Hot And Sour Soup Nutrition & Calories - Complete data of all nutrients

Summary
In short, hot and sour soup is a low-calorie food consisting of 91% water and 9% nutrients.
One hundred grams of the soup contains 4.35g of carbs, 2.58g of proteins, and 1.21g of fats.
The soup contains some levels or all minerals and vitamins, each of them covering less than 15% of the daily need. Hot and sour soup is high only in sodium (876 mg), as one cup covers 38% of the daily need.
Introduction
The main ingredients in the hot and sour soup are mushrooms, day lily buds, bamboo shoots, and firm tofu. The soup may contain carrots, peppers, ginger, eggs, and soy sauce. Sometimes, it may be flavored with pork blood or contain pork meat.
Nutrition
As many recipes exist for hot and sour soup, this article will focus on the nutrition of the soup from a Chinese restaurant, the country where the soup originated.
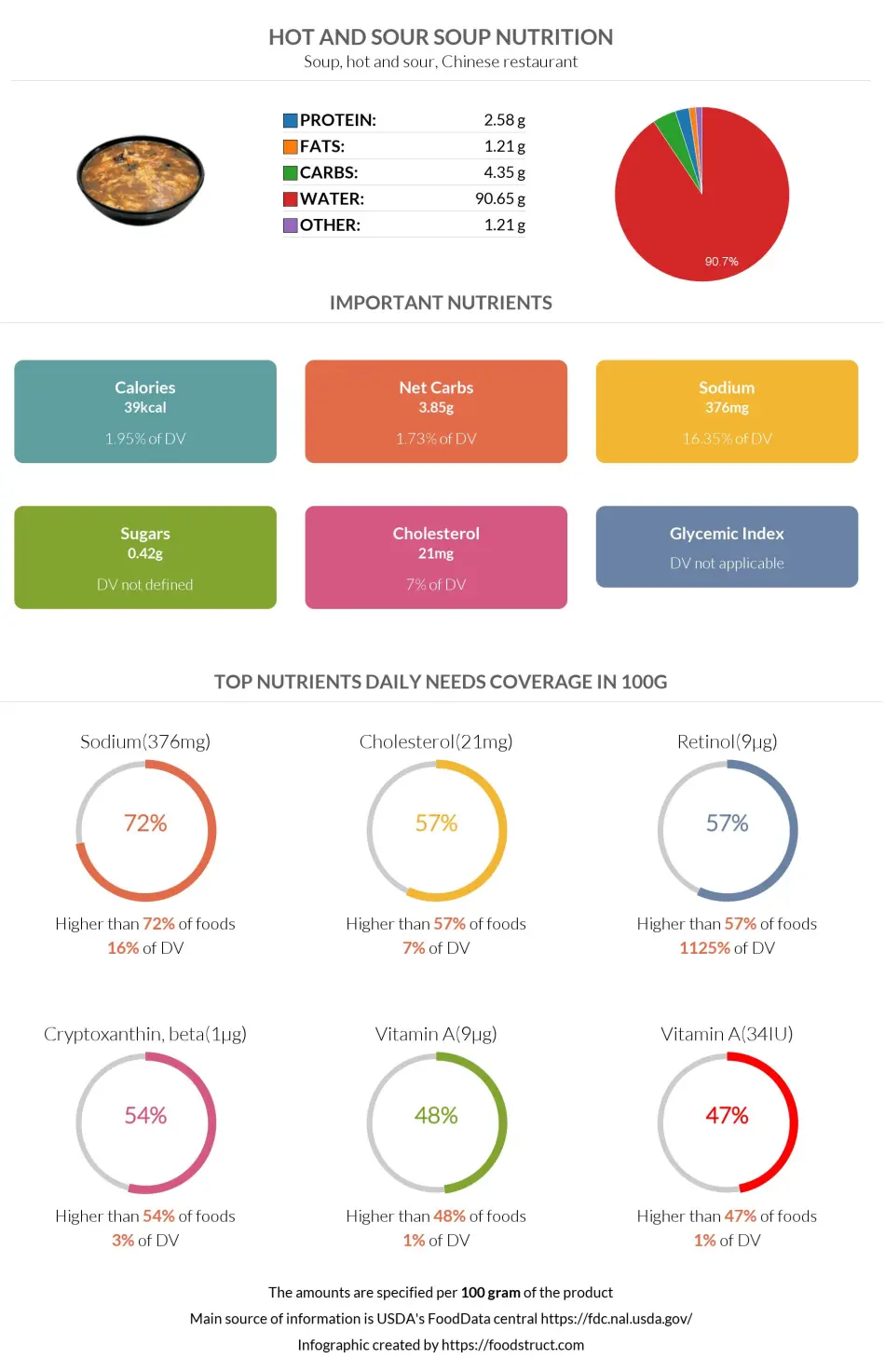
Overall, hot and sour soup is not very dense in nutrients, consisting of 88% water and only 12% nutrients, mainly protein.
