Pizza vs. Pasta — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Pizza has a richer nutritional profile compared to pasta. However, pizza is higher in sodium, fats, and carbs. Pasta has a lower glycemic index. It is cheaper and has a longer shelf life. Pasta is healthier than a pizza. However, they are dependent on the toppings and sauces.
Introduction
Pizza originated in Italy, but it has since expanded throughout the world and has become one of the most popular fast foods. Fast food does not relate to the original pizza. The dough, sauce, and cheese are the three essential components of pizza. It's highly versatile, and we can make it vegan, vegetarian, or with meat components.
When it comes to pasta, there is a debate on where the origin of pasta is. Some say that Marco Polo brought it with him from China during his travels as noodles. The Italians got inspired by it and came up with pasta. Some even considered that pasta has originated from Sicilia and spread around Italy and the world with time. Italy has a type of hard wheat that can produce semolina flour which is the best flour to prepare the pasta dough.
Culinary world
Pizza is very versatile; it can be a traditional thin dough Italian pizza, a New York fast-food pizza, or even a Chicago-style pizza. In addition to these, they can be vegetarian, seafood-based, pepperoni, salami, and prosciutto pizzas. As the types vary, their nutritional content varies with it.
On the other hand, pasta is more versatile than pizza. The pasta itself can be spaghetti, penne, fusilli, lasagna, and many more. In addition to this difference, the pasta sauce can be different; the sauce can be pesto, arrabbiata, alfredo, and many others. They can be with meat, chicken, seafood, and even vegan or vegetarian.
Price
The simplest cooked pasta overall is much cheaper than a simple pizza. Considering a simple pasta cup with tomato sauce vs. a pizza with tomato sauce and mozzarella cheese.
Shelf life
An essential feature of pasta is its shelf life. We can store any pasta brought from the market for at least a year, whereas pizza is either frozen or fresh made.
Healthy ingredients
Thin dough, homemade pizza is a healthier option than a fast-food pizza. Healthier cheeses eaten with pizza are mozzarella cheese, provolone cheese, and swiss cheese. Healthier toppings are vegetables and low-fat proteins like chicken breast. These vegetables increase the mineral and vitamin profile of the pizzas. On the other hand, pasta is similarly dependent on the sauce and toppings which are used. Using butter and cream-based sauces causes the pasta to be less healthy. Tomato-based sauces, low-fat ground meat, and vegetables are among the healthiest sauces and toppings to be added to pasta preparation.
Preparation method
Pizza needs more effort and processing time to prepare as compared to pasta. Pasta is very quick to prepare; in about 12 min a quick pasta meal can be prepared where pizza requires more time because there is a baking step.
In this article, we will compare the difference between pizza and pasta based on their nutritional data, health impacts, and weight loss programs. The pizza that we are going to take into consideration is a fast-food-type plain cheese thin dough pizza. On the other hand, the pasta is plain pasta without any additional sauces or toppings.
Nutritional data comparison
Calories
Pasta has fewer calories compared to pizza. Thus, we have to consider that any additional toppings like sauces, protein, and cheese will increase the calories of the pasta.
Glycemic index
Pasta has a lower glycemic index compared to pizza. Pasta is categorized in the low glycemic index foods and pizza on the medium glycemic index food.
Carbs
Pizza is higher in carbs compared to pasta. Pizza contains one and a half times the amount of carbs as pasta. It is important to note that both are considered high in carbohydrates.
Protein
Pizza is richer in protein than pasta. It is almost double the number of proteins.
Fats
The amounts of fats are primarily due to the toppings added on top of pizza and pasta. The more cheese, meat, chicken, seafood, and oil or butter are added, the higher the amounts of fat would be.
Cholesterol and trans fats
It is also important to note that cholesterol and trans fats increase or decrease as toppings vary. For example, the more the toppings are meat-based, for example, pepperoni, salami, ground beef, or even some fish products, the higher the cholesterol amounts will be. In addition to that, more processed or fried elements are added. For example, different processed cheeses or fried elements added to pizza, the higher the trans fat content would be. It is important to take into consideration the amounts of cholesterol and trans fats.
Minerals
Pizzas are overall richer in minerals compared to pasta. Pizza is richer in calcium, iron, phosphorus, and manganese. However, pizza is considered high in pizza.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+33.3%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+3033.3%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+616.7%
Contains
more
IronIron
+117.5%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+12.9%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+139.3%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+242.9%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+60.7%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+∞%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-99%
Vitamins
Similar to minerals, pizza has a better vitamin profile than pasta. They are richer in folate, vitamin A and B1.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+1050%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+86.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+30%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+285.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+135.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+200%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+45.3%
Note
It is important to consider the different topics and sauces that are added to both pizza and pasta. As mentioned above, the pasta taken into consideration is plain cooked pasta. On the other hand, the pizza taken into consideration is a thin-crusted tomato sauce with cheese pasta. As the toppings and sauces change, the nutritional content changes with them.
