Radicchio vs. Red cabbage — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
In short, red cabbage is higher in carbohydrates, both net carbs and dietary fiber, and calories. Red cabbage provides 41 times more vitamin A and 7 times more vitamin C. However, radicchio can be a better source of minerals such as copper, zinc, and phosphorus.
Red cabbage and radicchio are full of health-beneficial effects due to their high anthocyanin content. However, red cabbage is much better researched in this field.
Introduction
Red cabbage and radicchio are often mistaken for each other; however, the two are entirely different vegetables. In this article, we will be discussing what similarities red cabbage and radicchio share and what sets them apart.
Classification
Despite all the similarities, red cabbage and radicchio botanically belong to separate families. Red cabbage is the purple-leafed variety of cabbage belonging to the Brassicaceae family and Oleracea species. Radicchio, on the other hand, is a part of the Asteraceae family and Chicorium genus.
Red cabbage and radicchio are often referred to as leaf or leafy vegetables, which are plant leaves used as vegetables.
Appearance
The two vegetables look alike; however, radicchio has distinct white-veined leaves and is usually smaller and more oblong in size. Radicchio also has a stronger reddish hue to its purple leaves.
Taste and Use
Red cabbage and radicchio are sometimes interchangeably used in recipes despite the difference in their flavors and textures. Radicchio has thin leaves with a bitter taste, while red cabbage has a milder taste and crunchier leaves.
Nutrition
The nutritional information below will be presented for raw red cabbage and radicchio.
Macronutrients and Calories
Red cabbage is slightly denser in nutrients, consisting of 91% water, while radicchio contains 94% water.
The average serving size of red cabbage per person is one cup of shredded cabbage, equal to 70g. At the same time, one cup of shredded radicchio weighs 40g.
Calories
Red cabbage and radicchio are both very low-calorie foods. However, red cabbage is slightly higher in calories, containing 31 calories in a 100g serving. A hundred-gram serving of radicchio provides only 23 calories.
One cup of chopped red cabbage contains 22 calories, while the same serving size of radicchio has 9 calories.
Protein and Fats
Like most leafy vegetables, red cabbage and radicchio are very low in protein and fats.
The two vegetables provide the same exact amount of protein - 1.43g per 100g serving.
Red cabbage and radicchio contain negligible amounts of fats.
Vegetables naturally do not contain cholesterol or trans fats.
Carbohydrates
Red cabbage is richer in carbohydrates by 65%. Per 100g serving, red cabbage provides 7.37g of carbohydrates, while radicchio contains 4.48g.
Red cabbage contains 1.5 times more net carbs and is 2.3 times higher in dietary fiber.
Vitamins
Red cabbage and radicchio are rich sources of several vitamins; however, red cabbage wins in this category.
Red cabbage provides 41 times more vitamin A, 7 times more vitamin C, and 4 times more vitamins B1 and B6. Red cabbage is also richer in vitamins B2 and B3.
At the same time, radicchio contains 20 times more vitamin E, 7 times more vitamin K, 3 times more folate, and 2 times more vitamin B5.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+1954.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+83%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+568.1%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+233.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+612.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+5500%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+300%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+146.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+63.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+266.7%
Minerals
Inversely, radicchio wins in the mineral category. Radicchio is 20 times richer in copper and 3 times richer in zinc. Radicchio also provides slightly more phosphorus and potassium and less sodium.
Red cabbage, on the other hand, is richer in calcium, iron, and magnesium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+24.3%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+1905.9%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+181.8%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+33.3%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-18.5%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+50%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+23.1%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+136.8%
Contains
more
IronIron
+40.4%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+76.1%
Health Impact
Health Benefits
Leafy vegetables are known to contain phytochemicals that provide various beneficial health effects.
Red cabbage and radicchio get their red coloring from containing phytochemicals called anthocyanins. Anthocyanins have antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and antiproliferative properties, which can help protect against diabetes, cardiovascular disease, cancer, and neurological disorders (1, 2).
Overall, the health impact of red cabbage is better researched in the scientific field when compared to that of radicchio.
Cardiovascular Health
Red cabbage has been researched to potentially protect against cardiovascular disease by lowering low-density lipoprotein, triglyceride, cholesterol, and inflammatory cytokine levels (3, 4).
Studies on the effect of radicchio on cardiovascular health have not yet been carried out. However, the impact can be assumed to be beneficial due to radicchio’s high content of phytochemicals, vitamins, and minerals.
Diabetes
Research carried out on animals found red cabbage to have antidiabetic properties, lowering blood glucose levels and improving kidney and liver function in diabetic rats (5, 6).
While not much research has been done regarding radicchio and diabetes, chicory plants have been found to have antidiabetic effects (7). Radicchio and chicory are very closely related.
