Egg Drop Soup vs. Hot and sour soup — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison

Summary
Whereas the hot and sour soup has greater proteins, lipids, and calories, the two soups have comparable carb counts.
Egg drop soup is higher in vitamin A and vitamin A RAE, while hot and sour soup is higher in B-complex and has a higher mineral content overall.
Because both soups contain a lot of sodium, there could be adverse health implications.
Introduction
The famous Chinese soups, egg drop soup, and hot and sour soup are contrasted in this article.
A meat-based soup with seasonings, tofu, mushrooms, and bamboo shoots is called hot and sour soup.
You make egg drop soup by adding hot chicken broth to thinly beaten eggs. The soup occasionally might include tofu, peppers, and scallions. Egg drop soup can also be made with vegetable broth as the foundation.
Taste and Dishes
While egg drops introduce softer flavors to your palate, hot and sour soup offers a curious combination of sweet and spicy flavors. An old favorite for hot and sour soup is fried rice.
The robust tastes of the soup combine with the savory flavor of the fried rice to create a delicious combination. It's sweet, sour, and spicy. Steamed dumplings with hot and sour soup are another option. The rich soup pairs perfectly with the delicate texture of the dumplings. Sweet and sour chicken makes a delicious addition to egg drop soup.
The soup's simplicity and the chicken's tart sweetness create a wonderful meal.
Ingredients
Hot and Sour Soup includes a variety of components like white vinegar, light and dark soy sauce, sugar, chicken bouillon powder, and toasted sesame oil, along with unique add-ons such as tofu, bamboo shoots, and various mushroom types, resulting in a distinctive tangy and spicy flavor profile. Egg Drop Soup, on the other hand, centers around the simplicity of unsalted chicken stock or vegetable broth and the use of raw, beaten eggs to create thin, silky strands within the soup, along with the option of diverse garnishes like scallions, tofu, bean sprouts, and corn.
Egg drop soups and wonton soups are both high in salt. Both have about 900 mg of salt per cup or about 40% of the daily recommended intake (1).
Nutrition
The nutritional values for egg drop soup and hot and sour soup are presented in this article.
Soups are served in one-cup portions, which equal around 241g for egg drop soup and approximately 233g for hot and sour soup.
Macronutrients and Calories
Regarding nutrition, hot and sour soup and egg drop soup are comparable. But there is a little bit more protein and fat in hot and sour soup. In both, water makes up 91%.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+122.4%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+98.4%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+13.1%
Calories
The soups, egg drops, and hot and sour are low in calories. The calories in one serving of egg drop soup and hot and sour soup are 27 and 39, respectively.
Protein
There are 2.8 g of proteins in a cup of wonton soup and 6 g of proteins in a cup of hot and sour soup.
Fats
Although the fat content of both soups is minimal, the fat content of the hot and sour soup is nearly twice as high. A serving of hot and sour soup has 2.82g of fat, compared to 1.47g in a cup of egg drop soup.
There is very little cholesterol in the soups.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-27.5%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+50.8%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+141.1%
Carbohydrates
Each cup of soup supplies 8–9% of the daily recommended consumption of carbohydrates (1). Nearly 10.1 grams of carbohydrates are found in one serving of egg drop soup and hot and sour soup.
Starch comprises the full carbohydrate content of egg drop soup and hot and sour soup.
Egg drop and hot and sour soups may or may not be regarded as keto-friendly, depending on the ingredients and carbohydrate level of the soup.
Carbohydrate type comparison
Contains
more
SucroseSucrose
+∞%
Contains
more
GlucoseGlucose
+∞%
Vitamins
Egg Drop Soup contains higher levels of Vitamin A (89 IU vs. 34 IU) and Vitamin A RAE (20 g vs. 9 g). However, Hot and Sour Soup surpasses Egg Drop Soup in Vitamin E (0.39mg vs. 0.13mg) and Vitamin C content (0mg vs. 6.5mg). Hot and Sour Soup shows higher levels of B-complex vitamins. Moreover, hot and sour soup exhibits more folate (8 g vs. 7 g) and vitamin B12 (0.1 g vs. 0.03 g) than egg drop soup. The two soups have comparable levels of vitamin D and vitamin K.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+122.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+100%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+200%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+36.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+63.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+225%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+89.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+220%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+233.3%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+14.3%
Minerals
In terms of mineral content, hot and sour soup generally exhibits higher levels compared to egg drop soup. Hot and Sour Soup contains more calcium (19mg vs. 7mg), iron (0.64mg vs. 0.26mg), magnesium (9mg vs. 2mg), phosphorus (32mg vs. 15mg), potassium (55mg vs. 22mg), zinc (0.22mg vs. 0.09mg), copper (0.026mg vs. 0.019mg), and manganese (0.085mg vs. 0.011mg). Both soups show the same level of selenium at 0.4µg.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+350%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+171.4%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+150%
Contains
more
IronIron
+146.2%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+36.8%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+144.4%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+113.3%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+672.7%
Glycemic Index
Glycemic index values for egg drop and hot and sour soups have not been calculated.
Acidity
Potential renal acid load, or PRAL, measures how much acid or base is produced in the body by food consumption. Egg Drop Soup has a PRAL value of -0.5, indicating that it is slightly alkaline-forming, whereas hot and sour soup has a PRAL value of 0.8, suggesting it is more acid-forming.