Macronutrients chart
Serving Size
The average serving size of hot and sour soup is one cup, weighing ~233g. However, the infographic charts below present the nutritional values of a 100g serving of hot and sour soup.
Calories
Hot and sour soup is a low-calorie food.
One hundred grams of the soup provides 39 calories; consequently, one cup or one serving provides 91 calories.
Compared to all foods in our database, hot and sour soup is in the top 10% of foods low in calories.
Protein
Despite proteins being the main macronutrient, hot and sour soup is not particularly rich in it, as one cup of it covers only 12% of the daily protein needed.
A 100g serving of hot and sour soup contains 2.58g of proteins, and one serving of the soup contains 6g of proteins.
Hot and sour soup is relatively rich in amino acids lysine, leucine, and threonine and low in tryptophan and methionine.
Protein quality breakdown
Carbohydrates
Carbs are the predominant macronutrients in hot and sour soup.
A 100g hot and sour soup serving contains 4.35g of carbs, and one cup contains 10.1g of carbs.
In Chinese-American cuisine, corn starch is added to hot and sour soup to make it more thick. This may increase the carbohydrate content of this soup.
Net Carbs
As previously mentioned, 100g of hot and sour soup contains 4.35g of carbs, almost 90% (3.85g) being net carbs.
The hot and sour soup contains mainly starch, as well as insignificant levels of sucrose and glucose.
Carbohydrate type breakdown
Dietary Fiber
The hot and sour soup contains 0.5g of dietary fiber per 100g serving, covering only 2% of the daily need.
Fiber content ratio for Hot and sour soup
Fats
Hot and sour soup is low in fats: 1.21g of fats per 100g and 2.82g of fats per cup.
The soup contains both saturated and unsaturated fats, with a slightly higher level of unsaturated fats.
Fat type information
Vitamins
The hot and sour soup contains almost all vitamins but in low amounts. The soup is absent only in vitamin C.
Vitamin coverage chart
Minerals
The hot and sour soup is not particularly rich in minerals either.
The hot and sour soup is relatively higher in sodium, as one serving of the soup covers 38% (0.876g) of the daily sodium needed.
2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend to consume less than 2.3g of sodium per day (1). High sodium consumption increases blood pressure, increasing cardiovascular disease and stroke risks (2).
Mineral coverage chart
Phytochemicals
The phytochemical content of this soup depends on the ingredients used in the making.
Jelly ear mushrooms are rich in flavonoids, alkaloids, saponins, and tannins (3). Shiitake mushrooms also contain flavonoids, glycosides, alkaloids, and triterpenoids (4).
Common Ingredients
From recipe to recipe, ingredients vary. Here are some common ingredients and their nutritional values:
Mushrooms: Various types of mushrooms are used in hot and sour soup. The most commonly used varieties are shiitake, jelly ear, and cloud ear fungus. Mushrooms are low in macronutrients but rich in minerals and vitamins, such as copper, phosphorus, and B complex vitamins.
