Crab stick nutrition facts, calories and full health analysis

Introduction
Crab sticks have many names: seafood sticks, imitation crab meat, surimi, or kanikama in Japanese. A crab stick doesn’t contain real and fresh crab meat despite its name. It is sometimes spelled as a krab stick to highlight its lack of real crabs.
This article will talk about everything necessary regarding crab sticks, discussing what they’re made from, their nutritional value, and their impact on health, among other things.
Ingredients
The main ingredient in crab sticks is the fish meat found in the surimi. In addition to the fish, imitation crab contains water, egg whites, wheat starch, sometimes soy protein, sugars such as sorbitol and sucrose, various vegetable oils, salt, and natural dyes.
Imitation crab usually contains only a tiny amount of an extract of real crab to give it its distinct flavor.
Typically, imitation crab consists of 25% water, 55% surimi, 8% egg white, 5% starch, 2.5% crab essence, 2.3% seasoning, and 1.5% salt (1).
Varieties
The different kinds of imitation crab sold at the stores are usually based on the shape and texture of the product. Imitation crab can be flaked, shredded, or, more commonly, sold as sticks.
Flaked imitation crab or flake-style imitation crab is fake crab meat highly compressed into chunky pieces. This kind of imitation crab is dense and slightly tough and is often used in seafood salads and imitation crab cakes.
The most popular kind of imitation crab is crab sticks. Crab sticks can easily be pulled apart to get shredded imitation crab. Crab sticks are commonly used as snacks or in California rolls.
How It’s Made
Crab stick is a highly processed food made of whitefish meat or surimi to imitate the texture, shape, and flavor of the leg meat of a crab. This food originated in Japan in 1974 and later found popularity in Western countries, especially in the United States.
Surimi is a paste made from fish meat and literally means “groundfish” in Japanese. Surimi is also known as fake crab or fish paste. Whitefish is a term for several fish species, such as Atlantic cod, pollock, and others.
Surimi has been used in Japanese culture for centuries, mainly to produce a kind of seafood called kamaboko, commonly added to soups. Katsuichi Osaki, the son of the founder of a company producing kamaboko products, figured that adding red coloring to kamaboko and slicing it into a stick shape could make it resemble real crab meat without the expensive price (18).
The most common fish used in surimi, and therefore in crab sticks, is the Alaska pollock or walleye pollock. The myofibrillar proteins of the fish form a gel, and sugars, like sucrose and sorbitol, are added as cryoprotectants to keep the gel from degradation in low temperatures. Wheat starch and egg whites are added to improve the texture and stabilize the gel. Vegetable oil may be used to better its texture and appearance.
Natural and artificial flavorings are added to achieve the taste of crab meat. The natural flavoring is usually made from the aqueous extraction of edible crab.
Finally, seasonings, such as monosodium glutamate, vegetable protein, and mirin, are added. The red coloring is achieved by adding natural dyes, often carmine, but sometimes paprika and annatto extract.
Cooking and Use
Imitation crab meat is already cooked during production, so it is safe to eat as it is. Crab sticks are often used without cooking in various salads and sushis.
If you steam the crab sticks, it’s better to steam them for less than 10 minutes; otherwise, the meat can disintegrate into pieces.
Microwave reheating is advised against due to the textural changes that may be caused (19).
Crab sticks are commonly used in seafood salads. They are the main ingredient in many types of sushi, the most popular ones being California rolls, Kani maki sushi rolls, Kimbap Korean sushi, and Kanikama sushi or Nigiri.
Imitation crab can be used in a variety of ways in the kitchen. Crab sticks can be sauteed on the stove, deep-fried, or cooked in the oven.
Nutrition
The nutrition of crab sticks is based on the main ingredient, fish, and the added components: sugars, starch, egg whites, vegetable oil, flavorings, and seasonings.
Depending on the production method and added ingredients, the nutrition of different brands of crab sticks can vary.
The nutritional values below are presented for imitation Crustaceans crab, made from surimi, using Alaska kingfish.
