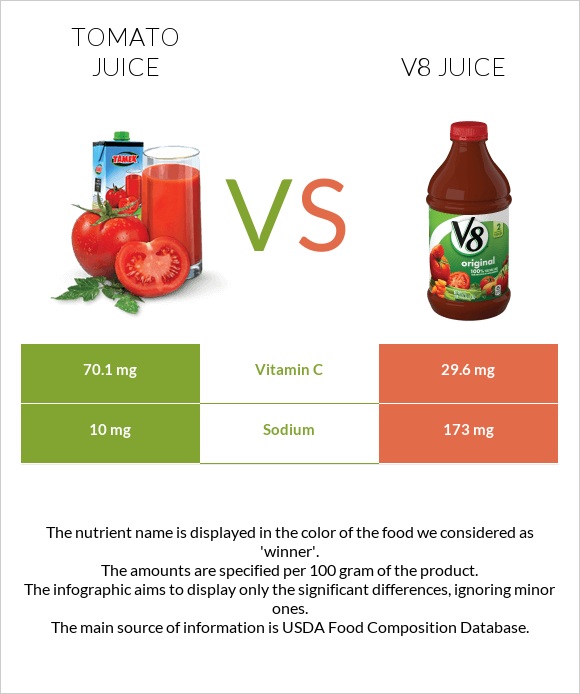
V8 Juice vs. Tomato Juice — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Although both V8 juice and tomato juice are vegetable juices and have many similarities, they differ in the nutrients they provide. V8 is higher in calories, carbs, and vitamin A, while tomato juice is richer in minerals and vitamin C.
Introduction
This article compares V8 juice and tomato juice, focusing on their nutritional content and health impact.
The key difference between these juices is that V8 contains purees of all kinds of vegetables, while tomato juice is prepared from tomatoes only.
Nutrition
The nutritional differences here are depicted for Campbell's V8 vegetable juice and canned tomato juice without added salt.
Macronutrients and Calories
V8 and tomato juice differ in the distribution of various macronutrients. The quantities of nutrients they contain are shown and described below.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+∞%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+16.7%
Calories
V8 and tomato juice are vegetable juices. Hence, they both are low-calorie products.
Carbohydrates
In terms of carbs, V8 is slightly higher compared to tomato juice.
V8 provides 0.8g of dietary fiber per 100g, while the same serving of tomato juice contains only 0.4g.
V8 juice contains double the amount of fiber compared to tomato juice.
Protein and fats
Their protein and fat contents are insignificant.
Vitamins
Tomato juice has a richer vitamin profile.
Tomato juice is an excellent source of vitamin C: it is more than two times higher in vitamin C (70.1mg per 100g) than V8 (29.6mg per 100g).
Tomato juice is also richer in B-complex vitamins, vitamin E and K, while V8 provides more vitamin A.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+136.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+∞%
Minerals
Tomato juice wins this section too. It is higher in copper, phosphorus, iron, and potassium.
V8 is higher in calcium and sodium.
You can check the mineral composition of these two juices in the chart below.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+∞%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+12.4%
Contains
more
IronIron
+30%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+∞%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+∞%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+∞%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-94.2%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+∞%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+∞%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+60%
Health Impact
Tomato juice with no added sugar is an excellent option for those who want to maintain heart health and prevent cancer. On the other hand, V8 has some drawbacks you should consider before using it.
Tomato juice contains a significant amount of lycopene, an antioxidant that reduces heart disease risks such as high blood pressure and cholesterol levels (1).
Research shows that people who consumed more tomato-made products had a lower risk of heart disease than those who used less tomato in their meals (2).
Being a tomato-containing food product, tomato juice may prevent skin and prostate cancer development (3, 4).
Although V8 juice is a better option to get nutrients for those who use harmful drinks (soda, energy drinks) too much, it is not a complete replacement for vegetables you should use in your meal plan. Firstly, this juice is processed and pasteurized; thus, the heat can destroy many nutrients it should provide, such as enzymes, vitamins, and so on. Moreover, most of the fiber is removed during the preparation of V8. Additionally, V8 can contain added salt, thus having a high sodium content, which is a risk for the cardiovascular system.
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin C | 70.1mg | 29.6mg | 45% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.1mg | 8% | |
| Sodium | 10mg | 173mg | 7% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.078mg | 6% | |
| Copper | 0.042mg | 5% | |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.07mg | 5% | |
| Folate | 20µg | 5% | |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.673mg | 4% | |
| Magnesium | 11mg | 3% | |
| Phosphorus | 19mg | 3% | |
| Vitamin A | 23µg | 3% | |
| Manganese | 0.068mg | 3% | |
| Fiber | 0.4g | 0.8g | 2% |
| Vitamin E | 0.32mg | 0mg | 2% |
| Vitamin K | 2.3µg | 2% | |
| Fructose | 1.33g | 2% | |
| Calcium | 10mg | 16mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 217mg | 193mg | 1% |
| Iron | 0.39mg | 0.3mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.11mg | 1% | |
| Selenium | 0.5µg | 1% | |
| Choline | 6.8mg | 1% | |
| Calories | 17kcal | 21kcal | 0% |
| Protein | 0.85g | 0.82g | 0% |
| Fats | 0.29g | 0g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 3.13g | 3.32g | N/A |
| Carbs | 3.53g | 4.12g | 0% |
| Sugar | 2.58g | 3.29g | N/A |
| Saturated fat | 0.019g | 0g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.005g | 0g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.027g | 0g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.006mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.026mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.017mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.024mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.026mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.005mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.026mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.017mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.014mg | 0% | |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.005g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 0.022g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






