McGriddles vs. Egg McMUFFIN — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
The amount of cholesterol in McGriddles is significantly lower, but in contrast, it is higher in calories and overall fats. Egg McMuffin is higher in vitamin B2, calcium, and iron, while McGriddles are higher in phosphorus. Egg McMuffin contains less sugar.
Introduction
This article compares two famous fast foods from McDonald’s menu - Egg McMuffin(1) and sausage McGriddles(2). Please go through the sections of the article to find out helpful information about their nutrition and health impact.
Actual differences
Egg McMuffin is prepared from freshly cracked egg placed on an English Muffin, topped with Canadian bacon, butter, and American cheese. At the same time, McGriddles contains sausage and Applewood smoked bacon instead of Canadian bacon.
People following a vegetarian diet can use Egg McMuffin.
Nutrition
This section will compare the nutritional composition of a 100g serving of Egg McMuffin and McGriddles. Consider that the serving size for Egg McMuffin equals 126g, while McGriddles’ serving size is 135 g.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+83.9%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+44.2%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+62.2%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+31.1%
Calories
McGriddles and EggMcMuffin are classified as medium-calorie foods. However, McGriddles is higher in calories than Egg McMuffin: it provides 84 more calories.
Carbs
McGriddles are significantly richer in sugar. McGriddles contain 31.3g of carbs. In comparison, Egg McMuffin contains 21.7g of carbs. They are both high in carbs. However, Egg McMuffin contains fewer carbs.
Carbohydrate type comparison
Contains
more
SucroseSucrose
+1440%
Contains
more
GlucoseGlucose
+877.5%
Contains
more
LactoseLactose
+63.6%
Contains
more
FructoseFructose
+207.1%
Contains
more
MaltoseMaltose
+18.8%
Protein
Egg McMuffin is richer in proteins than McGriddles. It provides 13.6g of protein per 100g, whereas McMuffin has 8.4g.
Fats
McGriddles is nearly two times higher in fats than Egg McMuffin. It provides 17.8g of fats per 100g compared to 9.7g in Egg McMuffin. McGriddles are significantly higher in monounsaturated fats.
Surprisingly, Egg McMuffin contains 143mg more cholesterol than McGriddles.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+176.8%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+49.3%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-33.9%
Minerals
Egg McMuffin is richer in calcium, iron, potassium, zinc, and magnesium. McGriddles is higher in phosphorus and sodium: it covers 136% of the DV of phosphorus.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+58%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+42.9%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+204.8%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+19.3%
Contains
more
IronIron
+62%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+69.7%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-16.3%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+18.7%
Vitamins
Egg McMuffin is the winner in this section as well. It is higher in all vitamins. Egg McMuffin provides 1.2mg of vitamin C per 100g, while McGriddles do not contain any amounts of it.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+25.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+135.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+117.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+34.3%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+113.5%
Health impact
Cardiovascular health
The sodium content of both of these foods is one of the critical issues. As a result of their high sodium content, almost one serving of Egg McMuffin and McGriddles together can exceed the DV for sodium.
Excessive sodium intake increases the risk of hypertension and the severity of cardiovascular disease (3)(4). If you have issues with your blood pressure, you should try eating foods that are lower in sodium.
Egg McMuffin has more cholesterol. Recent meta-analytic investigations, however, have demonstrated that dietary cholesterol is not the only factor linked to a higher risk of hyperlipidemia and overall mortality rates. Hyperlipidemia is linked to high-calorie intake, saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol. Consider that only a tiny amount of the 100 mg of dietary cholesterol consumed is absorbed (5)(6).