Cancer
Anthocyanins have been demonstrated to have anti-cancer qualities, potentially protecting against skin, colon, esophageal, and lung cancer (8).
Due to high anthocyanin levels, radicchio or red chicory has also been found to potentially decrease the risk of cancer, colon cancer in particular (9).
Similarly, red cabbage has also been researched for its anti-cancer activities (10, 11, 12).
Sources.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8308553/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1082894/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27933986/
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/13880209.2016.1200633
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2529380/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/262835482
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32768902/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2582525/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3771420/
- https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2020/ra/d0ra07861a
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/344521531
- http://www.ijpacr.com/files/31-08-2019/04.pdf
Infographic
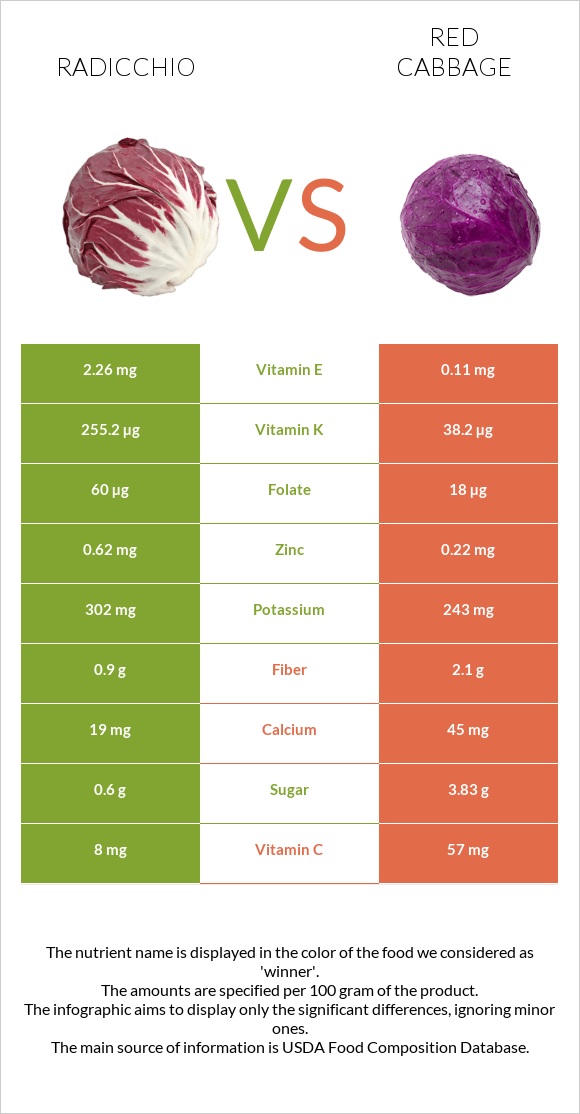
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin K | 255.2µg | 38.2µg | 181% |
| Vitamin C | 8mg | 57mg | 54% |
| Copper | 0.341mg | 0.017mg | 36% |
| Vitamin E | 2.26mg | 0.11mg | 14% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.057mg | 0.209mg | 12% |
| Folate | 60µg | 18µg | 11% |
| Vitamin A | 1µg | 56µg | 6% |
| Fiber | 0.9g | 2.1g | 5% |
| Manganese | 0.138mg | 0.243mg | 5% |
| Zinc | 0.62mg | 0.22mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.016mg | 0.064mg | 4% |
| Calcium | 19mg | 45mg | 3% |
| Iron | 0.57mg | 0.8mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.028mg | 0.069mg | 3% |
| Potassium | 302mg | 243mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.269mg | 0.147mg | 2% |
| Fructose | 1.48g | 2% | |
| Carbs | 4.48g | 7.37g | 1% |
| Magnesium | 13mg | 16mg | 1% |
| Phosphorus | 40mg | 30mg | 1% |
| Selenium | 0.9µg | 0.6µg | 1% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.255mg | 0.418mg | 1% |
| Choline | 10.9mg | 17.1mg | 1% |
| Calories | 23kcal | 31kcal | 0% |
| Protein | 1.43g | 1.43g | 0% |
| Fats | 0.25g | 0.16g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 3.58g | 5.27g | N/A |
| Sugar | 0.6g | 3.83g | N/A |
| Sodium | 22mg | 27mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.06g | 0.021g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.01g | 0.012g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.11g | 0.08g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.026mg | 0.012mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.04mg | 0.039mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.085mg | 0.034mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.062mg | 0.046mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.056mg | 0.049mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.008mg | 0.014mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.034mg | 0.036mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.065mg | 0.048mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.024mg | 0.024mg | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more FatsFats | +56.3% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +64.5% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +37.5% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -65% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +20% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Radicchio - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168564/nutrients
- Red cabbage - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169977/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