Weight loss and diets
Pizza is regarded as one of the most customizable foods. If necessary, they can be modified to meet a healthy diet. Although most of the excellent portions of the pizza, such as the pepperoni, additional cheese, and dipping the dough in sauces, would be eliminated. The goal of sticking to a diet for a long time is to eat as few restricted foods as possible. The more restricted meals are in a diet, the more cravings for that specific meal will occur.
A homemade pizza would be a healthy alternative to a fast-food pizza. Knowing what ingredients are being utilized helps in the preparation procedure. The way to go is with thin dough, less cheese, and more veggie toppings. Of course, the number of slices consumed should be limited.
When it comes to pasta, although it is high in carbs, athletes eat pasta on the side of proteins because of the carbs that they provide. In addition to that, it has a lower glycemic index, meaning that it does not cause a spike in insulin levels and is absorbed slowly into the system. This keeps the person fuller for longer and energized.
Keto
Pizza is included in the keto diet, with a few adjustments. The dough is the source of carbs in pizza, thus changing the wheat-based dough is difficult. Cauliflower-based dough or almond flour-based dough are two other options. Low-carbohydrate, high-fat cheese can be consumed.
When it comes to toppings, it's critical to look for low-carb choice toppings.
Pasta cannot be eaten in the keto diet. An alternative to pasta can be made with zucchini. For example, zucchini spaghetti or lasagna can be prepared, which is keto-friendly.
Vegan
Both pasta and pizza can be consumed in the vegan diet; however, the toppings and sauces should be considered.
Gluten-free diets
Celiac disease and non-celiac gluten sensitivity (gluten intolerance) restrict people from consuming gluten. Gluten consumption will result in an inflammatory response and disease-associated symptoms. Hence, gluten should be avoided by people with celiac disease or gluten intolerance. When it comes to pizza dough and pasta made of wheat, then gluten-free dough and pasta should be consumed instead.
Health impacts
Cardiovascular health
Pizza, being fast food, is one of the leading causes of cardiovascular disease in adults. Pizza is harmful to the heart and circulatory system.
Pizzas have a high sodium content. The risk of getting hypertension is increased if salt levels are not monitored for long periods. (1) (2) (3)
Pasta consumption had overall regular effects on the overall diet because it balances out everyday food consumption. In moderation, pasta can be consumed without any harmful effects on the cardiovascular system. (4)
Obesity
Pizza consumption has been linked to an increase in obesity risks. (1)
Compared to pizza, pasta has a lower glycemic index, decreasing fat deposition in the body and maintaining a healthier blood glucose level and weight control when consumed in moderation. (5)
Diabetes
After eating pizza, measuring blood glucose levels revealed a significant increase in blood sugar levels, resulting in high hyperglycemia thresholds. Type 2 diabetes would develop if this hyperglycemic condition were maintained regularly. (6)
The pasta's low glycemic index doesn't cause a spike in blood insulin levels and maintains a regular blood glucose level. In turn, reducing risks of developing metabolic disorders and diabetes. (5)
Health benefits
Eating a well-balanced, healthful homemade pizza has its advantages.
Obesity risks are reduced by eating the above-mentioned healthy pizza, according to research.
The baker's yeast used in pizzas is beneficial to one's general health. It boosts your immune system, boosts your metabolism, and improves your digestion and absorption of meals. (7) (8)
Pasta can be prepared in a healthy way that can contain the perfect amount of carbs, proteins, and all other necessary elements required in a daily diet.