References
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173307/nutrients
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172059/nutrients
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34579105/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29565029/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26109578/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27739004/
Infographic
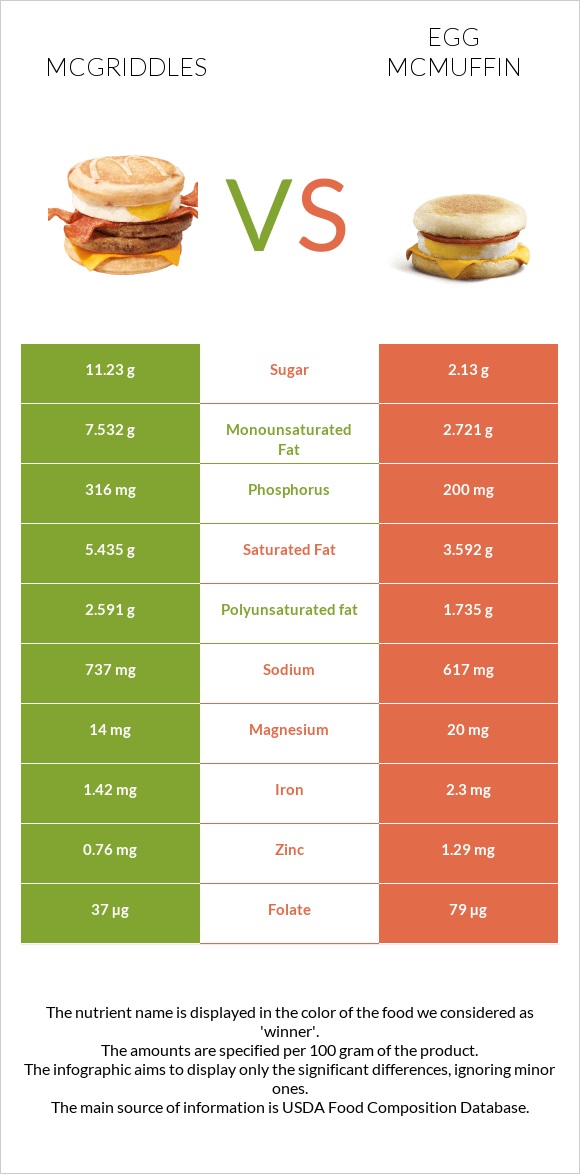
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Cholesterol | 24mg | 165mg | 47% |
| Phosphorus | 316mg | 200mg | 17% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.156mg | 0.368mg | 16% |
| Calcium | 63mg | 192mg | 13% |
| Fats | 17.76g | 9.66g | 12% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 7.532g | 2.721g | 12% |
| Iron | 1.42mg | 2.3mg | 11% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.27µg | 11% | |
| Folate | 37µg | 79µg | 11% |
| Protein | 8.41g | 13.64g | 10% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.384mg | 0.836mg | 9% |
| Saturated fat | 5.435g | 3.592g | 8% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 2.591g | 1.735g | 6% |
| Zinc | 0.76mg | 1.29mg | 5% |
| Sodium | 737mg | 617mg | 5% |
| Calories | 312kcal | 228kcal | 4% |
| Vitamin E | 0.59mg | 4% | |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.209mg | 0.262mg | 4% |
| Carbs | 31.25g | 21.67g | 3% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.108mg | 0.145mg | 3% |
| Manganese | 0.198mg | 0.235mg | 2% |
| Vitamin C | 0mg | 1.2mg | 1% |
| Magnesium | 14mg | 20mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 145mg | 173mg | 1% |
| Copper | 0.079mg | 0.084mg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 30.25g | 20.57g | N/A |
| Sugar | 11.23g | 2.13g | N/A |
| Fiber | 1g | 1.1g | 0% |
| Vitamin B3 | 3.082mg | 3.102mg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0.956g | 0.109g | N/A |
| Fructose | 0.14g | 0.43g | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.002g | N/A | |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.021g | N/A | |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.114g | N/A | |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.006g | N/A | |
| Omega-3 - Eicosatrienoic acid | 0.002g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.001g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Dihomo-gamma-linoleic acid | 0.012g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.01g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 1.416g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- McGriddles - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172059/nutrients
- Egg McMUFFIN - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173307/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.