Health Benefits
Egg drops and hot and sour soups are healthful meals that, depending on what's in them, may offer a high supply of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Because the soups are low in calories, they can be included in a diet low in calories. Low-calorie diets enhance glycemic control, lessen the severity of obesity-related diseases, and lower the risk of cardiovascular, liver, and renal illness (2). Most of the vitamins are present in both soups, although, to varying degrees, the hot and sour soup is high in vitamins B3, B6, and B12. These vitamins are necessary for producing red blood cells, good skin, and normal brain function (3).
The physiological antioxidant vitamin C is abundant in egg drop soup. The immune system, wound healing, tissue development and repair, and iron absorption are all aided by vitamin C (4).
Soups that are hot and sour are excellent sources of iron, as they can provide up to 22.5% of the daily required intake (1). The production of hemoglobin, a protein that carries oxygen from the lungs to tissues, depends on iron. Iron is also necessary for many other processes, including growth, brain development, hormone synthesis, DNA synthesis, and many more (5).
Risks
Salt content is high in egg drops and hot and sour soups. Consuming excessive amounts of sodium raises the risk of cancer, osteoporosis, kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease (6). To reduce your risk of heart disease, think about consuming low-sodium foods.
Sources
- https://www.dietaryguidelines.gov/sites/default/files/2020-12/Dietary_Guidelines_for_Americans_2020-2025.pdf
- https://jpp.krakow.pl/journal/archive/10_18/pdf/10.26402/jpp.2018.5.02.pdf
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002399.htm
- https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminC-HealthProfessional/
- https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Iron-HealthProfessional/
- https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/salt-and-sodium/
Infographic
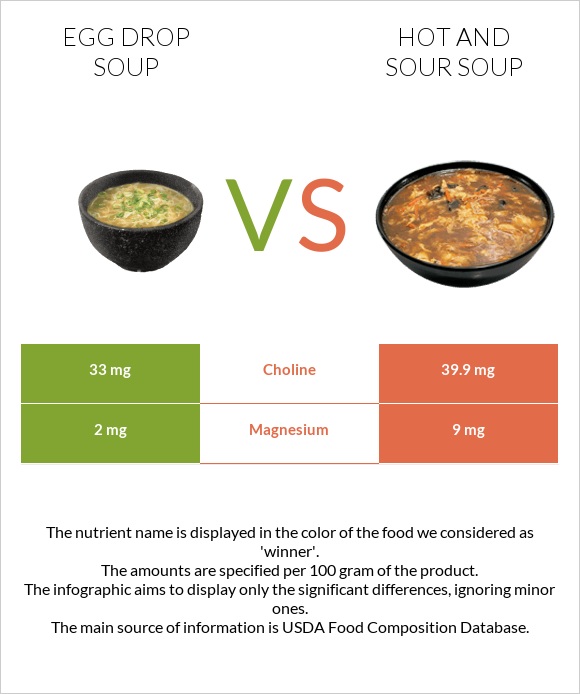
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin C | 6.5mg | 0mg | 7% |
| Lysine | 0.052mg | 153mg | 7% |
| Iron | 0.26mg | 0.64mg | 5% |
| Protein | 1.16g | 2.58g | 3% |
| Manganese | 0.011mg | 0.085mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.02mg | 0.064mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.03µg | 0.1µg | 3% |
| Magnesium | 2mg | 9mg | 2% |
| Phosphorus | 15mg | 32mg | 2% |
| Vitamin E | 0.13mg | 0.39mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.156mg | 0.507mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.12mg | 0.227mg | 2% |
| Calories | 27kcal | 39kcal | 1% |
| Fats | 0.61g | 1.21g | 1% |
| Cholesterol | 23mg | 21mg | 1% |
| Calcium | 7mg | 19mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 22mg | 55mg | 1% |
| Copper | 0.019mg | 0.026mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.09mg | 0.22mg | 1% |
| Vitamin A | 20µg | 9µg | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 0.2µg | 0.1µg | 1% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.019mg | 0.026mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.019mg | 0.031mg | 1% |
| Choline | 33mg | 39.9mg | 1% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.129g | 0.311g | 1% |
| Net carbs | 3.89g | 3.85g | N/A |
| Carbs | 4.29g | 4.35g | 0% |
| Vitamin D | 6 IU | 5 IU | 0% |
| Sugar | 0.09g | 0.42g | N/A |
| Fiber | 0.4g | 0.5g | 0% |
| Starch | 2.45g | 2.43g | 0% |
| Sodium | 370mg | 376mg | 0% |
| Selenium | 0.4µg | 0.4µg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 1.2µg | 1.1µg | 0% |
| Folate | 7µg | 8µg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0.001g | 0g | N/A |
| Saturated fat | 0.166g | 0.229g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.191g | 0.288g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.025mg | 0.019mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.037mg | 0.111mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.028mg | 0.08mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.047mg | 0.151mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.019mg | 0.039mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.028mg | 0.085mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.037mg | 0.092mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.013mg | 0.058mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.001g | 0g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.007g | 0.03g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Dihomo-gamma-linoleic acid | 0.001g | 0g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 0.112g | 0.273g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Egg Drop Soup - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174807/nutrients
- Hot and sour soup - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174808/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





