0.87g | N/A |
| Sodium | 5mg | 7mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 0.1µg | 0µg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.049mg | 0.052mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.1mg | 0.131mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.147mg | 0.157mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.259mg | 0.261mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.073mg | 0.239mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.059mg | 0.096mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.184mg | 0.185mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.162mg | 0.185mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.077mg | 0.127mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0g | 0.015g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Couscous - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169700/nutrients
- Quinoa - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168917/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.




