Naan vs. Paratha — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Paratha is richer in fiber and fats. Naan is higher in calcium, phosphorus, and B-complex vitamins. Paratha covers your daily need for Fiber 19% more than Naan. Naan can be a healthier alternative to flatbread for the nervous and cardiovascular systems.
Introduction
This article summarizes the differences between two flatbreads of Indian cuisine - paratha and naan. Go through the sections of the article to learn about the nutritional and health impact differences between these bread types.
Actual differences
Paratha and naan are famous Indian breakfast flatbreads. These foods are made by using different preparation methods. Paratha is usually fried in tawa, getting rolled out multiple times during preparation. Naan is often done in a tandoor, pulled out of it, and brushed with butter.
Naan is like pita bread: it can be filled with meat, vegetables, and other ingredients, while paratha is usually consumed as a dessert bread, topped with butter and caramelized sugar.
Nutrition
Protein
Naan is higher in protein than paratha. It provides 10.2g of protein per 100g, compared to 6.4g of paratha.
Fats
Paratha is two times higher in fats than naan. It is higher in both saturated and unsaturated fats.
See the visual representation of fat composition on the chart shown below.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-50.1%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+97.2%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+97.5%
Carbs
Naan contains more carbohydrates per 100g than paratha. Naan provides 46.2g of carbs, while the same amount of paratha has 45.4g. Both types of bread contain high amounts of starch. However, naan is richer in starch. Paratha contains more sugar. Hence, it can seem sweeter.
Fiber
Fiber type in wheat-based products is usually soluble.
Paratha is two times higher in terms of fiber content. It provides 9.6g of dietary fiber per 100g compared to 4.8g in naan.
Minerals
Naan is the winner in this section.
Naan is higher in all essential minerals compared to paratha. It contains more phosphorus, calcium, and magnesium than paratha. Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+83.8%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+136%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+33.1%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+51.2%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+56.7%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+32.8%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+60.6%
Vitamins
Looking at the vitamin comparison chart shown below, we will see that naan is higher in vitamins. Naan is significantly higher in B-complex vitamins.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+60%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+136.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+95.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+60%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+60%
Calories
Naan and paratha are classified as high-calorie foods. Paratha is 40 calories higher per 100g.
Glycemic index
The glycemic index is significant for managing diabetes. Paratha’s GI equals 53, and naan’s GI is 71. For more information, check our glycemic index chart.
Acidity
Based on PRAL values, paratha (3.4) and naan(5.5) are acidic.
Health impact
Naan bread, made from whole wheat flour, is rich in dietary fiber. It is linked with improved colon health and a lower risk of heart disease (1).
Being rich in B-complex vitamins, naan bread provides high amounts of vitamin B3, which is needed to prevent neurological conditions (2).
Infographic
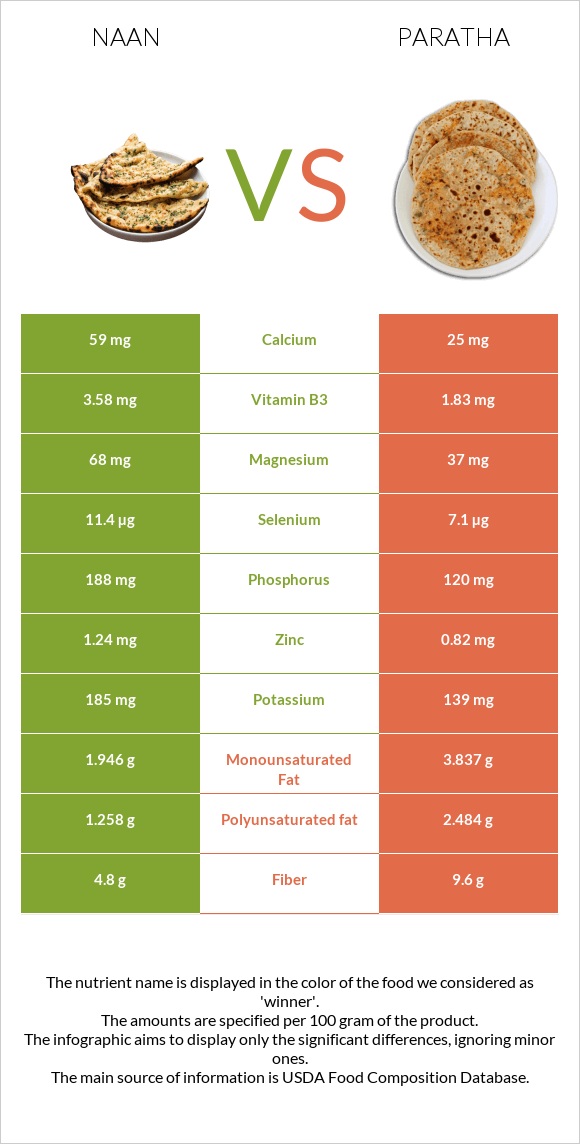
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Fiber | 4.8g | 9.6g | 19% |
| Manganese | 1.4mg | 1.054mg | 15% |
| Saturated fat | 2.907g | 5.826g | 13% |
| Vitamin B3 | 3.58mg | 1.83mg | 11% |
| Fats | 6.7g | 13.2g | 10% |
| Phosphorus | 188mg | 120mg | 10% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.465mg | 9% | |
| Protein | 10.2g | 6.36g | 8% |
| Selenium | 11.4µg | 7.1µg | 8% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.18mg | 0.076mg | 8% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 1.258g | 2.484g | 8% |
| Magnesium | 68mg | 37mg | 7% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.176mg | 0.11mg | 6% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 1.946g | 3.837g | 5% |
| Zinc | 1.24mg | 0.82mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.128mg | 0.08mg | 4% |
| Calcium | 59mg | 25mg | 3% |
| Calories | 286kcal | 326kcal | 2% |
| Iron | 1.73mg | 1.61mg | 2% |
| Starch | 36g | 31.5g | 2% |
| Folate | 16µg | 10µg | 2% |
| Potassium | 185mg | 139mg | 1% |
| Copper | 0.158mg | 0.146mg | 1% |
| Sodium | 467mg | 452mg | 1% |
| Choline | 10.1mg | 6.3mg | 1% |
| Fructose | 0.8g | 0.35g | 1% |
| Net carbs | 41.41g | 35.75g | N/A |
| Carbs | 46.21g | 45.35g | 0% |
| Cholesterol | 1mg | 1mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 3.4g | 4.15g | N/A |
| Vitamin A | 2µg | 2µg | 0% |
| Vitamin E | 1.32mg | 1.35mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 3.3µg | 3.4µg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0.034g | N/A | |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.064g | N/A | |
| Omega-3 - Eicosatrienoic acid | 0.003g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.006g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.002g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 2.386g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +60.4% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +25.2% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +97% |
Carbohydrate type comparison
| Contains more StarchStarch | +14.3% |
| Contains more GlucoseGlucose | +71.4% |
| Contains more FructoseFructose | +128.6% |
| Contains more LactoseLactose | +∞% |
| Contains more SucroseSucrose | +∞% |
| Contains more MaltoseMaltose | +13.3% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Naan - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174077/nutrients
- Paratha - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174076/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.



