Fajita vs. Burrito — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Burritos contain nine times more Folate and two times more Vitamin B1, iron, and magnesium than fajitas. They also have lower sodium, glycemic index, and cholesterol. On the other hand, fajitas contain more Vitamin B3, Vitamin B6, and phosphorus and have fewer calories than burritos.
Introduction
Burritos and fajitas are popular Mexican dishes. Both are prepared with tortillas; therefore, usually, it is hard to differentiate them.
In this article, we will compare the differences between burritos and fajitas, focusing on their nutritional content and health impact.
Actual Differences
Externally, burritos and fajitas may seem similar; however, they have very little in common.
The main difference between them is their ingredient content: fajita usually contains grilled meat and veggies, while burrito is a tortilla wrapped with meat, beans, and other fillings inside.
Besides, the burrito is wrapped in an extra-large-sized tortilla, but the fajita is wrapped in the small ones.
Varieties
There are different burritos; the most popular are Wet burritos, Poncho burritos, and Bean-and-Cheese burritos. Bean-and-Cheese was the first burrito that spread across the United States.
Fajitas are usually made from meat, grilled or sauteed peppers, and onions. However, fajita has different variations, such as Cheesy Enchilada Rice, Pineapple Slaw, and Coconut Rice.
Culinary
Burritos and fajitas are the most popular Mexican food around the world. However, they are usually prepared as fast food. Some cuisines took the burrito concept, made it into a burrito bowl, and turned it into healthy food.
On the other hand, fajitas have the healthiest variations, such as chicken fajitas or fajitas without tortillas.
Nutrition
At the bottom of this page, you can find a nutrition table, which will help you better understand the differences in the nutrition of burritos and fajitas.
Macronutrients
The protein amount of a fajita is three times higher than a burrito's. Fajitas has 18.56 g protein per 100 g, while burrito has 6.48 g protein per 100 g. In comparison, burritos contain more carbohydrates and more fats than fajitas. However, fajita is high in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. You can read more detailed information in the sections below.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+186.4%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+34.4%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+55.7%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+1376.2%
Carbs
The level of carbs in burritos is way higher than in fajita. It contains 32.92 g of carbs, while fajitas have only 2.23 g. What is interesting, burritos are lower in sugar.
Fats
Burritos have higher amounts of fats than fajitas. The saturated fat in the burrito fills 15% of the daily value, while, in fajitas, it is less as it is 7% of the daily value. The amount of saturated fat in the burrito is two times higher than that of fajita. It has 3.2 g per 100 g, whereas fajita has 1.6 g per 100 g.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-49.7%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+97.6%
Calories
Overall, burritos are higher in calories than fajitas due to their combination of different fillings, such as sour cream, salsa, etc. Burritos have 206 calories per 100 g, while fajitas have only 135 calories per 100 g.
Minerals
The mineral amount of the burrito is significantly higher than that of the fajita. Fajita contains five times higher phosphorus and two times higher zinc than a burrito.
Conversely, a burrito has four times more copper and three times more calcium than a fajita. The burrito also has higher levels of magnesium and iron. Both have an equal level of potassium. Burritos contain more potassium than fajitas. It has 301 mg per 100 g, while fajita contains 284 mg per 100 g.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+95.7%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+515.6%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+65.3%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+81.8%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+300%
Contains
more
IronIron
+110.1%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+480%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-43.2%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+506.1%
Vitamins
Burritos and fajitas are packed with vitamins in different amounts. Fajitas lack Vitamin C, Vitamin A, and Vitamin D, whereas burritos have moderate amounts of these vitamins. Moreover, Vitamin B1, Vitamin B2, B5, and Folate are also higher in burritos. On the other hand, fajitas contain more Vitamin B3 and Vitamin B6 than burritos. Both foods have an equal level of Vitamin 12.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+155.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+176.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+190%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+31.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+26.7%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+900%
Glycemic Index
The food's glycemic index is a value based on how slowly or how quickly food can cause increases in blood glucose levels. The glycemic index of a burrito is equal to 37; fajita has a GI of 42. Both are considered low-glycemic index foods.
Acidity
The acidity of foods is described by the potential renal acid load (PRAL), which indicates the acid production of the food within the body. The acidity of a burrito is about 3.2 (alkaline), while that of a fajita is 12.6 (acidic).
Health Impact
Both burritos and fajitas can be modified from healthy foods to junk food.
Weight Loss
From the very start, it is necessary to point out that burritos and fajitas are not often associated with weight loss. Usually, they are high in calories; however, you can make some adaptations to make them acceptable for people craving them, even when on a diet. Choose the Fajitas Bowl or Burrito Bowl; they are prepared without tortillas, with about 100 calories each. Also, they contain healthy ingredients, such as Vitamin C and fiber; therefore, they are the healthiest of all varieties (1).
Diabetes
According to the Indian study, there is a correlation between burrito consumption and high BMI (body measure size), leading to increased risks of developing diabetes. In contrast to a burrito, fajitas are the safest and most delicious low-carb dish for people with diabetes. The meat and vegetables in fajita are grilled and contain fewer carbs and no sugar. If flour tortillas are replaced, fajitas can be diabetic-friendly (2).
