Egg vs. Frozen yogurt — In-Depth Nutrition Comparison
Compare
What are the main differences between eggs and frozen yogurt?
- Eggs have more copper, selenium, choline, vitamin B12, vitamin B2, vitamin D, phosphorus, folate, and iron than frozen yogurt.
- Eggs' daily need coverage for copper is 221% higher.
- Frozen yogurt has 29 times less vitamin D than eggs. Eggs have 87IU of vitamin D, while frozen yogurt has 3IU.
- Frozen yogurt is lower in cholesterol.
- Frozen yogurt has a higher glycemic index (51) than eggs (0).
We used Egg, whole, cooked, hard-boiled and Frozen yogurts, flavors other than chocolate types in this comparison.
Infographic
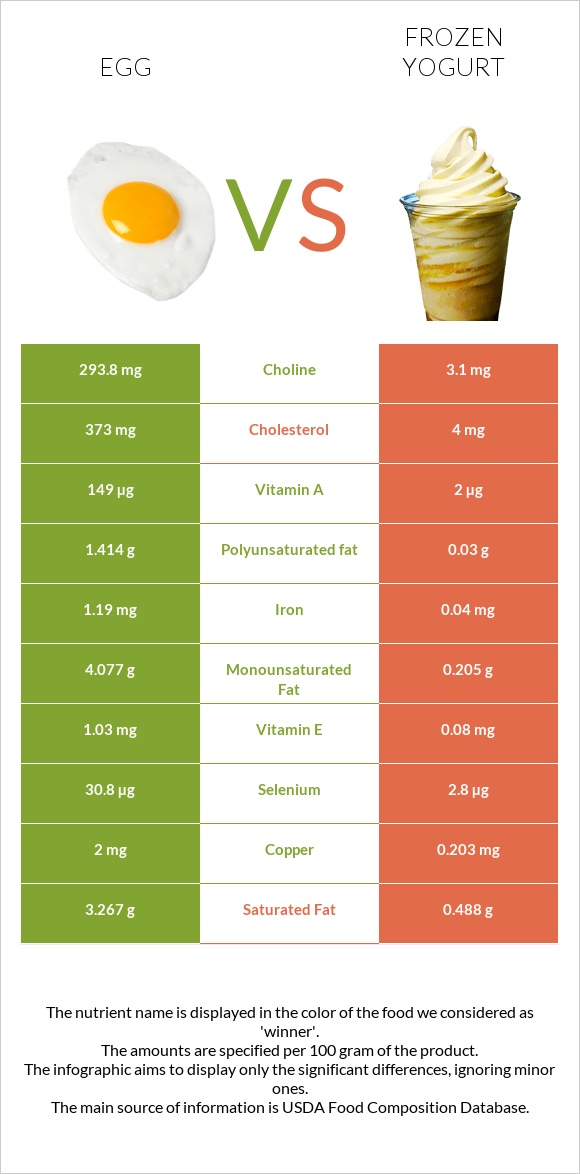
Infographic link
Mineral Comparison
Mineral comparison score is based on the number of minerals by which one or the other food is richer. The "coverage" charts below show how much of the daily needs can be covered by 300 grams of the food.
| Contains more IronIron | +158.7% |
| Contains more CopperCopper | +22122.2% |
| Contains more ZincZinc | +275% |
| Contains more PhosphorusPhosphorus | +93.3% |
| Contains more ManganeseManganese | +∞% |
| Contains more SeleniumSelenium | +1521.1% |
| Contains more CalciumCalcium | +100% |
| Contains more PotassiumPotassium | +23.8% |
| Contains less SodiumSodium | -49.2% |
Vitamin Comparison
Vitamin comparison score is based on the number of vitamins by which one or the other food is richer. The "coverage" charts below show how much of the daily needs can be covered by 300 grams of the food.
| Contains more Vitamin AVitamin A | +204.1% |
| Contains more Vitamin EVitamin E | +1044.4% |
| Contains more Vitamin DVitamin D | +2100% |
| Contains more Vitamin B1Vitamin B1 | +65% |
| Contains more Vitamin B2Vitamin B2 | +185% |
| Contains more Vitamin B5Vitamin B5 | +∞% |
| Contains more Vitamin B6Vitamin B6 | +202.5% |
| Contains more Vitamin B12Vitamin B12 | +1485.7% |
| Contains more FolateFolate | +1000% |
| Contains more CholineCholine | +1171.9% |
| Contains more Vitamin CVitamin C | +∞% |
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Copper | 2mg | 0.009mg | 221% |
| Cholesterol | 373mg | 13mg | 120% |
| Selenium | 30.8µg | 1.9µg | 53% |
| Choline | 293.8mg | 23.1mg | 49% |
| Vitamin B12 | 1.11µg | 0.07µg | 43% |
| Vitamin B5 | 1.398mg | 28% | |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.513mg | 0.18mg | 26% |
| Protein | 12.58g | 3g | 19% |
| Phosphorus | 172mg | 89mg | 12% |
| Vitamin D | 87IU | 3IU | 11% |
| Vitamin D | 2.2µg | 0.1µg | 11% |
| Fats | 10.61g | 3.6g | 11% |
| Vitamin A | 149µg | 49µg | 11% |
| Folate | 44µg | 4µg | 10% |
| Iron | 1.19mg | 0.46mg | 9% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 1.414g | 0.1g | 9% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 4.077g | 0.986g | 8% |
| Carbs | 1.12g | 21.6g | 7% |
| Zinc | 1.05mg | 0.28mg | 7% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.121mg | 0.04mg | 6% |
| Vitamin E | 1.03mg | 0.09mg | 6% |
| Calcium | 50mg | 100mg | 5% |
| Saturated fat | 3.267g | 2.326g | 4% |
| Sodium | 124mg | 63mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.066mg | 0.04mg | 2% |
| Calories | 155kcal | 127kcal | 1% |
| Manganese | 0.026mg | 1% | |
| Potassium | 126mg | 156mg | 1% |
| Vitamin C | 0mg | 0.7mg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 1.12g | 21.6g | N/A |
| Magnesium | 10mg | 10mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 1.12g | 19.92g | N/A |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.064mg | 0.07mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 0.3µg | 0.3µg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.153mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.604mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.686mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 1.075mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.904mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.392mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.668mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.767mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.298mg | 0% | |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.005g | 0g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.038g | 0g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
Macronutrient breakdown side-by-side comparison
Protein:
12.58 g
Fats:
10.61 g
Carbs:
1.12 g
Water:
74.62 g
Other:
1.07 g
Protein:
3 g
Fats:
3.6 g
Carbs:
21.6 g
Water:
71.2 g
Other:
0.6 g
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +319.3% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +194.7% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +78.3% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +1828.6% |
~equal in
Water
~71.2g
Fat Type Comparison
Fat type breakdown side-by-side comparison
Saturated fat:
Sat. Fat
3.267 g
Monounsaturated fat:
Mono. Fat
4.077 g
Polyunsaturated fat:
Poly. Fat
1.414 g
Saturated fat:
Sat. Fat
2.326 g
Monounsaturated fat:
Mono. Fat
0.986 g
Polyunsaturated fat:
Poly. Fat
0.1 g
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +313.5% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +1314% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -28.8% |