Tomato Sauce vs. Tomato Paste — What’s the Difference?


Summary
Tomato paste and tomato sauce are made by cooking tomatoes; however, the water in tomato paste is reduced afterward, making it thicker. On the other hand, tomato sauce has a thinner consistency and a smoother texture.
Tomato paste naturally has an intense tomato flavor, whereas tomato sauce needs various ingredients to give it a rich flavor.
As for the nutritional profile, tomato paste is denser than tomato sauce and contains more calories, proteins, carbs, and fats. Tomato sauce comprises 91% water, whereas tomato paste comprises 73.5%.
Introduction
In the 16th century, the Spanish explorers brought tomatoes to Europe from Central America, and after some time, the Italians started cultivating and using them in cooking.
Tomato sauce came from Naples and was called Napoli, Napoletana, or Neapolitan sauce. Tomato sauce is any sauce made from tomatoes, but it differs from ketchup; they have different ingredients and sugar contents and are served differently.
In the UK, tomato paste is also known as tomato puree or concentrate, whereas, in the US, tomato paste is simply concentrated tomato solids with no seeds or skin, and tomato purée is its’ thinner version.
Preparation & Consistency
Tomato paste and tomato sauce are made by cooking fresh tomatoes packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. The moisture or water content in tomato paste is reduced afterward.
Tomato paste is concentrated and thicker, whereas tomato sauce has a thinner consistency, a smoother texture, and is a liquid.
Ingredients
The ingredients vary from recipe to recipe.
Tomato paste naturally has an intense tomato flavor; apart from the tomatoes, it contains olive oil (extra-virgin or regular) and salt. It may also contain lemon juice (or citric acid) and peppers (bell or Italian).
The ingredients in tomato sauce vary and depend on personal taste. Tomato sauce may contain spices, garlic (or garlic powder), onions (or onion powder), vinegar, butter, olive oil, and herbs like basil and oregano. Baking soda, vinegar, or sugar may be added for a better and more balanced taste.
Uses
Tomato sauce and tomato paste are versatile and can be a substitute for each other. They can also be substituted for tomato soup,
Tomato sauce can be used as a dip for different munching foods or served with Mexican salsas, meat and vegetables, pasta sauces, pizza, soups, and stews. It is prepared based on the Napoletana style and can be used as a pizza sauce or as a base for arrabbiata or bolognese sauce.
Tomato paste often adds intense flavor to soups, stews, sauces, chili, meatballs, and meatloaf. It can also be used as a base for tomato sauce when diluted with water or broth.
Nutrition
The nutritional values in this article are presented for 100g of canned tomato sauce and tomato paste without added salt.
Tomato paste is denser in nutrients than tomato sauce and contains more calories, proteins, carbs, and fats. Their nutritional values may change slightly depending on the ingredients used, but the overall nutritional profile will be consistent.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+260%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+56.7%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+256.1%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+46.6%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+24.2%
Moisture
Tomato sauce comprises 91% water, whereas tomato paste comprises 73.5%.
Calories
Tomato sauce and paste are considered low-calorie foods. 100g of tomato sauce provides 24 calories, whereas tomato paste provides 82.
Proteins & Fats
Tomato paste contains 3.6 times more proteins than tomato sauce per 100g serving: 4.32g for tomato paste and 1.2g for tomato sauce.
Both are very low in fat, containing less than 0.5g.
Carbohydrates
Tomato paste contains 3.6 times more total carbs per 100g serving. 100g of tomato sauce contains 19g of carbs, whereas tomato sauce contains 5.3g.
From the total carbs, 3.6g are simple sugars, and 1.5g is dietary fiber in tomato sauce. The same amount of tomato paste contains 12.18g of simple sugars and 4.1g of dietary fiber.
Most carbs in these tomato products are glucose and fructose in similar percentages. Tomato sauce also contains a little sucrose, whereas tomato paste contains some starch, sucrose, and maltose.
Carbohydrate type comparison
Contains
more
StarchStarch
+∞%
Contains
more
SucroseSucrose
+328.6%
Contains
more
GlucoseGlucose
+215.9%
Contains
more
FructoseFructose
+250.3%
Contains
more
MaltoseMaltose
+∞%
Vitamins
Tomato paste is richer in most vitamins and minerals. Tomato sauce is richer only in vitamin B5, whereas tomato paste is richer in other B-complex and fat-soluble vitamins A, E, and K.
Tomato paste is over 3.5 times richer in vitamins A and K and 3 times richer in vitamins E, C, and B3.
Both are naturally absent in vitamin B12 and vitamin D.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+212.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+245.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+198.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+150%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+135.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+210.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+120.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+307.1%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+33.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+117.6%
Minerals
Tomato paste is comparably high in copper, iron, and potassium and is richer in all minerals than tomato sauce.
Tomato paste is 4 times richer in iron, 3.4 times richer in potassium, and 3 times richer in copper.
