Halibut vs. Cod — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Halibut is higher in vitamin B6, selenium, phosphorus, potassium, polyunsaturated fat, and monounsaturated fat.
On the other hand, cod is richer in vitamin D, vitamin B3, folate, and magnesium but lower in saturated fats.
Introduction
Cod belongs to the Gaddidae family (1), while halibut belongs to the Pleuronectidae family (2).
Cod is known for its product, cod liver oil which provides high doses of omega-3 fatty acids.
The stocks of cod are decreasing mainly due to overfishing and no recovery afterward (3). Halibut is more expensive than cod, the difference being 3.7$.
This article will examine the differences between cod and halibut, highlighting their nutritional composition and the health benefits associated with each.
Weight Loss and Diets
| Low Fat | Cod is preferred over halibut in a low-fat diet. |
| DASH | Cod has less sodium content compared to halibut and, therefore, may be preferred in a DASH diet. |
| Low Carb/ Low GI | Both of these fishes lack starch, fiber, and sugars. They are great sources of lean protein in low-carb and low-GI diets. |
| Vegan/ Vegetarian/ Pescetarian | Both fish are not permitted in vegetarian and vegan diets but are permitted in a pescatarian diet. |
| Low Calorie | Cod is favored over halibut in a low-calorie diet. |
Taste and Flavor
Cod has a non-fishy mild flavor, with a bit of a sweet taste, while halibut has a relatively stronger flavor.
Nutrition
Check out the infographics below to compare the nutritional composition of cod and halibut.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+1962.8%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+402.6%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+23.9%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+22.7%
Minerals
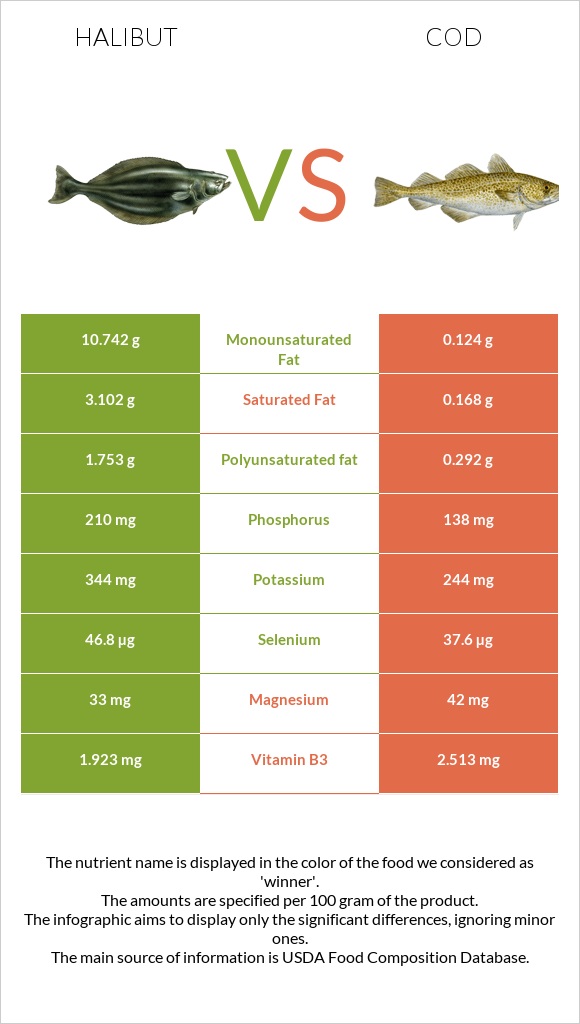
Halibut contains more potassium, selenium, and phosphorus than cod.
Cod is richer in calcium, magnesium, and less sodium compared to halibut.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+41%
Contains
more
IronIron
+73.5%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+52.2%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+24.5%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+27.3%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+250%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+13.7%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-24.3%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+33.3%
Vitamins
Halibut is richer in vitamin B5, vitamin A, and vitamin B6.
Cod contains more vitamin D, vitamin B3, and folate(vitamin B9).
Finally, both fish have equal vitamin A, vitamin B12, and vitamin K content.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+28.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+30.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+60%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+71.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+20.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+30.7%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+700%
Calories
Halibut is 1.5 times higher in calories than cod. Halibut has 239 calories per 100g, while cod contains only 105 calories.
Carbohydrates
Both fish lack carbohydrates (including fibers and sugars).
Proteins
Cod is higher in proteins compared to halibut.
Cod is particularly richer in the following essential amino acids: tryptophan, threonine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, valine, and histidine.
Fats
300 grams of halibut contains 64% fat while 300 grams of cod contains only 3% fat. Cod is lower in saturated fats and cholesterol. Halibut is higher in polyunsaturated fats and monounsaturated fats.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+8562.9%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+500.3%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-94.6%
Health Benefits
Cardiovascular Health
Halibut has almost 68 times the monounsaturated fat content and around 6 times the polyunsaturated fat content of cod.
