Elk meat vs. Deer meat — Nutrition and Health Impact Comparison

Summary
Deer meat is richer in vitamins B1, B2, B3, B6, B12, and potassium. Elk is richer in vitamin B5, copper, and zinc. Their health impacts are mainly based on their nutritional differences. Both meats are rich in protein, iron, selenium, and phosphorus.
Introduction
Deer and elk meats are considered one of the most commonly consumed game meats out there, but what is the difference between them?
This article showcases and explains the differences between deer meat and elk meat regarding their nutritional contents and health impacts.
Nutrition
This section will compare 100 grams of roasted venison (deer meat) to 100 grams of elk meat regarding their nutrients.
Calories
Deer and elk meat have nearly similar calories.
Fats
They are considered lean meats. However, deer meat is even leaner than elk meat. Elk meat contains 3.4 g of fatty acids, and deer meat contains 2.4g.
Elk meat contains less cholesterol.
The saturated fat content of both is low.
You can read about the differences between deer meat and pork.
Proteins
Perfect sources of protein. Venison and elk meat are very rich in protein.
They have similar amounts of protein, averaging 30g per 100g. Their amino acid profile is rich in all amino acids.
Carbs
Their carb content is negligible. Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+45.1%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+63.6%
Minerals
Deer meat is richer in potassium, and elk meat is richer in copper and zinc. They are both rich in phosphorus, iron, and selenium. Yet, they have similar amounts of the 3 minerals.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+37.4%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-12.3%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+13.8%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+10.7%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+15.8%
Vitamins
Their vitamin content is very rich in B complex vitamins. Deer is richer in vitamins B1, B2, B3, B6, and B12. Elk meat is richer in vitamin B5.
They both have a rich profile in B complex vitamins. Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+41.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+12.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+80.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+52.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+42.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+26.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+22.3%
You can also check the nutritional composition of beef vs deer meats.
Health Impacts
Deer meat or elk meat, which one is the healthiest?
No specific peer-reviewed paper has a clear-cut answer regarding which one is healthier. Overall, moderate consumption of red meat, including deer meat or elk meat, can be considered healthy. However, when it comes to comparisons between them, there are some differences between mineral and vitamin profiles, but overall, saying deer or elk is healthier won't be scientifically accurate.
You can check the nutritional composition of beef vs elk meat.
Considering that they are red meat, both should be consumed in moderation. They are highly nutritious meats regarding their mineral, vitamin, and macronutrient profiles; however, consumption of red meat in high amounts and frequency, significantly when char-grilled and burnt, can increase the risks of some cancers, such as colorectal cancer (1).
Venison, such as deer and elk meat, should be considered for some parasites and microbes since they are consumed from unregulated sources and hunted. Considering the hunters' hunting process, how long was the meat not kept refrigerated, and where was it cleaned? All these factors can affect the quality of the meat.
Most health benefits from elk or deer come from their nutritional composition.
Deer is richer in most B complex vitamins, which are essential for the normal functioning of the body, and in addition, vitamin B12 and iron, which decrease the risks of anemias (2)(3)(4).
Elk, in comparison, is richer in zinc and copper, essential minerals to maintain the immune system, hair, and skin, and copper also has some antioxidative effects (5)(6).
Deer venison and elk meat are on the top list of healthy game meats.
They are high in protein and lean. However, it is important to consider the hunting, refrigeration, and handling of the animal. It is also essential to consider the amounts of salt we add while eating.
Venison is considered a high-quality meat. I would also include elk as a high-quality meat.
As a medical professional, I recommend always eating meat, especially those hunted in the wilderness, as well done. However, astronomically, this will make the meat a bit dry.
So, venison should be eaten well-done. Elk meat should also be eaten well-done, even if this will compromise a bit of texture. It's better to be safe than sorry.
General differences
Many people have a palate for game meat, such as deer and elk. Game meat is where an animal is hunted in its wild location for meat consumption.
Nowadays, we have farmed elk or deer meat aswell.
Game meats such as deer or elk meats are usually leaner and need more preparation skills because the animals usually run and graze in the wilderness. During the hunting process, the meat can harden due to the stress put on the animal. Thus, game meat needs proper handling when it comes to consumption. And lastly, one of the most critical aspects of game meat and hunting is ethics.