Gluten-free pasta and pizza on overall health
Gluten-free pasta and pizza are prepared with alternatives to wheat such as rice or potato, and they are higher in carbs and glycemic index. It was shown that blood glucose levels were much higher in gluten-free pizza and pasta than compared to blood glucose levels after eating a regular pizza or pasta. This is a question to be asked, which is healthier? The gluten-free or the regular. Overall, it is important to stay away from gluten-free foods if they have celiac disease and gluten intolerance. Anything other than that might not be a healthier choice for the person. (9)
Video Summary
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4772793/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3381762/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6770596/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7426435/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29615407/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8462382/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24160252/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18335702/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28771262/
Infographic
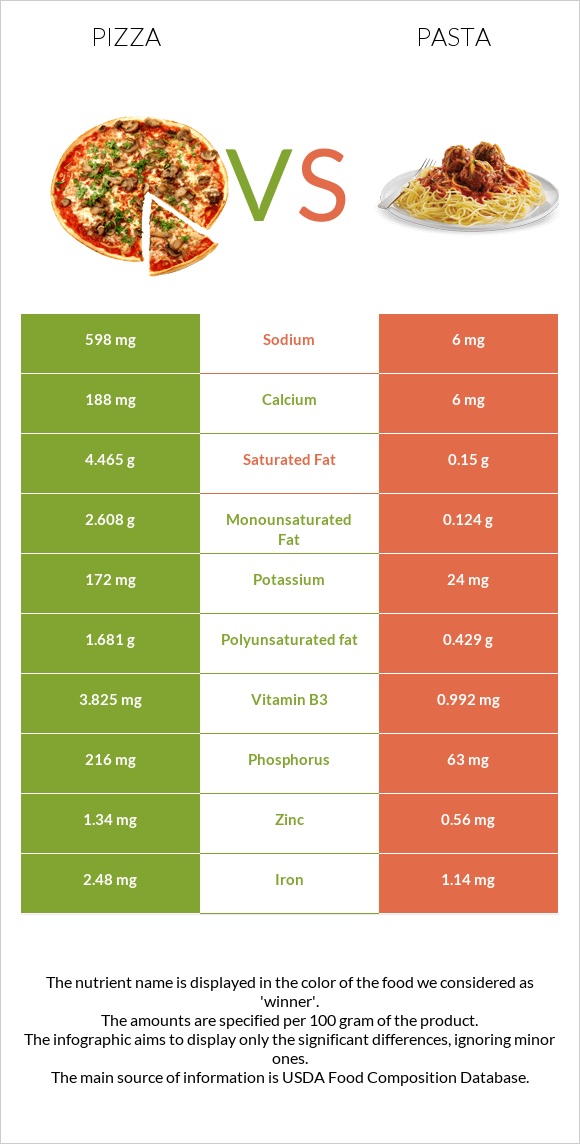
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Selenium | 19.9µg | 36% | |
| Sodium | 598mg | 6mg | 26% |
| Phosphorus | 216mg | 63mg | 22% |
| Saturated fat | 4.465g | 0.15g | 20% |
| Calcium | 188mg | 6mg | 18% |
| Vitamin B3 | 3.825mg | 0.992mg | 18% |
| Iron | 2.48mg | 1.14mg | 17% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.39mg | 0.209mg | 15% |
| Fats | 9.69g | 1.05g | 13% |
| Protein | 11.39g | 5.15g | 12% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.42µg | 0.14µg | 12% |
| Starch | 26.95g | 11% | |
| Fiber | 2.3g | 9% | |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 1.681g | 0.429g | 8% |
| Calories | 266kcal | 131kcal | 7% |
| Zinc | 1.34mg | 0.56mg | 7% |
| Vitamin A | 69µg | 6µg | 7% |
| Folate | 93µg | 64µg | 7% |
| Vitamin E | 0.83mg | 6% | |
| Manganese | 0.36mg | 0.224mg | 6% |
| Vitamin K | 6.7µg | 6% | |
| Monounsaturated fat | 2.608g | 0.124g | 6% |
| Cholesterol | 17mg | 33mg | 5% |
| Potassium | 172mg | 24mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.183mg | 4% | |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.08mg | 0.034mg | 4% |
| Carbs | 33.33g | 24.93g | 3% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.195mg | 0.15mg | 3% |
| Choline | 16.4mg | 3% | |
| Vitamin C | 1.4mg | 0mg | 2% |
| Magnesium | 24mg | 18mg | 1% |
| Copper | 0.105mg | 0.093mg | 1% |
| Fructose | 1g | 1% | |
| Net carbs | 31.03g | 24.93g | N/A |
| Sugar | 3.58g | N/A | |
| Trans fat | 0.241g | N/A | |
| Tryptophan | 0.065mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.41mg | 0.134mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.564mg | 0.197mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.139mg | 0.348mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.77mg | 0.097mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.264mg | 0.079mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.664mg | 0.247mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.72mg | 0.217mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.355mg | 0.103mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.004g | N/A | |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.175g | N/A | |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.004g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.003g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Dihomo-gamma-linoleic acid | 0.009g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.003g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 1.367g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +121.2% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +822.9% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +33.7% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +680.6% |
| Contains more WaterWater | +58.8% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +2003.2% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +291.8% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -96.6% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Pizza - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173292/nutrients
- Pasta - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169728/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






