Cranberries vs. Cherry — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison

Summary
Cherry is richer in minerals, contains 19 times more Vitamin A, seven times more Folate, and has a lower GI than cranberry. Cranberries have 17 times more Vitamin A, two times more Vitamin K, and contain low sugar and sodium than cherry.
Introduction
Externally, cherries and cranberries may look quite similar, but they don’t have much in common nutritionally. Fresh cherries and cranberries are seasonal fruits; however, you can find frozen versions in grocery stores through winter.
Fully ripe cranberries turn a deep red, while unripe ones are pale pink or white color. Cherries are heart-shaped to nearly globular and vary in color from yellow through red to nearly black.
Varieties
Cranberries belong to the family Ericaceae. The taste of cranberries is as tart as lemons because of their low sugar content. There are more than 100 varieties of cranberries, of which the most famous are; Ben Lear, Crimson Queen, and Early Black. Cherry is the fruit of many plants which belong to the genus Prunus. The taste of cherries is sweet with a touch of acidity. The most common cherries types are Big Cherries (sweet cherry), Rainier Cherries, Queen Cherries, and Montmorency Cherries.
Uses
Cranberries are used in making cranberries juice or can be cooked into jelly and compote. They also can be used in making muffins, cakes, and bread. Several alcoholic cocktails, such as Cosmopolitan, are made from cranberry juice.
Cherry is used as food and medicine. Cherries are often used in desserts, jams, salads, cakes, etc.
Nutrition
In this section of the article, we will discuss the nutritional data of cranberry and cherry, focusing on the differences.
You can find nutrition infographics at the bottom of this page that visually show the differences between these products.
Micronutrients
The amounts of protein and carbs are almost equal in these fruits. However, cherries contain more mono- and polyunsaturated fat, but cranberries contain more fiber and less sugar. Both fruits contain no cholesterol.
Vitamins
Both fruits contain different vitamins in different amounts. Cherries contain 19 times more Vitamin A, seven times more Folate, and two times more Vitamin B3 than cranberries. The levels of Vitamin B2 and Vitamin B1 are also higher in cherry. On the other hand, cranberries contain 17 times more Vitamin E and two times more Vitamin K. Cranberries are also richer in Vitamin C, Vitamin B6, and B5.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+40%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+1785.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+106.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+29.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+138.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+2033.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+150%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+100%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+296%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+700%
Minerals
Cherry is relatively higher in minerals than cranberry. It has two times more potassium, calcium, magnesium, copper, iron, and phosphorus than cranberry. It is essential to highlight that cranberries have less sodium than cherries. Both have an equal amount of zinc.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-33.3%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+138.4%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+∞%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+50%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+100%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+116.3%
Contains
more
IronIron
+39.1%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+85.7%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+11.1%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+36.4%
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index of cherry is lower than that of cranberry. The GI of cherry is equal to 22; cranberry has a GI equal to 45 [1].
Acidity
On average, the acidity of cranberries is lower than that of cherry, which means cranberries are more acidic. Cherry has a pH equal to 3, whereas cranberry has a pH equal to 1.3.
Calories
Cherries have a few more calories than watermelon. It has 50 calories per 100 g, while cranberry has 46 calories per 100 g.
Health Impact
Weight Loss
Cherries are low in calories; they are also rich in vitamins and have a moderate water content, which means they can help flush out the toxins from your body. According to studies, cherries can help reduce overall fat levels and the risk of diseases associated with a high-fat diet, including type-2 diabetes and heart disease [2].
Cranberries alone can never make you lose weight; nevertheless, they are low in calories, rich in fiber, and can be included in your diet.
Cardiovascular Health
Cherries are rich in powerful antioxidants, such as polyphenols, anthocyanins, and flavonols, which may play an essential role in fighting against cellular damage and keeping your heart healthy. One study showed that a high intake of polyphenols is connected to decreasing heart disease risk [3].
Both of these products contain flavonols, which may reduce cardiovascular mortality, especially in men with diabetes, hypertension, and male smokers, although more research is needed [4,5].
Сherry and cranberry also have antihypertensive and antiatherogenic effects due to the presence of flavonoids in them and may protect the heart from ischemia damage [6].
Cranberries are also high in antioxidants that may be beneficial for heart health. According to studies, cranberry juice can help lower LDL cholesterol (bad cholesterol is an integral component of atherosclerotic plaque) levels and decrease stiffness in blood vessels among people with heart disease [7]. It lowers LDL levels, thereby reducing coronary heart disease risk.
Diabetes
Cranberries contain high levels of PACS, which may help keep glucose levels balanced. Research shows that drinking unsweetened cranberry juice helps people with type 2 diabetes manage their blood sugar levels [8]. Cherries could be a healthy part of your diabetic diet due to their high vitamin C and potassium content. According to the rat study, the extract of cherries can help control blood glucose levels; also, cherries appear to aid in diabetes control [9].
Cancer
Based on several studies, antioxidants found in cherries may help to slow the growth of cancer cells. Moreover, they are rich in melatonin, which shows cancer-preventive potential in laboratory studies. The animal study showed that these compounds reduced the growth of colon cancer cells in mice. However, more research is needed [10].
Cranberry phytocompounds also have a strong protective effect against cancer. Studies show that proanthocyanidins seem to influence gene expression to decrease the growth of cancer cells and increase their self-destruction [11].