Chicken meat: Chicken meat is rich in proteins and fats (contains two times more unsaturated fats than saturated fats) and contains no carbs. Chicken meat is relatively richer in vitamins B3 and B6, selenium, phosphorus, and zinc.
Chili Pepper: Chili pepper is high in vitamin C, as one pepper (45g) covers 72% of the daily vitamin C need. Chili pepper is relatively richer in carbs, copper, iron, and vitamin B6.
Black Pepper: Black pepper is rich in carbs (from which 40% is dietary fiber), proteins, manganese, copper, iron, and vitamin K.
White pepper: White pepper is richer in proteins and carbs (from which 38% is dietary fiber), manganese, copper, iron, and vitamin C.
Soy sauce: Soy sauce is high in protein, manganese, phosphorus, and iron. Soy sauce is very high in sodium. One tbsp of soy sauce alone contains 878mg of sodium, covering 38% of the daily need.
Bamboo shoot: Bamboo shoot is relatively higher in vitamin B6, copper, and potassium.
Ginger: Ginger is not particularly rich in minerals and vitamins. It is best known for its health-promoting phytochemicals showing antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, anticancer, and anti-diabetic effects (5).
Acidity
Potential Renal Acid Load
Potential renal acid load or PRAL value measures how much acid or base is produced in the organism by the given food. The PRAL value of hot and sour soup is -0.8, making it acid-producing.
Comparison to Similar Foods
Hot and sour soup is often compared to egg drop soup and wonton soup. The soups have similar nutritional contents, with predominantly insignificant differences.
However, compared to egg drop soup, hot and sour soup is slightly higher in macronutrients, calories, calcium, iron, zinc, B complex vitamins, and vitamin E. In contrast, egg drop soup is slightly higher in vitamins A and C.
Compared to wonton soup, hot and sour soup is slightly richer in proteins and fats, calories, dietary fiber, minerals, and fat-soluble vitamins. In contrast, wonton soup is slightly richer in carbs and starch and lower in cholesterol.
To know more about their nutritional differences, you can visit our "Hot and sour soup vs. Wonton soup" and "Hot and sour soup vs. Egg drop soup" pages.
Top nutrition facts for Hot and sour soup

| Calories ⓘ Calories for selected serving | 39 kcal |
| Net Carbs ⓘ Net Carbs = Total Carbohydrates – Fiber – Sugar Alcohols | 4 grams |
| Default serving size ⓘ Serving sizes are mostly taken from FDA's Reference Amounts Customarily Consumed (RACCs) | 1 cup (233 grams) |
| Acidity (Based on PRAL) ⓘ PRAL (Potential renal acid load) is calculated using a formula. On the PRAL scale the higher the positive value, the more is the acidifying effect on the body. The lower the negative value, the higher the alkalinity of the food. 0 is neutral. | 0.8 (acidic) |
Hot and sour soup calories (kcal)
| Calories for different serving sizes of hot and sour soup | Calories | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Calories in 100 grams | 39 | |
| Calories in 1 cup | 91 | 233 g |
Mineral chart - relative view
Vitamin chart - relative view
All nutrients for Hot and sour soup per 100g
| Nutrient | Value | DV% | In TOP % of foods | Comparison |
| Vitamin A | 9µg | 1% | 52% | |
| Calories | 39kcal | 2% | 91% |
1.2 times less than Orange
|
| Protein | 2.6g | 6% | 73% |
1.1 times less than Broccoli
|
| Fats | 1.2g | 2% | 73% |
27.5 times less than Cheese
|
| Vitamin C | 0mg | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Net carbs | 3.9g | N/A | 60% |
