Provolone vs. Mozzarella — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Provolone provides more sodium coverage and contains more vitamin B12, vitamin A, RAE, and monounsaturated fat compared to mozzarella. There is mozzarella that has not been artificially lowered in salt. Additionally, mozzarella has lower levels of saturated fat than provolone and typically has a lower sodium content, which is generally considered a low-sodium cheese.
Table of contents
Introduction
Provolone is a semi-soft, cow's-milk cheese hailing from southern Italy. Like mozzarella, it undergoes a process involving plastic curd cheese, resulting in a smooth, pliable, creamy yellow interior. Provolone is often shaped into various forms, like pigs, fruits, or sausages, with its distinctive brown, oily rind wrapped in cords that leave grooves. Frequently displayed in Italian food shops, it offers a slightly firmer texture than the soft, high-moisture white cheese known as mozzarella, which originates from Italy and is typically made from Italian buffalo or cow's milk.
Appearance, Taste, and Use
Provolone exhibits a diverse range of flavors, spanning from sharp to very mild, with a homogeneous, slightly smooth texture. Its smooth, golden skin adds to its appeal. In contrast, mozzarella presents a smooth, glossy surface, a white color, and a mild milk taste. Known for its delicate and slightly acidic flavor, mozzarella finds widespread use in cooking, featuring prominently in salads and various dishes, including pizzas and other Italian delicacies, both in its fresh and shredded forms. Provolone, known for its adaptability, is not only used as a table cheese and in sandwiches but also finds its way into baked pasta dishes and casseroles. Smoked provolone adds a unique aroma and flavor to various culinary creations.
Nutrition
You may find a nutrition infographic to help you better understand the nutritional differences between provolone and mozzarella at the bottom of this page.
Calories
In a 100-gram serving, mozzarella typically contains 280 calories, whereas provolone contains 351 calories.
Protein
Both mozzarella and provolone provide a respectable quantity of protein. Compared to mozzarella, which provides 27.5g of protein per 100g, provolone has 25.58g.
Fats
More fats are found in provolone than in mozzarella. While Mozarella includes 17,1g of fat per 100g, it has 26,62g. Provolone contains more saturated fat as a result. In a 100-gram serving, mozzarella has 10.867 grams of saturated fat and 4.844 grams of monounsaturated fat, while provolone has 17.078 grams of saturated fat and 7.393 grams of monounsaturated fat. Furthermore, mozzarella includes 0.509 grams of polyunsaturated fat compared to 0.769 grams of provolone.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+52.6%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+51.1%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-36.4%
Cholesterol
More cholesterol is present in provolone than mozzarella. Compared to mozzarella, which has 54 mg of cholesterol per 100g, it has 69 mg.
Carbohydrates
There are very few carbohydrates in both. The carb content of mozzarella is 3.1 g per 100g, while that of provolone is 2.14g.
Vitamins
Although their nutritional profiles are nearly identical, provolone contains higher amounts of vitamin A, vitamin A RAE, and vitamin B12.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+72.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+53.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+66.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+30%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+58.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+22.2%
Minerals
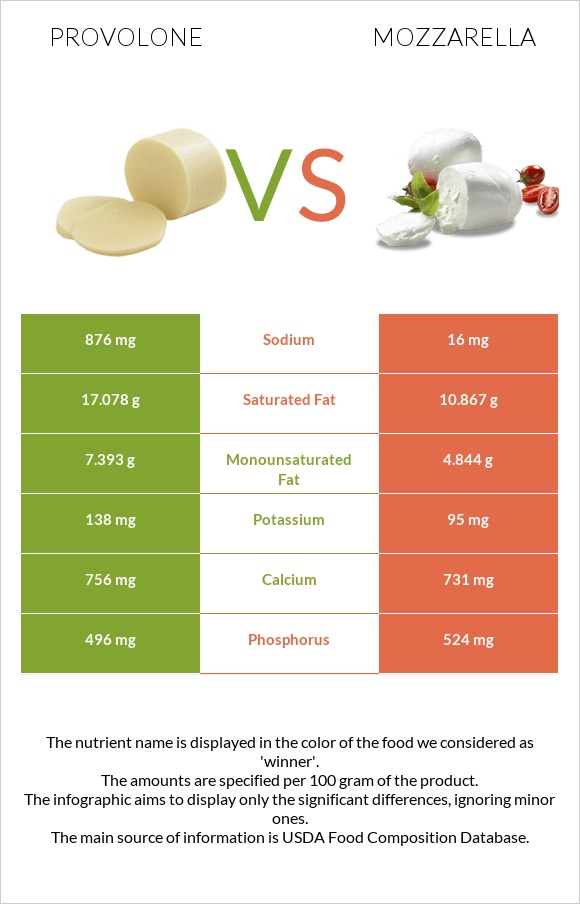
More potassium (138 mg) and sodium (876 mg) are present in provolone. Mozzarella has a higher phosphorus content (524 mg) and a lower sodium content (16 mg).
Both are among the top 5% of foods for calcium sources and have about equal amounts of zinc, magnesium, and copper. There is mozzarella, whose sodium has not been artificially reduced; go to this link for more information.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+45.3%
Contains
more
IronIron
+108%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+∞%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-98.2%
Glycemic Index
Both kinds of cheese have the same glycemic index. Their glycemic index is low. The glycemic index of mozzarella and provolone is 27.
Acidity
Both mozzarella and provolone are considered acidic based on their potential renal acid load (PRAL) values. However, mozzarella has a higher PRAL value of 20.7 compared to provolone, which has a PRAL value of 17.4.
Weight Loss and Diets
Provolone and mozzarella are suitable for a wide range of diets, including the Keto, Dash, Atkins, Mediterranean, and Paleo diets, given their lower carbohydrate content and rich nutritional profile.
