Salmon vs. Snapper — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Salmon is richer in B complex vitamins, vitamins A, E, and D. It is also richer in selenium, choline, phosphorus, and omega-3 fats. In comparison, snapper is a leaner fish with less fat and fewer calories. Salmon is packed with nutrients and has several more positive health impacts.
Introduction
This article compares two types of fish; snapper vs. salmon. The snapper fish is a family of fish that have 113 different species. One of the most famous is the red snapper, the most sought-after type of snapper. It has a mild sweet flavor, and it is a lean fish.
In comparison, we have salmon fish containing different species like the chinook, coho, chum, pink, and sockeye. Salmon is a fattier fish that has a rich and oily taste.
In this article, we will compare their nutritional content and health impacts.
Nutritional content comparison
This section will compare 100g of each fish in its raw state.
Calories
Salmon is higher in calories by 1.5 times. Snapper contains 100 calories, and salmon contains 150 calories.
Carbs
The carb content of both fish is negligible.
Fats
Salmon contains 9.5 times more fat compared to snapper. Snapper is low-fat lean fish. Salmon contains about 12.3g of fats. Salmon is richer in unsaturated fats.
Salmon is richer in Omega-3 fats.
Protein
The protein content of both fish is similar. They are rich in proteins, nearly 20g per 100g.
Minerals
Salmon is richer in selenium, phosphorus, and choline. Snapper is also a good source of selenium and phosphorus, comparatively salmon is richer.
Below we can visualize their mineral distributions.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
IronIron
+41.7%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+25.4%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+23.3%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+166.7%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+35.9%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+18.4%
Vitamins
Salmon is richer in all vitamins compared to snapper. Salmon is richer in B complex vitamins, D, A, and E.
Below we can visualize their vitamin distributions.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+131.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+97.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+541.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+3275%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+2225.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+69.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+40.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+466.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+25%
Health impacts
We will focus on the different health impacts each fish provides.
Omega-3 benefits
Salmon is richer in omega-3 fats and has several positive health impacts on overall health. Omega-3 fats are important to be added to our diets as they positively affect our nervous system and cardiovascular system by decreasing levels of triglycerides. (1)(2)(3)(4)
You can also read about Trout vs. Salmon. They are rich in omega-3 fats and are both fatty fish. However, it is important to explore their differences.
Muscle building
Although snapper is a leaner fish, intuitively, people would tend to go for snapper fish because it's a leaner fish. However, salmon is packed with B complex vitamins, vitamins A, E, and D, and minerals, providing an additional health impact in athletic dietary options. (5)
Anemia
Snapper and salmon are great vitamin B12 and iron sources, salmon being richer in both.
Snapper and salmon consumption decrease vitamin B12 deficiency or megaloblastic anemia risks; they may also partake in anemia treatment. They also decrease the risk of iron deficiency or microcytic anemia. (6)(7)
Vitamin D
Salmon is a fish that is richer in vitamin D. In turn, vitamin D has several benefits, such as maintaining normal immune, bone health, and calcium levels. In addition, salmon is a good option to be consumed in countries with low sun exposure. (8)
