Pork vs. Beef - Nutrition, Cholesterol, Protein, Fats & Health Impact


Summary
Choosing the right cuts of both foods and not using the processed versions is very important. When comparing good cuts of both, pork appears to be slightly better nutritionally, except beef is richer in vitamin B12, iron, and zinc.
Beef is consumed two times less in the world overall. It is also drastically more damaging to the environment.
Various conversations about pork being more “dirty” and full of bacteria seem to have no scientific evidence, assuming it is cooked using the USDA’s recommended temperature. Both pork and beef consumption is safe for children, as well as adults, and can be eaten harmlessly as long as your religious views allow it.
Overall, the answer to the question of which is better depends entirely on what you’re looking for.
Enjoy and share the comparison infographic and in-depth vitamin and mineral comparison below. 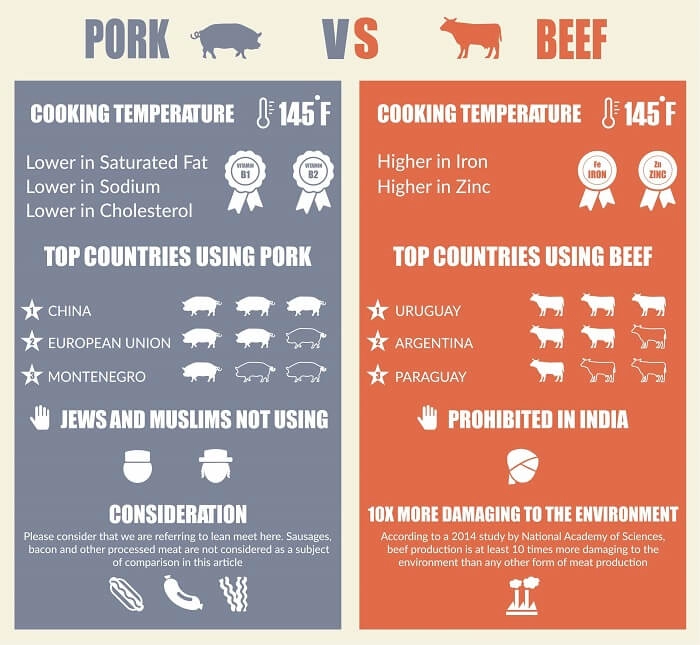
Introduction
Pork vs. Beef. Which is healthier to eat and in which condition? These are the sort of questions you may ask yourselves at least once in a while. Then you suddenly remember something your grandma kept saying and go with the answer. We decided to dig deeper and explore the differences between pork and beef from a more scientific perspective.
Considerations
Please consider that we are referring to lean meat here. Sausages, bacon, and other processed meat are not considered a subject of comparison in this article. Comparing beef with pork sausage, for instance, might result in conclusions very different from the ones that we’ll have here.
Bans and Religion
Several religions ban the consumption of pig meat altogether. Although there are some mentions of not eating pork in the Christian Bible, the modern church allows its consumption. However, most Jewish communities prohibit it. Jewish dietary law “Kashrut” states that only the animals which chew their cud and have divided hoofs should be eaten by the followers of the religion. Pigs do not satisfy the first condition, which puts them on the blacklist. Thus, pork is not kosher.
Islam has its list of prohibited foods called “Haram” based on a similar approach which puts pork out of the permitted food list.
On the other hand, beef is a respected creature of God in Hinduism. There are laws in India prohibiting cow slaughtering, which vary by state. Depending on your state, you can go to jail for 6 months up to 10 years if you slaughter a cow in India.
Nutrition comparison
It’s time to discuss the most interesting and scientific part of the comparison - nutrition. In order to nutritionally compare two foods, we have to fix their states, i.e., cooked or raw, salted or not, etc. We chose these two similar states of beef and pork:
Beef, ground, 85% lean meat / 15% fat, patty, cooked, broiled
Pork, fresh, loin, whole, separable lean and fat, cooked, broiled
The numbers below are presented for 100g servings of these two types of meat. However, one average serving size per person is 3 ounces or 85g for pork and beef.