Anti-inflammatory Effect
Both cherries and cranberries are rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds. These compounds can help combat oxidative stress, leading to multiple chronic diseases like diabetes, cancer, heart diseases, etc.
In addition, cherries are high in carotenoid pigments such as beta-carotene and Vitamin C, which have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
According to the study, eating cherries reduce inflammation in 70 % of cases [12].
Side Effects
Using cherry juice in large amounts can lead to indigestion and diarrhea. Besides, cherries contain sorbitol, which may exacerbate symptoms in irritable bowel syndrome or fructose malabsorption.
Kidney Stones
Most kidney stones are made of calcium oxalate, so excessive amounts of oxalate in your urine are one of the main risk factors. Cranberries contain high levels of oxalates. Therefore, they are considered a risk factor for kidney stones when consumed in high amounts [13].
Allergy
Allergy to fruits like cherries is often called “pollen-food syndrome.” The symptoms of this allergy commonly include itchy on the mouth and face upon eating raw or fresh fruit.
Cranberries are rich in salicylic acid and aspirin. Therefore people who are allergic or sensitive to aspirin may also have an allergy to cranberries. The symptoms often include a runny or stuffy nose, headaches, itching or skin rashes, and stomach pain [14] [15].
References
- https://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/diacare/suppl/2008/09/18/dc08-1239.DC1/TableA1_1.pdf
- https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/10/3/368
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6266343/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35565940/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18038941/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20837053/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16923231/
- https://pubs.rsc.org/fi/content/articlelanding/2017/fo/c7fo00900c/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22280223/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12706854/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5039576/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6259571/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7245443/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S009167490200057X
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0091674999701673
Infographic
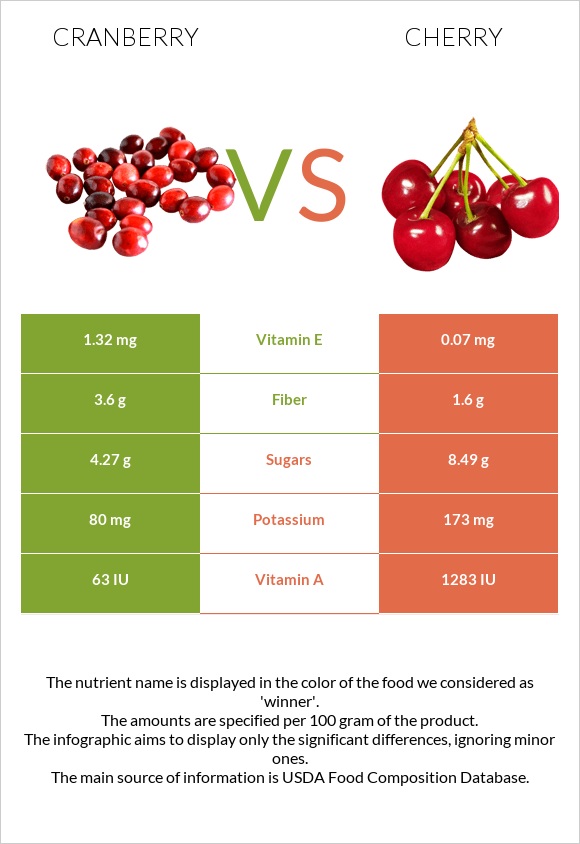
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Fiber | 3.6g | 1.6g | 8% |
| Vitamin E | 1.32mg | 0.07mg | 8% |
| Vitamin A | 3µg | 64µg | 7% |
| Manganese | 0.267mg | 0.112mg | 7% |
| Copper | 0.056mg | 0.104mg | 5% |
| Vitamin C | 14mg | 10mg | 4% |
| Fructose | 0.67g | 3.51g | 4% |
| Potassium | 80mg | 173mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.295mg | 0.143mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.012mg | 0.03mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.02mg | 0.04mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.101mg | 0.4mg | 2% |
| Vitamin K | 5µg | 2.1µg | 2% |
| Folate | 1µg | 8µg | 2% |
| Protein | 0.46g | 1g | 1% |
| Magnesium | 6mg | 9mg | 1% |
| Calcium | 8mg | 16mg | 1% |
| Iron | 0.23mg | 0.32mg | 1% |
| Phosphorus | 11mg | 15mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.057mg | 0.044mg | 1% |
| Calories | 46kcal | 50kcal | 0% |
| Fats | 0.13g | 0.3g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 8.37g | 10.58g | N/A |
| Carbs | 11.97g | 12.18g | 0% |
| Sugar | 4.27g | 8.49g | N/A |
| Zinc | 0.09mg | 0.1mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 2mg | 3mg | 0% |
| Selenium | 0.1µg | 0µg | 0% |
| Choline | 5.5mg | 6.1mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.008g | 0.068g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.018g | 0.082g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.055g | 0.09g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.003mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.028mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.033mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.053mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.039mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.003mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.036mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.045mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.018mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +117.4% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +130.8% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +225% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -88.2% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +355.6% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +63.6% |
Carbohydrate type comparison
| Contains more SucroseSucrose | +400% |
| Contains more GlucoseGlucose | +21.5% |
| Contains more FructoseFructose | +423.9% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Cranberries - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171722/nutrients
- Cherry - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173954/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