In general, deer meat is mainly known as venison. However, elk meat can also be termed venison elk.
Taste and texture
It is comparatively more robust in flavor, and depending on its different cuts, it can range from tender to a bit chewier. Elk meat, in comparison, is more tender and has a flavor that is less earthy and gamey compared to venison.
Elk meat tastes more like prime beef with a hint of an earthy flavor. Elk has a gamey taste.
They are considered leaner types of meats than beef or other farm-raised animals. Many recipes include venison or elk steaks, burgers, and soups.
Cooking
Elk meat is cooked like deer meat. It is important not to overcook them since they are lean and will become dry once overcooked. They are often used interchangeably. You can sear, grill, roast, pan-fry, and stew. Since they are lean meats, they quickly lose moisture and become dry.
References
- https://progressreport.cancer.gov/prevention/red_meat
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35933667/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18330026/
- https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/anemia/vitamin-b12-deficiency-anemia
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8970836/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22071549/
Infographic
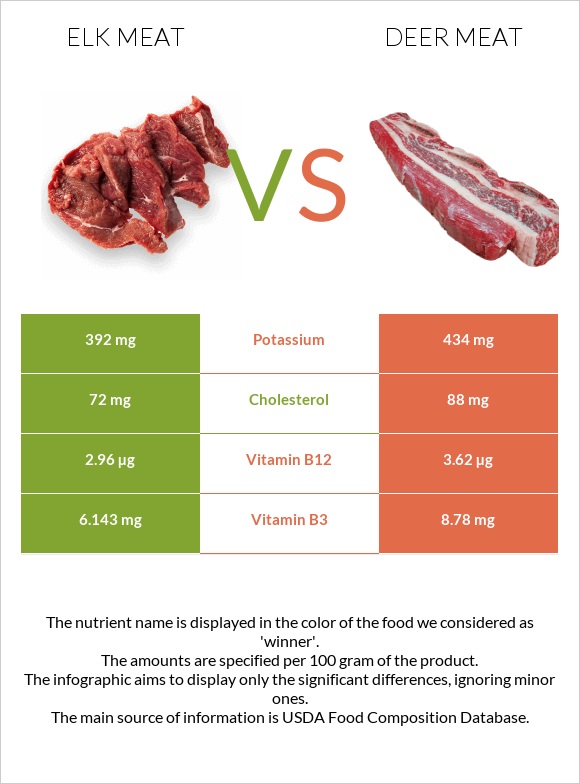
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B12 | 2.96µg | 3.62µg | 28% |
| Vitamin B3 | 6.143mg | 8.78mg | 16% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.37mg | 0.563mg | 15% |
| Copper | 0.349mg | 0.254mg | 11% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.144mg | 0.26mg | 10% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.485mg | 0.614mg | 10% |
| Vitamin B5 | 1.212mg | 0.856mg | 7% |
| Cholesterol | 72mg | 88mg | 5% |
| Protein | 30.76g | 29.9g | 2% |
| Fats | 3.41g | 2.35g | 2% |
| Iron | 4.07mg | 4.25mg | 2% |
| Phosphorus | 285mg | 299mg | 2% |
| Calories | 162kcal | 149kcal | 1% |
| Magnesium | 29mg | 33mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 392mg | 434mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 4.12mg | 3.99mg | 1% |
| Selenium | 10.5µg | 11µg | 1% |
| Saturated fat | 1.342g | 1.142g | 1% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.97g | 0.554g | 1% |
| Calcium | 5mg | 5mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 50mg | 57mg | 0% |
| Vitamin E | 0.55mg | 0.62mg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.019mg | 0.022mg | 0% |
| Folate | 9µg | 9µg | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.161g | 0.127g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.275mg | 0.266mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 1.236mg | 1.133mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 1.291mg | 1.287mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 2.293mg | 2.28mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 2.513mg | 2.434mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.755mg | 0.7mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 1.126mg | 1.133mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.428mg | 1.455mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.948mg | 0.895mg | 0% |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.002g | 0.001g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.002g | 0g | N/A |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +75.1% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +26.8% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -14.9% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Elk meat - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174429/nutrients
- Deer meat - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174430/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.