Both are cooked and broiled, and both contain a similar fat percentage. So with this selection, we have pork winning in 3 important categories; namely, it is somewhat Lower in Saturated Fats, Lower in Cholesterol, and Lower in Sodium. Though the difference is not so big, the winner takes it all anyway. Besides, it is lower in calories and overall fats. Pork’s protein quality is also higher because it contains more of all the essential amino acids.
Protein
Pork contains 1.4g more protein per every 100g serving. As mentioned above, it is richer in all essential amino acids.
Fats
Generally, beef is higher in fats, containing 1.5g more per 100g serving. However, pork is almost 3 times higher in polyunsaturated fats while being somewhat lower in saturated fats and cholesterol.
To sum up, pork has a more favorable fat profile.
Cholesterol
Ground beef with 15% fat has a cholesterol content of 80, while the cholesterol content of fresh pig’s whole loin is 88. The highest cholesterol level in both beef and pork is found in the liver.
However, cholesterol content can vastly differ depending on what part of the meat it is. The highest amount of cholesterol in beef meat is found in a beef brisket with 106mg per 100g. The lowest is found in strip steak (58mg per 100g).
Ground pork with 28% fat has 100mg of cholesterol per 100g. Pulled pork contains only 35mg of cholesterol in a 100g serving.
While it all depends on the type of meat, pork generally tends to have lower cholesterol levels than beef.
Vitamins comparison
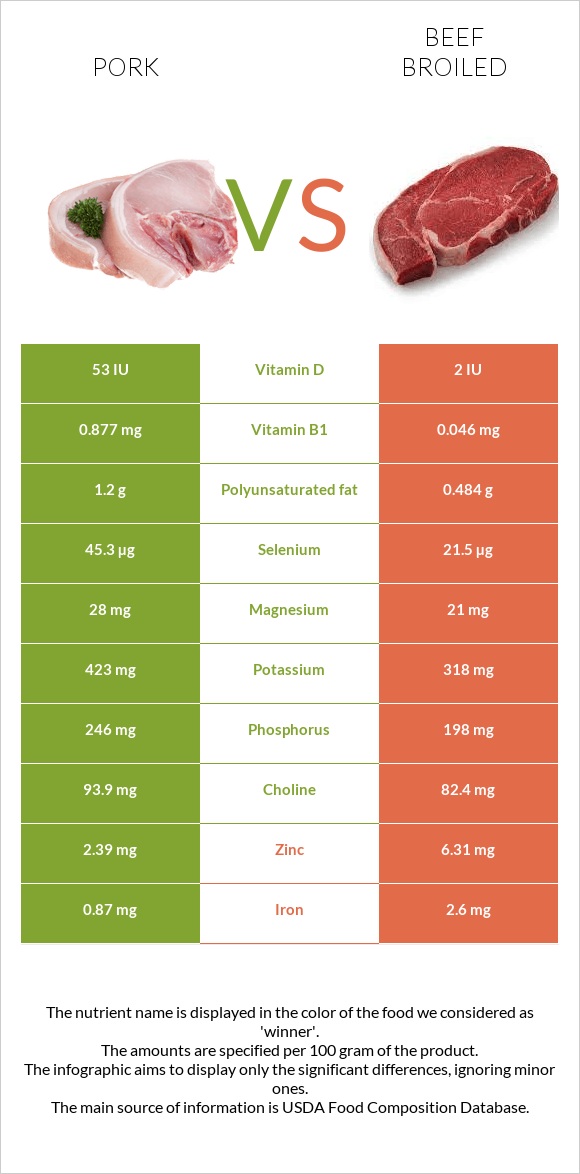
Let’s move to vitamins now. Pork is drastically (19 times) richer in vitamin B1 and fairly (2 times) richer in vitamins B2 and E.