Both are low in sodium: tomato paste contains 59mg, whereas tomato sauce contains 11mg. The recommended intake of sodium is less than 2300mg daily.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+180%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+157.1%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+241.4%
Contains
more
IronIron
+210.4%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+217.4%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+186.4%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+207.4%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+167.3%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+783.3%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-81.4%
Glycemic Index
Tomato sauce has a glycemic index value of 31, which is considered low. The exact glycemic index value of tomato paste is yet to be calculated; however, considering the low glycemic index values of other tomato-based products and tomatoes and its high dietary fiber content, it is likely to fall into the low glycemic index range.
Infographic
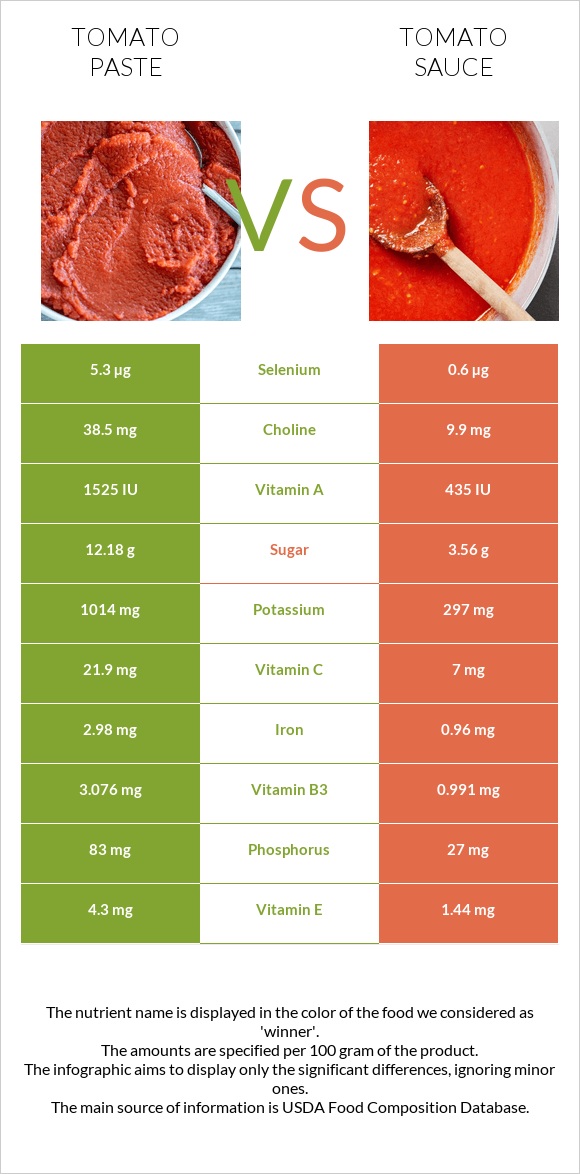
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Copper | 0.365mg | 0.115mg | 28% |
| Iron | 2.98mg | 0.96mg | 25% |
| Potassium | 1014mg | 297mg | 21% |
| Vitamin E | 4.3mg | 1.44mg | 19% |
| Vitamin C | 21.9mg | 7mg | 17% |
| Vitamin B3 | 3.076mg | 0.991mg | 13% |
| Fiber | 4.1g | 1.5g | 10% |
| Selenium | 5.3µg | 0.6µg | 9% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.216mg | 0.098mg | 9% |
| Phosphorus | 83mg | 27mg | 8% |
| Manganese | 0.302mg | 0.113mg | 8% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.153mg | 0.065mg | 7% |
| Vitamin K | 11.4µg | 2.8µg | 7% |
| Protein | 4.32g | 1.2g | 6% |
| Magnesium | 42mg | 15mg | 6% |
| Vitamin A | 76µg | 22µg | 6% |
| Carbs | 18.91g | 5.31g | 5% |
| Choline | 38.5mg | 9.9mg | 5% |
| Fructose | 5.85g | 1.67g | 5% |
| Zinc | 0.63mg | 0.22mg | 4% |
| Calories | 82kcal | 24kcal | 3% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.06mg | 0.024mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.142mg | 0.309mg | 3% |
| Calcium | 36mg | 14mg | 2% |
| Sodium | 59mg | 11mg | 2% |
| Folate | 12µg | 9µg | 1% |
| Fats | 0.47g | 0.3g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 14.81g | 3.81g | N/A |
| Sugar | 12.18g | 3.56g | N/A |
| Starch | 0.22g | 0% | |
| Saturated fat | 0.1g | 0.041g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.067g | 0.044g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.16g | 0.121g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.031mg | 0.009mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.133mg | 0.037mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.089mg | 0.025mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.124mg | 0.034mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.134mg | 0.037mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.027mg | 0.008mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.13mg | 0.036mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.088mg | 0.025mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.071mg | 0.02mg | 0% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +52.3% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +32.2% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -59% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Tomato paste - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170459/nutrients
- Tomato sauce - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169074/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.