Monounsaturated fats are known to decrease LDL cholesterol (low-density lipoprotein, also known as bad cholesterol) and, in turn, reduce the risk of heart disease (4).
Polyunsaturated fat also decreases bad cholesterol and thus protects from heart disease (5). A study has also shown that polyunsaturated fat consumption is correlated with a decrease in blood pressure in hypertensive patients (6).
Studies suggest that regular consumption of fish is associated with a lower risk of CVD (cardiovascular disease)-related mortality. While halibut typically contains higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids, both fish are low in saturated fats and cholesterol, making them heart-healthy choices when included as part of a balanced diet (7).
Cancer
A study showed that cod liver oil, a product derived from cod, stopped the growth of a tumor in rats (8). Moreover, daily use of cod liver oil for a year lowered the risk of death in tumor patients (9).
On the other hand, there are no studies showing a direct link between halibut consumption and cancer.
Vitamin B5
The recommended amount of vitamin B5 intake for adults is 5 mg daily (10). One hundred grams of halibut provides 0.25mg of vitamin B5.
Studies show that vitamin B5 might have beneficial wound-healing effects (11). Vitamin B5 might also have cholesterol-lowering effects and thus serve as a cardioprotective agent (12).
Vitamin D
Sufficient vitamin D consumption lowers the risk of some cancer types (13). Vitamin D also has an essential hormone production regulation function (14).
Folate
Cod contains 67% more folate than halibut.
Folate deficiency may lead to anemia. Low folate levels have been associated with an increased risk of cancer (15).
Phosphorus
Halibut is richer in phosphorus than cod. Phosphorus can be beneficial in the treatment of osteoporosis (16).
Anti-inflammatory Effects
Halibut is richer in polyunsaturated fats compared to cod. Omega-3 fatty acids have potent anti-inflammatory effects (17).
Downsides and Risks
Mercury Levels
Cod and halibut contain mercury and may be neurotoxic if not consumed in moderate amounts (18, 19).
Pregnant women should also be aware of the mercury content of the fish as it may harm the baby (20).
California halibut have elevated mercury levels, while Pacific halibut, Greenland turbot, and Atlantic halibut have moderate levels of mercury (20). Alaska, US, and Canada Pacific cod have moderate amounts of mercury, while Atlantic cod is low in mercury (21).
References
- https://books.google.am/books?hl=en&lr=&id=F_z6GhN3lPcC&oi
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0044848604002777
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S235198941400050X
- https://www.proquest.com/openview/80c82b61688f4c63faa8f92b0bfd7ee6/1
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1365-2621.1987.tb14045.x
- https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/british-journal-of-nutrition
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19064523/
- https://cancerres.aacrjournals.org/content/27/1/95-0
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19444919/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23193625/
- https://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/vitamins/pantothenic-acid
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6365107/
- http://anaturalhealingcenter.com/documents/Thorne/articles/vitamin_d10-2.pdf
- https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/80/6/1689S/4690513?login=true
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/01635589409514336
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14708952/
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11883-004-0087-5
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/6237436
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/233176690
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1281313/
- https://seafood.edf.org/halibut
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Monounsaturated fat | 10.742g | 0.124g | 27% |
| Fats | 17.74g | 0.86g | 26% |
| Selenium | 46.8µg | 37.6µg | 17% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.485mg | 0.283mg | 16% |
| Choline | 83.7mg | 15% | |
| Saturated fat | 3.102g | 0.168g | 13% |
| Phosphorus | 210mg | 138mg | 10% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 1.753g | 0.292g | 10% |
| Protein | 18.42g | 22.83g | 9% |
| Calories | 239kcal | 105kcal | 7% |
| Vitamin D | 46 IU | 6% | |
| Vitamin D | 1.2µg | 6% | |
| Iron | 0.85mg | 0.49mg | 5% |
| Vitamin E | 0.81mg | 5% | |
| Vitamin B3 | 1.923mg | 2.513mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.96µg | 1.05µg | 4% |
| Potassium | 344mg | 244mg | 3% |
| Magnesium | 33mg | 42mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.103mg | 0.079mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.288mg | 0.18mg | 2% |
| Folate | 1µg | 8µg | 2% |
| Vitamin C | 0mg | 1mg | 1% |
| Cholesterol | 59mg | 55mg | 1% |
| Calcium | 4mg | 14mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.51mg | 0.58mg | 1% |
| Sodium | 103mg | 78mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.073mg | 0.088mg | 1% |
| Copper | 0.038mg | 0.036mg | 0% |
| Vitamin A | 18µg | 14µg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.015mg | 0.02mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 0.1µg | 0% | |
| Tryptophan | 0.206mg | 0.256mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.808mg | 1.001mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.849mg | 1.052mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.497mg | 1.856mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 1.692mg | 2.097mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.545mg | 0.676mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.719mg | 0.891mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.949mg | 1.176mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.542mg | 0.672mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.674g | 0.004g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.504g | 0.154g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.114g | 0.013g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Halibut - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174232/nutrients
- Cod - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171956/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