Considered very important lately, vitamin D is completely absent from beef, while pork provides 13% of the daily value in just 100 grams. Pork is also somewhat higher in vitamin B6.
On the other hand, beef is radically higher in vitamin B12 (nearly 4 times). A 100g serving of beef entirely covers the daily needed amount of intake for this vitamin. The same serving of pork only covers 30%.
Beef also contains vitamin K, which pork lacks, and is higher in vitamin B9 or folate and vitamin A.
Minerals comparison
What about minerals? Here we have a slightly different picture. Beef is almost 3 times higher in iron and zinc. Pork is slightly richer in selenium, magnesium, potassium, phosphorus, and choline, while beef beats pork in copper and manganese content.
Pork is also somewhat lower in sodium.
Thus, the nutrition comparison summary is, in a way, on the side of pork, except for when it comes to vitamin B12. In any case, it’s definite that it is not worse by the results of surface nutritional analysis.
Which is safer for babies?
Actually, many forums still recommend not giving pork to children at the age when they can freely eat beef. Other blogs insist it is at least as healthy as beef and recommend it for babies as early as 7 or 8 months old.
Looking at the most official source - USDA’s recommendations for babies we can see that both foods are listed together without any reservations and warnings, and both are safe to eat starting from the same age.
What makes some think Pork is bad?
What makes some people think that pork is evil, then? Why is it prohibited in many religions, and why many of us do not give it to our children for a long time? There are various statements that some resources keep stating. Please find the more common ones below.
- While talking about meat, some refer to processed pork, such as sausages, bacon, or salami.
Many processed forms of red meat may really be dangerous for health, but we are not discussing them now and are talking about lean pork such as tenderloin, sirloin chops, or top loin chops (1).
- Does pork contain more bacteria, viruses, toxins, or parasites?
As we all know, most harmful microbes die if you cook meat at a high enough temperature. For this reason, the USDA has defined its recommended temperatures for cooking various types of meat.
More importantly, the recommended temperature is the same for both foods. It’s 145 °F for beef and pork and 160°F for ground meat. So whatever microbes these types of red meat may initially carry, they die at the same temperature, according to scientists.
- The pig is a dirty animal and eats whatever it wants.
This partially depends on how the cow, the pig, or the chicken are handled on what they are being fed. Grass-fed beef can significantly differ from not grass-fed beef, which is a topic for a future article. We should always consider how the animal was kept and fed, regardless of the type of meat.
Consumption comparison
Not seeing any scientific evidence in the old religious customs, we can go on with our analysis and look at the usage statistics.
The USDA’s Foreign Agricultural Service data states that pork consumption globally is twice as big as beef consumption. However, looking at the numbers in the US separately reveals approximately equal results, with beef being ahead by a small amount.
Pork seems to be popular in states like China, European Union, Taiwan, South Korea, Montenegro, and Vietnam. Beef is extremely popular in Uruguay and Argentina, followed by Paraguay, the United States, and Brazil. Among the countries with low pork consumption are India, Nigeria, the Philippines, Thailand, and Iran. (the data we are referring to is for the year 2015) (2). 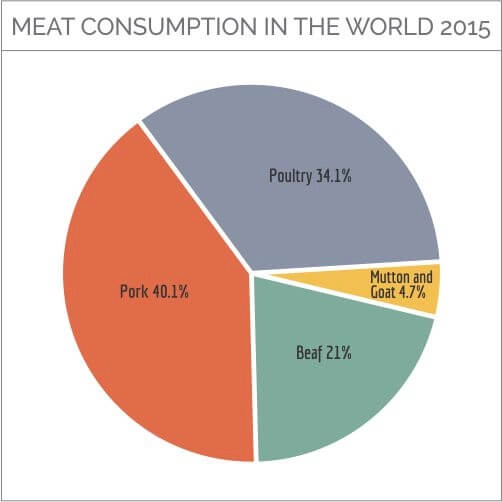
Environment impact
The National Academy of Sciences published a study in February 2014 which revealed that beef is highly damaging to the environment. The study compared the environmental cost spent to feed and raise animals that are used as protein sources for humans.