Choline
Choline is essential for the homeostasis of homocysteine and acetylcholine. Consumption of bioavailable choline is highly important; in this case, salmon fish is a rich source of choline. (9)
Selenium
Selenium is a mineral that has importance in maintaining normal immunity and cognitive performance. In addition, selenium intake is linked with decreased risks of autoimmune thyroid diseases and lower viral urinary tract infections in males and females. (10)
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15366399/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29350557/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31422671/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30601174/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4422265/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28189173/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12643357/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30335299/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32993309/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22381456/
Infographic
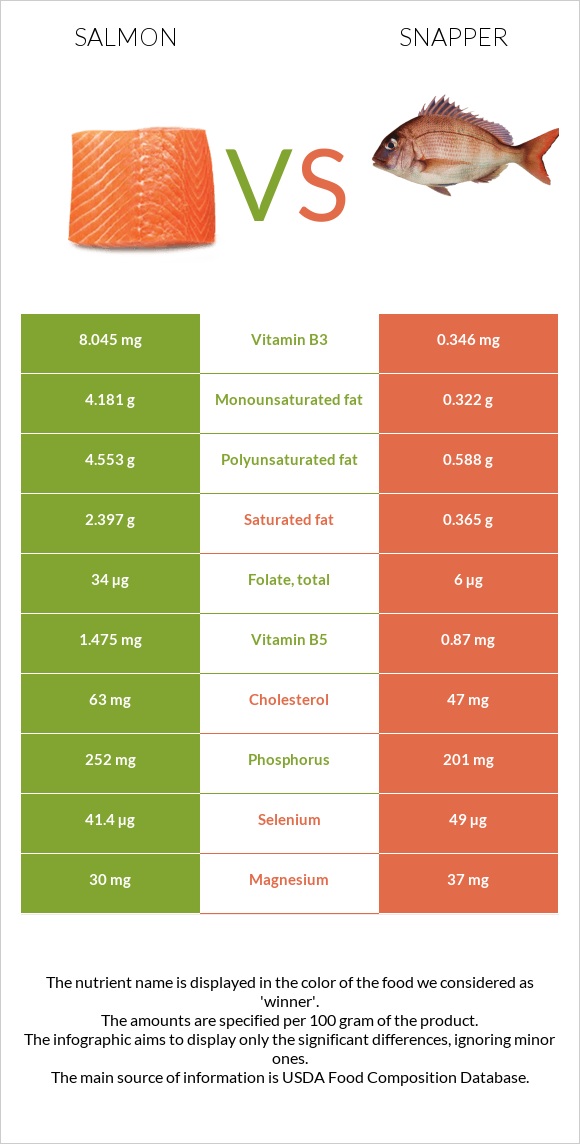
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin D | 526 IU | 66% | |
| Vitamin D | 13.1µg | 66% | |
| Vitamin B3 | 8.045mg | 0.346mg | 48% |
| Vitamin B12 | 2.8µg | 3.5µg | 29% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 4.553g | 0.588g | 26% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.34mg | 0.053mg | 24% |
| Fats | 12.35g | 1.72g | 16% |
| Choline | 90.5mg | 16% | |
| Selenium | 41.4µg | 49µg | 14% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.647mg | 0.46mg | 14% |
| Vitamin B5 | 1.475mg | 0.87mg | 12% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.135mg | 0.004mg | 10% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 4.181g | 0.322g | 10% |
| Saturated fat | 2.397g | 0.365g | 9% |
| Protein | 22.1g | 26.3g | 8% |
| Vitamin E | 1.14mg | 8% | |
| Phosphorus | 252mg | 201mg | 7% |
| Folate | 34µg | 6µg | 7% |
| Cholesterol | 63mg | 47mg | 5% |
| Calories | 206kcal | 128kcal | 4% |
| Potassium | 384mg | 522mg | 4% |
| Vitamin A | 69µg | 35µg | 4% |
| Calcium | 15mg | 40mg | 3% |
| Vitamin C | 3.7mg | 1.6mg | 2% |
| Magnesium | 30mg | 37mg | 2% |
| Iron | 0.34mg | 0.24mg | 1% |
| Copper | 0.049mg | 0.046mg | 0% |
| Zinc | 0.43mg | 0.44mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 61mg | 57mg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.016mg | 0.017mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 0.1µg | 0% | |
| Tryptophan | 0.248mg | 0.294mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.969mg | 1.153mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 1.018mg | 1.212mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.796mg | 2.137mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 2.03mg | 2.415mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.654mg | 0.778mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.863mg | 1.027mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.139mg | 1.355mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.651mg | 0.774mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.69g | 0.048g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 1.457g | 0.273g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.17g | 0.022g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more FatsFats | +618% |
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +19% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +103.8% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +1198.4% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +674.3% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -84.8% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Salmon - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/175168/nutrients
- Snapper - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173699/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.