Health Benefits
Cardiovascular Health
The sodium content in Provolone is comparatively high compared to Mozzarella at 876mg, necessitating caution for individuals adhering to a reduced sodium diet due to health considerations such as high blood pressure, heart failure, or renal failure (1). Provolone and mozzarella feature Lactobacillus helveticus, potentially aiding in reducing arterial blood pressure by hindering the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) (2, 3, 4). Nevertheless, it's crucial to note that Provolone and Mozzarella, akin to other tyramine-containing cheeses, can potentially trigger a hypertensive crisis, notably in those using MAO inhibitors, an antidepressant category (5, 6). Furthermore, the saturated fats in Provolone may elevate the risk of cardiovascular disease, primarily by increasing LDL (bad cholesterol) levels (7). Conversely, mozzarella cheese comes in various types with varying cholesterol levels, with the cholesterol content notably rising during storage (8). It's imperative to be cautious regarding cholesterol levels, particularly for those with specific dietary considerations.
Diabetes
Calcium is abundant in both varieties of cheese, which may lessen dairy products' insulin resistance. Eating dairy products has been shown to lower insulin resistance risk by 21% (9). Furthermore, the glycemic index of wide cheese varieties is low, preventing insulin spikes and facilitating rapid glucose absorption (10).
Digestive Health
Mozzarella is notably rich in lactobacilli, which act as probiotics, promoting a healthy balance of gut microflora and aiding digestion (11). Provolone, on the other hand, is abundant in threonine, an essential amino acid crucial for maintaining the integrity of the intestinal mucosa and facilitating the digestion and absorption of nutrients (12).
Cancer
The consumption of foods rich in Lactobacillus helveticus, found in Provolone and Mozzarella, has been linked to various health benefits, including the prevention of colon cancer cell and breast cancer cell growth (13). Additionally, while calcium-rich foods like mozzarella may decrease the risk of colorectal cancer, they may also potentially increase the risks associated with prostate cancer when consumed in high amounts (14, 15).
Bone Health
Provolone and Mozzarella, rich in calcium and phosphorus, play vital roles in supporting bone health, as these minerals are highly abundant in bone structure (16). While Mozzarella contains a higher phosphorus content (524 mg), both cheeses rank among the top 5% of foods for calcium sources. The abundance of calcium significantly aids in promoting bone health and mitigating the effects of osteoporosis. With most of the body's calcium (99%) and phosphorus (80%) stored in bones, their consumption is essential for maintaining bone density and strength. Moreover, Provolone's elevated protein content further contributes to preserving healthy bones (17).
Downsides and Risks
Lactose intolerance and Milk allergy
- A lack of the enzyme lactase, which either breaks down or facilitates the digestion of the milk sugar lactose, is the hallmark of lactose intolerance. Cheeses like Provolone, mozzarella, and others can cause symptoms such as bloating, diarrhea, and flatulence in people who are lactose intolerant (18).
- All dairy products, including provolone and mozzarella cheese, contain casein, a milk protein. A condition known as casein intolerance occurs when the body develops an allergy to the casein protein found in milk. When consuming casein-rich foods (like cheese or other dairy products), people who are allergic to casein may have harmful symptoms like wheezing, breathing difficulties, anaphylaxis (a potentially fatal acute allergic reaction), severe discomfort, vomiting, rashes, and more (19).Approximately 3% of children under the age of one year suffer from casein allergy. By the time the child becomes five, the allergy usually goes away, although it can come back at some point in the future. Casein allergies are 2% common in adults.
Sources
- https://journals.lww.com/co-cardiology/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/
- https://journals.asm.org/doi/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/
- https://jamanetwork.com/journals/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22951238/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/
- https://scialert.net/abstract/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11966382/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23945722/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22981567/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12869397/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16522915/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22081690/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22139564/
- https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2002/0501/p1845.html
- https://pro.uptodatefree.ir/show/2386
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Sodium | 876mg | 16mg | 37% |
| Saturated fat | 17.078g | 10.867g | 28% |
| Vitamin B12 | 1.46µg | 0.92µg | 23% |
| Fats | 26.62g | 17.1g | 15% |
| Vitamin A | 236µg | 137µg | 11% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.476mg | 10% | |
| Monounsaturated fat | 7.393g | 4.844g | 6% |
| Cholesterol | 69mg | 54mg | 5% |
| Calories | 351kcal | 280kcal | 4% |
| Protein | 25.58g | 27.5g | 4% |
| Phosphorus | 496mg | 524mg | 4% |
| Calcium | 756mg | 731mg | 3% |
| Iron | 0.52mg | 0.25mg | 3% |
| Selenium | 14.5µg | 15.7µg | 2% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.769g | 0.509g | 2% |
| Vitamin D | 20 IU | 13 IU | 1% |
| Potassium | 138mg | 95mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 3.23mg | 3.13mg | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 0.23mg | 0.15mg | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 0.5µg | 0.3µg | 1% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.321mg | 0.34mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.073mg | 0.08mg | 1% |
| Choline | 15.4mg | 18.4mg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 2.14g | 3.1g | N/A |
| Carbs | 2.14g | 3.1g | 0% |
| Magnesium | 28mg | 26mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 0.56g | 1.23g | N/A |
| Copper | 0.026mg | 0.027mg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.01mg | 0% | |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.019mg | 0.02mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.156mg | 0.12mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 2.2µg | 1.8µg | 0% |
| Folate | 10µg | 9µg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.345mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.982mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 1.091mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 2.297mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 2.646mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.686mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 1.287mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 1.64mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 1.115mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more FatsFats | +55.7% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +96.3% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +44.9% |
| Contains more WaterWater | +21.9% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Provolone - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170850/nutrients
- Mozzarella - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/167735/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