14.1 times less than Chocolate
|
| Carbs | 4.4g | 1% | 62% |
6.5 times less than Rice
|
| Cholesterol | 21mg | 7% | 43% |
17.8 times less than Egg
|
| Vitamin D | 0.1µg | 1% | 60% |
22 times less than Egg
|
| Magnesium | 9mg | 2% | 85% |
15.6 times less than Almonds
|
| Calcium | 19mg | 2% | 55% |
6.6 times less than Milk
|
| Potassium | 55mg | 2% | 91% |
2.7 times less than Cucumber
|
| Iron | 0.64mg | 8% | 72% |
4.1 times less than Beef broiled
|
| Sugar | 0.42g | N/A | 71% |
21.4 times less than Coca-Cola
|
| Fiber | 0.5g | 2% | 56% |
4.8 times less than Orange
|
| Copper | 0.03mg | 3% | 90% |
5.5 times less than Shiitake
|
| Zinc | 0.22mg | 2% | 83% |
28.7 times less than Beef broiled
|
| Starch | 2.4g | 1% | 95% |
6.3 times less than Potato
|
| Phosphorus | 32mg | 5% | 83% |
5.7 times less than Chicken meat
|
| Sodium | 376mg | 16% | 28% |
1.3 times less than White bread
|
| Vitamin E | 0.39mg | 3% | 62% |
3.7 times less than Kiwi
|
| Manganese | 0.09mg | 4% | 62% | |
| Selenium | 0.4µg | 1% | 91% | |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.03mg | 2% | 84% |
10.2 times less than Pea raw
|
| Vitamin B2 | 0.03mg | 2% | 87% |
4.2 times less than Avocado
|
| Vitamin B3 | 0.51mg | 3% | 78% |
18.9 times less than Turkey meat
|
| Vitamin B5 | 0.23mg | 5% | 79% |
5 times less than Sunflower seeds
|
| Vitamin B6 | 0.06mg | 5% | 74% |
1.9 times less than Oats
|
| Vitamin B12 | 0.1µg | 4% | 62% |
7 times less than Pork
|
| Vitamin K | 1.1µg | 1% | 77% |
92.4 times less than Broccoli
|
| Trans fat | 0g | N/A | 100% |
N/A
|
| Folate | 8µg | 2% | 68% |
7.6 times less than Brussels sprouts
|
| Choline | 40mg | 7% | 67% | |
| Saturated fat | 0.23g | 1% | 76% |
25.7 times less than Beef broiled
|
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.29g | N/A | 76% |
34 times less than Avocado
|
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.31g | N/A | 71% |
151.7 times less than Walnut
|
| Tryptophan | 0.02mg | 0% | 93% |
16.1 times less than Chicken meat
|
| Threonine | 0.11mg | 0% | 89% |
6.5 times less than Beef broiled
|
| Isoleucine | 0.08mg | 0% | 92% |
11.4 times less than Salmon raw
|
| Leucine | 0.15mg | 0% | 91% |
16.1 times less than Tuna Bluefin
|
| Lysine | 153mg | 7% | 88% |
338.5 times more than Tofu
|
| Methionine | 0.04mg | 0% | 90% |
2.5 times less than Quinoa
|
| Phenylalanine | 0.09mg | 0% | 92% |
7.9 times less than Egg
|
| Valine | 0.09mg | 0% | 92% |
22.1 times less than Soybean raw
|
| Histidine | 0.06mg | 0% | 90% |
12.9 times less than Turkey meat
|
| Fructose | 0g | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Caffeine | 0mg | 0% | 100% | |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0g | N/A | 100% |
N/A
|
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0g | N/A | 100% |
N/A
|
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.03g | N/A | 92% |
304.7 times less than Canola oil
|
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0g | N/A | 100% |
N/A
|
| Omega-3 - Eicosatrienoic acid | 0g | N/A | 100% | |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0g | N/A | 100% | |
| Omega-6 - Dihomo-gamma-linoleic acid | 0g | N/A | 100% | |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0g | N/A | 100% | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 0.27g | N/A | 94% |
45.1 times less than Almonds
|
Check out similar food or compare with current
NUTRITION FACTS LABEL
Serving Size ______________
Health checks
Hot and sour soup nutrition infographic
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.



