Pomelo vs. Passion fruit — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Passion fruit provides more fiber, iron, Vitamin B3, Vitamin B2, phosphorus, and magnesium; it is also lower in glycemic index.
Pomelo has more Vitamin C and Vitamin A. It is also lower in sugars, saturated fats, and sodium.
Introduction
We will discuss the similarities and differences between pomelo and passion fruit, focusing on nutrition and health impact.
What's The Actual Difference?
Passion fruits belong to the genus Passiflora, and pomelo is the largest citrus fruit from the Citrus genus.
Passion fruit has a solid shell, and the pulp on the inside has a jelly-like consistency and is filled with tiny seeds. On the outside, passion fruits are typically dark purple, sometimes wrinkly, spheres, while pomelos' pulp varies from pale yellow to pink. Pomelos have a thick, soft rind and can be stored for a long time.
Taste
Pomello tastes similar to grapefruit: it is tart, acidic, and has a sweet aftertaste. Read more about the differences between pomelo and grapefruit in this article.
In contrast, passion fruit has a unique taste that combines sweet and sour with citrusy notes.
Nutrition
Calories
Passion fruit has two times more calories than pomelo. It contains 97 calories per 100g, while pomelo contains only 38 calories per 100g. Pomelo is considered a low-calorie food.
Vitamins
Passion fruit contains more Vitamin A, Vitamin B2, Vitamin B3, and Vitamin B6 than pomelo.
Vitamin B3 is three times higher, and Vitamin A is 15 times higher in passion fruit than in pomelo.
On the other hand, pomelo is higher in Vitamin C and Vitamin B1. Moreover, pomelo falls in the range of the top 12% of foods as a source of Vitamin C.
Both have no Vitamin D and Vitamin B12.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+103.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+381.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+581.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+177.8%
Minerals
Passion fruit has a relatively higher amount of minerals—more calcium, copper, potassium, magnesium, zinc, iron, and phosphorus.
The amount of iron is 13 times higher in passion fruit. Besides, this fruit falls in the top 26% of foods as a source of potassium.
On the other hand, pomelo has less sodium than passion fruit.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-96.4%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+∞%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+383.3%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+200%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+61.1%
Contains
more
IronIron
+1354.5%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+79.2%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+25%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+300%
Fats
Both pomelo and passion fruit have fats of less than 1g.
Cholesterol
Both foods have no cholesterol.
Carbs
Passion fruit has two times more carbs than pomelo. It has 23.38g per 100g, whereas pomelo has only 9.62g per 100g.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
WaterWater
+22.2%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+189.5%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+1650%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+143%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+64.6%
Fiber
Passion fruit falls in the range of the top 10% of foods as a source of fiber. Passion fruit has ten times more fiber than pomelo: 10.4g per 100g, while pomelo contains only 1g of fiber.
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index of passion fruit is 16, considered a low GI. The glycemic index of pomelo is 78, which is considered a high GI.
Health Impact
Cardiovascular Health
Passion fruit and pomelo both offer significant cardiovascular benefits. Passion fruit is rich in antioxidants such as carotenoids and polyphenols, which reduce oxidative stress and inflammation. Similarly, pomelo contains high levels of antioxidants that may reduce cardiovascular risk (1, 2).
Both fruits are effective in regulating blood pressure due to their high potassium content. Passion fruit’s antioxidants further improve endothelial function, helping in blood pressure management. Pomelo’s flavonoids also contribute to better endothelial health and hypertension control.
Passion fruit and pomelo both help manage LDL (“bad” cholesterol) levels. Their soluble fiber binds to cholesterol in the digestive tract, promoting its excretion and thereby lowering overall levels. Additionally, both fruits’ antioxidants prevent LDL oxidation, a critical step in the development of atherosclerosis, the main cause of coronary heart disease and myocardial infarction (3, 4).
In conclusion, the inclusion of passion fruit and pomelo in a balanced diet is a significant step towards better cardiovascular health. Passion fruit, with its high soluble fiber content and potent antioxidants, is particularly effective in lowering LDL levels and preventing LDL oxidation. By incorporating both fruits into your diet, you can harness their complementary mechanisms for a healthier heart.
Diabetes
Although pomelo is classified as a high glycemic index fruit, it has a low glycemic load, which means that eating it does not cause a blood sugar spike (5).
According to another study (6), passion fruit is high in piceatannol. When taken as a supplement, this polyphenol may improve insulin sensitivity in overweight men, potentially lowering the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Besides, passion fruit is exceptionally high in fiber. Fiber may slow digestion and allow sugars to break down more slowly. Consumption of high dietary fiber foods may help prevent diabetes. According to the current study (7), higher dietary fiber intake was associated with a lower risk of type 2 diabetes.