This research showed that cows need around 28 times more land than pork or poultry, require 11 times more irrigation, produce much more greenhouse gas, and consume a lot more nitrogen. To summarize, beef production is 10 times more damaging to the environment than any other protein source (3).
Sources
- https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/cancer-carcinogenicity-of-the-consumption-of-red-meat-and-processed-meat
- USDA - FAS Production, Supply, and Distribution Online Database - https://apps.fas.usda.gov/opendataweb/home
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/264408978
Infographic
Mineral Comparison
| Contains more MagnesiumMagnesium | +33.3% |
| Contains more PotassiumPotassium | +33% |
| Contains more PhosphorusPhosphorus | +24.2% |
| Contains less SodiumSodium | -13.9% |
| Contains more SeleniumSelenium | +110.7% |
| Contains more IronIron | +198.9% |
| Contains more CopperCopper | +16.4% |
| Contains more ZincZinc | +164% |
| Contains more ManganeseManganese | +33.3% |
Vitamin Comparison
| Contains more Vitamin CVitamin C | +∞% |
| Contains more Vitamin EVitamin E | +141.7% |
| Contains more Vitamin DVitamin D | +∞% |
| Contains more Vitamin B1Vitamin B1 | +1806.5% |
| Contains more Vitamin B2Vitamin B2 | +82.4% |
| Contains more Vitamin B6Vitamin B6 | +21.5% |
| Contains more Vitamin AVitamin A | +50% |
| Contains more Vitamin B12Vitamin B12 | +277.1% |
| Contains more Vitamin KVitamin K | +∞% |
| Contains more FolateFolate | +80% |
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.7µg | 2.64µg | 81% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.877mg | 0.046mg | 69% |
| Selenium | 45.3µg | 21.5µg | 43% |
| Zinc | 2.39mg | 6.31mg | 36% |
| Iron | 0.87mg | 2.6mg | 22% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.321mg | 0.176mg | 11% |
| Phosphorus | 246mg | 198mg | 7% |
| Vitamin D | 1.3µg | 0µg | 7% |
| Vitamin D | 53 IU | 2 IU | 6% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.464mg | 0.382mg | 6% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 1.2g | 0.484g | 5% |
| Protein | 27.32g | 25.93g | 3% |
| Cholesterol | 80mg | 88mg | 3% |
| Potassium | 423mg | 318mg | 3% |
| Saturated fat | 5.23g | 5.895g | 3% |
| Fats | 13.92g | 15.41g | 2% |
| Magnesium | 28mg | 21mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B3 | 5.037mg | 5.378mg | 2% |
| Choline | 93.9mg | 82.4mg | 2% |
| Vitamin C | 0.6mg | 0mg | 1% |
| Copper | 0.073mg | 0.085mg | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 0.29mg | 0.12mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.698mg | 0.658mg | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 0µg | 1.2µg | 1% |
| Folate | 5µg | 9µg | 1% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 6.19g | 6.668g | 1% |
| Calories | 242kcal | 250kcal | 0% |
| Calcium | 19mg | 18mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 62mg | 72mg | 0% |
| Vitamin A | 2µg | 3µg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.009mg | 0.012mg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0.572g | N/A | |
| Tryptophan | 0.338mg | 0.094mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 1.234mg | 0.72mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 1.26mg | 0.822mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 2.177mg | 1.45mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 2.446mg | 1.54mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.712mg | 0.478mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 1.086mg | 0.725mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.473mg | 0.914mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 1.067mg | 0.604mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0g | 0.003g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0g | 0.001g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.044g | N/A | |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0g | 0.016g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.012g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more OtherOther | +30.9% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +10.7% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -11.3% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +147.9% |
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Pork - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/167820/nutrients
- Beef broiled - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174032/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.
