Pinto beans vs Black Turtle Beans — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Pinto beans are richer in fiber, manganese, zinc, selenium, folate, and vitamin B6. In comparison, black turtle beans are richer in copper, iron, and vitamin B1. Pinto beans have more cardiovascular health benefits, and in comparison, black beans have antidiabetic and anticarcinogenic properties.
Introduction
In this article, we will discuss the differences between 2 types of beans: pinto beans and black turtle beans.
In short, pinto beans and black turtle beans are not the same. They look different than one another, yet they share some nutritional similarities.
We will dig deep into the nutritional and health impact differences between them.
These beans are staple foods in Latin American cuisine, and they are considered part of the common beans family.
Black turtle beans are also known as black beans.
Nutrition Comparison
We will consider 100g of each in cooked forms.
Calories
They have similar amounts of calories.
Carbs
Pinto beans are slightly higher in carbs compared to black turtle beans. Pinto beans contain 26 grams of carbs, whereas black turtle beans contain 24 grams.
Fiber
Their fiber profile is very rich yet similar. Pinto contains slightly higher amounts of fiber, but the difference is irrelevant.
Pinto beans contain 9g of fiber, whereas black turtle beans contain 8.3g.
@carbtypebreakdown
Fat
Their fat content is negligible.
Protein
Their protein content is similar. Pinto beans contain 9g of protein, whereas black turtle beans contain 8.2g.
Their macronutrient profiles are nearly similar to one another.
Minerals
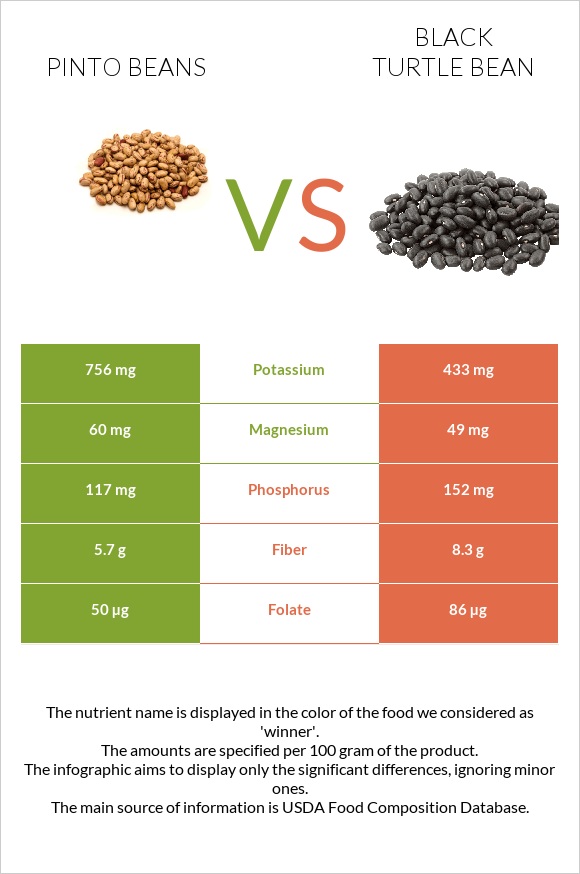
Pinto beans are richer in manganese, zinc, and selenium. In contrast, black turtle beans are richer in copper and iron. Both contain nearly identical amounts of magnesium and calcium.
@mineralcoverage
Vitamins
Pinto beans are richer in folate and vitamin B6. Black beans are richer in vitamin B1.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+197.4%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+100%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+16.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+65.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+23.8%
Health Impacts
Pinto beans are associated with reduced LDL cholesterol levels and a decreased risk of heart disease. In addition, pinto beans reduced average blood pressure (1)(2).
Pinto beans shown to improve gut microbiome and reduce total blood lipid levels aswell (3).
Overall, pinto beans are associated with a lower risk of heart disease and improvement of the gut microbiome (4)(5).
You can read about cranberry beans vs pinto beans in this article.
Black turtle beans are associated with lower blood sugar levels, and decreased risks of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes, and in addition, it is associated with improved gut microbiome and anticancer properties (6)(7).
You can read about navy beans vs white beans in this article.
Vegan/Vegetarian diet
Pinto beans and black turtle beans are excellent alternative sources of plant-based proteins.
Black turtle beans are richer in iron than pinto beans, which is important in vegan and vegetarian diets. However, to increase the bioavailability of this iron, it is important to mix these beans with vitamin C-rich foods (8).
Generalities
Pinto beans are larger than black turtle beans, and they are mostly mushier in texture. Pinto beans have an earthy flavor and nuttier taste than black beans.
Both these dishes are used in Mexican, Central American, and South American dishes and dips.
Black turtle beans are excellent to use in refried beans and soups. Both beans can be used for burritos, salads, and enchiladas.
Choosing either comes down to your personal preference since both are healthy beans that can be added to your diet.
Pinto beans and black beans are among the best beans you can consume. Now, regarding which one of them is better and healthier, well, they are both excellent types of beans it is somehow not very correct to say one is better than the other.
Black beans and pinto beans are served at one of the main sides at Chipotle that you should opt for instead of rice. Associating it with mild chili can be a good choice regarding nutrition and flavor profiles.
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31006805/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32917495/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17951475/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17634169/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33144228/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34441468/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29086840/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6940487/
Infographic
Mineral Comparison
| Contains more ZincZinc | +28.9% |
| Contains less SodiumSodium | -66.7% |
| Contains more ManganeseManganese | +38.5% |
| Contains more SeleniumSelenium | +416.7% |
| Contains more CalciumCalcium | +19.6% |
| Contains more IronIron | +36.4% |
| Contains more CopperCopper | +22.8% |
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Folate | 172µg | 86µg | 22% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.229mg | 0.077mg | 12% |
| Iron | 2.09mg | 2.85mg | 10% |
| Selenium | 6.2µg | 1.2µg | 9% |
| Copper | 0.219mg | 0.269mg | 6% |
| Starch | 15.15g | 6% | |
| Manganese | 0.453mg | 0.327mg | 5% |
| Fiber | 9g | 8.3g | 3% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.193mg | 0.225mg | 3% |
| Protein | 9.01g | 8.18g | 2% |
| Zinc | 0.98mg | 0.76mg | 2% |
| Calories | 143kcal | 130kcal | 1% |
| Vitamin C | 0.8mg | 0mg | 1% |
| Carbs | 26.22g | 24.35g | 1% |
| Calcium | 46mg | 55mg | 1% |
| Phosphorus | 147mg | 152mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.318mg | 0.527mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.21mg | 0.26mg | 1% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.235g | 0.149g | 1% |
| Fats | 0.65g | 0.35g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 17.22g | 16.05g | N/A |
| Magnesium | 50mg | 49mg | 0% |
| Potassium | 436mg | 433mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 0.34g | 0.32g | N/A |
| Sodium | 1mg | 3mg | 0% |
| Vitamin E | 0.94mg | 0.87mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.062mg | 0.056mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 3.5µg | 3.3µg | 0% |
| Choline | 35.3mg | 32.6mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.136g | 0.089g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.133g | 0.03g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.108mg | 0.097mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.331mg | 0.344mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.426mg | 0.361mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.765mg | 0.653mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.63mg | 0.562mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.117mg | 0.123mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.531mg | 0.442mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.519mg | 0.428mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.247mg | 0.228mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more FatsFats | +85.7% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +17.9% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +343.3% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +57.7% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -34.6% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Pinto beans - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/175200/nutrients
- Black turtle bean - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/175187/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.