Cancer
In one study (8), pomelo peel extract suppressed tumor growth, boosted the immune system, and killed mouse cancer cells. However, more research is needed on humans.
Passion fruit contains a lot of beta-carotene. Diets high in plant-based beta carotene have been linked to a lower risk of certain cancers, including prostate, colon, stomach, and breast (9).
Side Effects
Allergy
Passion fruit is generally safe for most people, but allergies can occur in rare cases. People who are allergic to latex are at risk. People allergic to citrus fruit peels are frequently allergic to limonene, a chemical found in pomelo. Itching in the lips, mouth, or throat may occur when an allergy occurs (10).
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9532706/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6033812/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/348940656
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/375642974
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29058284/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29057795/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8015811/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30966454/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14973107/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29723936/
Infographic
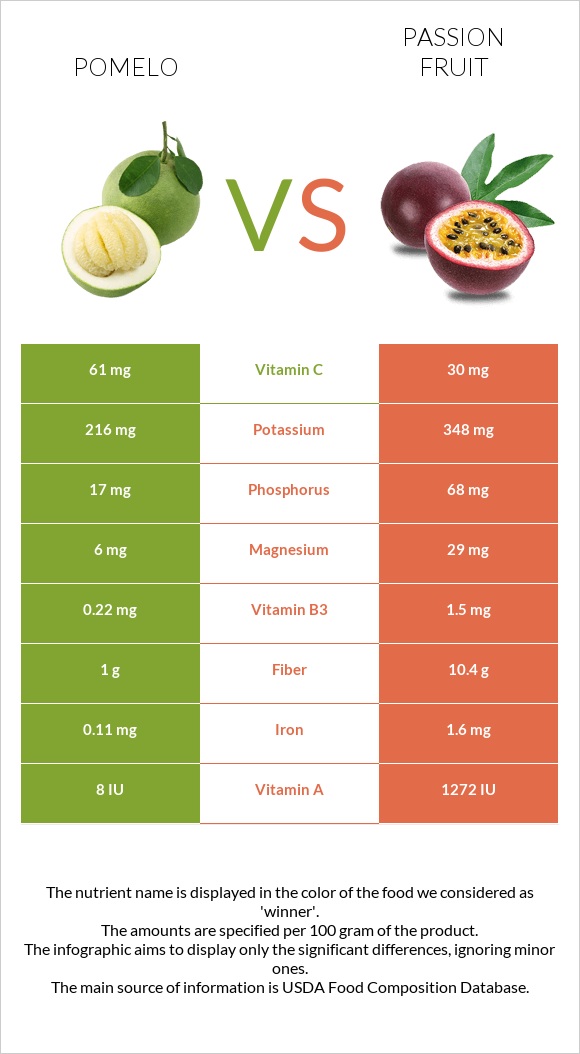
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Fiber | 1g | 10.4g | 38% |
| Vitamin C | 61mg | 30mg | 34% |
| Iron | 0.11mg | 1.6mg | 19% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.027mg | 0.13mg | 8% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.22mg | 1.5mg | 8% |
| Phosphorus | 17mg | 68mg | 7% |
| Vitamin A | 0µg | 64µg | 7% |
| Carbs | 9.62g | 23.38g | 5% |
| Magnesium | 6mg | 29mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.036mg | 0.1mg | 5% |
| Potassium | 216mg | 348mg | 4% |
| Copper | 0.048mg | 0.086mg | 4% |
| Folate | 14µg | 4% | |
| Calories | 38kcal | 97kcal | 3% |
| Protein | 0.76g | 2.2g | 3% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.034mg | 0mg | 3% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.411g | 3% | |
| Fats | 0.04g | 0.7g | 1% |
| Calcium | 4mg | 12mg | 1% |
| Sodium | 1mg | 28mg | 1% |
| Manganese | 0.017mg | 1% | |
| Selenium | 0.6µg | 1% | |
| Vitamin K | 0.7µg | 1% | |
| Choline | 7.6mg | 1% | |
| Net carbs | 8.62g | 12.98g | N/A |
| Sugar | 11.2g | N/A | |
| Zinc | 0.08mg | 0.1mg | 0% |
| Vitamin E | 0.02mg | 0% | |
| Saturated fat | 0.059g | 0% | |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.086g | 0% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Pomelo - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/167754/nutrients
- Passion fruit - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169108/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