Cardiovascular Health
Studies show burritos contain nearly 55% of the required daily trans fat. As mentioned above, consuming burritos is associated with high BMI, which increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Chicken fajitas are packed with nutritious ingredients, lean protein, and fiber, containing no trans fats. Eating fajitas is not an issue, but in any case, try to avoid using it daily (3) (4).
In summary, while burritos and fajitas can be part of a balanced diet, they tend to be a healthier option for cardiovascular health due to their lower calorie and fat content, especially when prepared with lean protein and plenty of vegetables. However, portion control and ingredient selection are crucial for both options.
Side Effects
Red Meat Allergy
Red meat allergy is common in any age group and race. People usually have this allergy if they are sensitive to cat serum albumin that cross-reacts with albumin in pork. These cases often relate to specific IgE to galactose-α-1,3-galactose (α-Gal), an oligosaccharide of non-primate mammals. Symptoms often include urticaria, vomiting, stomach cramps, and, in rare cases, anaphylaxis (5).
Infographic
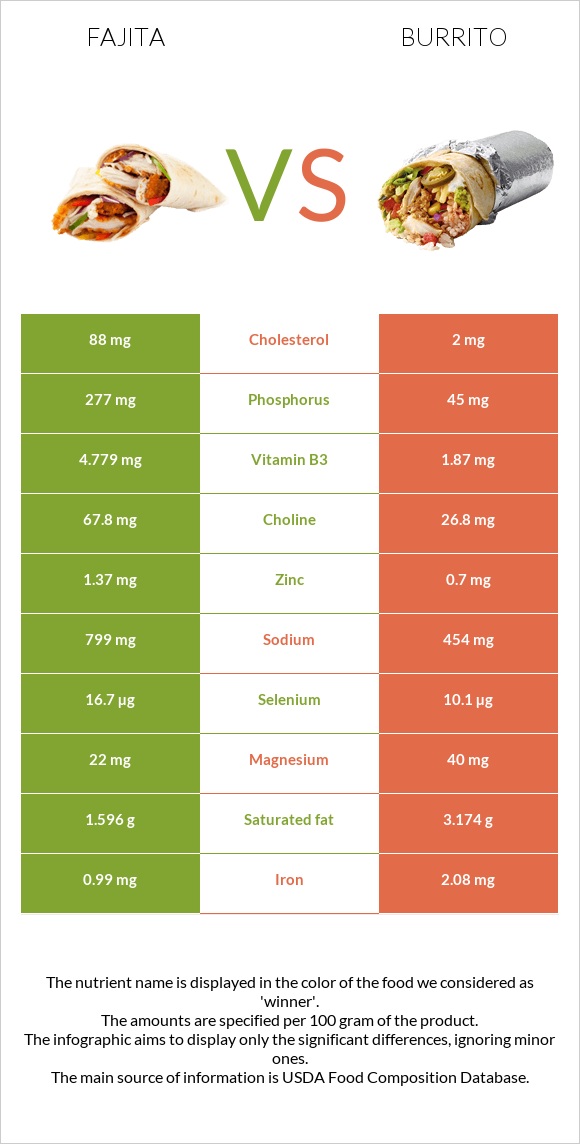
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Phosphorus | 277mg | 45mg | 33% |
| Cholesterol | 88mg | 2mg | 29% |
| Protein | 18.56g | 6.48g | 24% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.387mg | 0.14mg | 19% |
| Vitamin B3 | 4.779mg | 1.87mg | 18% |
| Copper | 0.03mg | 0.174mg | 16% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.1mg | 0.29mg | 16% |
| Sodium | 799mg | 454mg | 15% |
| Manganese | 0.066mg | 0.4mg | 15% |
| Iron | 0.99mg | 2.08mg | 14% |
| Selenium | 16.7µg | 10.1µg | 12% |
| Carbs | 2.23g | 32.92g | 10% |
| Folate | 4µg | 40µg | 9% |
| Choline | 67.8mg | 26.8mg | 7% |
| Saturated fat | 1.596g | 3.174g | 7% |
| Zinc | 1.37mg | 0.7mg | 6% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.213mg | 0.28mg | 5% |
| Calories | 135kcal | 206kcal | 4% |
| Magnesium | 22mg | 40mg | 4% |
| Calcium | 13mg | 52mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.726mg | 0.92mg | 4% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 1.089g | 0.551g | 4% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.54µg | 0.5µg | 2% |
| Fats | 5.73g | 6.22g | 1% |
| Vitamin C | 0mg | 0.9mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 284mg | 301mg | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 0.22mg | 1% | |
| Net carbs | 2.23g | 32.92g | N/A |
| Vitamin K | 0.2µg | 0% | |
| Monounsaturated fat | 2.333g | 2.184g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.2mg | 0.079mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.452mg | 0.244mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.813mg | 0.27mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.56mg | 0.504mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 1.857mg | 0.343mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.552mg | 0.107mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.763mg | 0.351mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.847mg | 0.319mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.68mg | 0.172mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.007g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.01g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






