Grouper vs. Halibut — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Grouper and halibut have many differences in nutritional content. Grouper is higher in protein, vitamin B1, and minerals. Halibut contains more cholesterol, B-complex vitamins, and higher calories. Two species promote heart health.
Introduction
Grouper and halibut are two of the most widespread fishes in the world. In this article, we will compare these fishes, focusing on their nutritional composition and health impact, and showing their actual differences.
Actual differences
Grouper (1) is a freshwater fish from the Serranidae family. This fish is usually widespread in the Gulf of Mexico and the coasts of South America. Grouper has a mild, a bit sweet taste. Grouper has a broader range of cooking methods: it is usually consumed in baked, broiled, fried, grilled, or steamed forms.
Halibut (2) is a kind of flatfish. In contrast to grouper, halibut has a sweet and subtle flavor. Typically, it is steamed, baked, poached, or grilled. The fish is found in the Atlantic Ocean and the California coasts. However, it is offered and accessible everywhere.
Nutrition
Here we will discuss grouper and halibut's macronutrient, mineral, and vitamin composition. Both of them do not provide any amounts of carbs.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+34.9%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+18.6%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+1264.6%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+292%
Protein
Grouper is higher in protein than halibut.
Both contain many essential amino acids, such as lysine, histidine, and phenylalanine.
Fat
Halibut is higher in fats than grouper. It is richer in both saturated and unsaturated fats. Halibut is an excellent source of omega-3 fatty acids.
Halibut is 12mg higher in cholesterol than grouper.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-90.4%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+3908.2%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+335%
Calories
Grouper is a low-calorie food, while halibut is classified as medium-calorie. Due to its higher fat composition, halibut provides more calories than grouper. It has two times more calories per 100g serving.
Minerals
The winner in this section is grouper.
Halibut provides more phosphorus than grouper. Grouper contains more calcium, iron, magnesium, zinc, and potassium. Grouper is 50g lower in sodium than halibut.
Check the mineral comparison chart below for a visual representation of the distribution of minerals.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+12.1%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+425%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+38.1%
Contains
more
IronIron
+34.1%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+18.4%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-48.5%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+46.9%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+25%
Vitamins
Grouper is richer in vitamins B1, B5, and folate. Halibut contains higher amounts of B-complex vitamins.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+177.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+202.1%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+900%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+1616.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+404.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+38.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+39.1%
Health impact
Cardiovascular health
Grouper and halibut consumption are connected to lower cardiovascular disease risk (3). This is due to omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acid composition. These two compounds are long-chain essential fatty acids that are not produced in the human organism. Hence we must get them with the food we eat. Research shows that the risk of heart disease increases when there is no balance between omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acid concentrations in the blood flow (4). Halibut and grouper boost omega-3 levels in the bloodstream of those with higher omega-6 levels (5) (6).
References
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171962/nutrients
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171965/nutrients
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7468748/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34371930/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7990530/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23351633/
Infographic
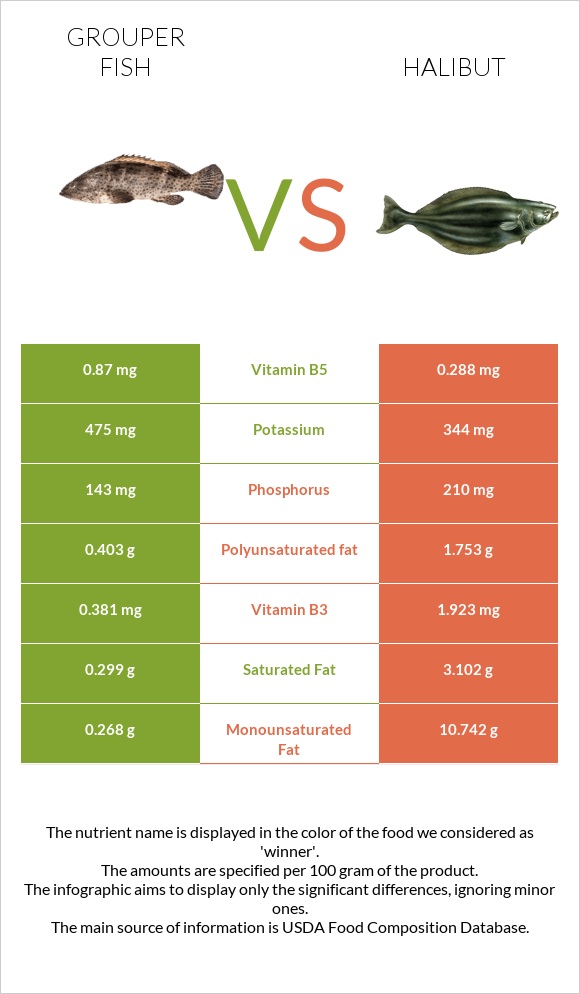
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.268g | 10.742g | 26% |
| Fats | 1.3g | 17.74g | 25% |
| Protein | 24.84g | 18.42g | 13% |
| Saturated fat | 0.299g | 3.102g | 13% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.87mg | 0.288mg | 12% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.69µg | 0.96µg | 11% |
| Phosphorus | 143mg | 210mg | 10% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.381mg | 1.923mg | 10% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.35mg | 0.485mg | 10% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.403g | 1.753g | 9% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.006mg | 0.103mg | 7% |
| Calories | 118kcal | 239kcal | 6% |
| Cholesterol | 47mg | 59mg | 4% |
| Potassium | 475mg | 344mg | 4% |
| Iron | 1.14mg | 0.85mg | 4% |
| Vitamin A | 50µg | 18µg | 4% |
| Calcium | 21mg | 4mg | 2% |
| Sodium | 53mg | 103mg | 2% |
| Folate | 10µg | 1µg | 2% |
| Magnesium | 37mg | 33mg | 1% |
| Copper | 0.045mg | 0.038mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.081mg | 0.073mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.51mg | 0.51mg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.012mg | 0.015mg | 0% |
| Selenium | 46.8µg | 46.8µg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.278mg | 0.206mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 1.089mg | 0.808mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 1.145mg | 0.849mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 2.019mg | 1.497mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 2.282mg | 1.692mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.735mg | 0.545mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.97mg | 0.719mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.28mg | 0.949mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.731mg | 0.542mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.035g | 0.674g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.213g | 0.504g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.017g | 0.114g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Grouper - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171963/nutrients
- Halibut - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174232/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