Macronutrients and Calories
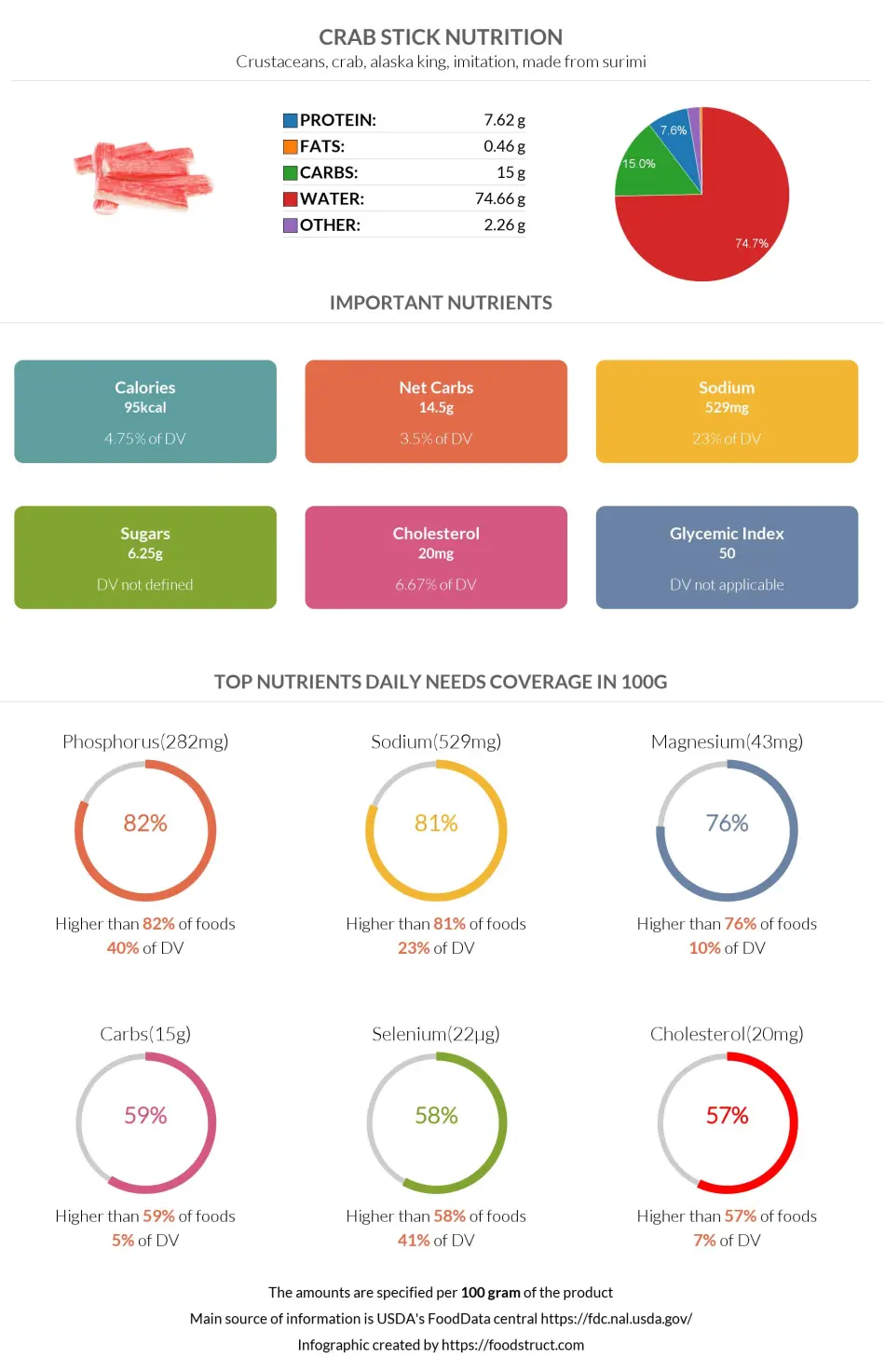
Crab sticks are a low-calorie food, containing only 95 calories per 100g serving.
The average serving size of crab sticks per person is 3oz or 85g. Therefore, one average serving size of crab sticks provides around 81 calories.
Crab sticks are relatively dense in nutrients, consisting of 75% water and 25% nutrients, such as carbohydrates, protein, fats, vitamins, and minerals.
In comparison, canned real blue crab is lower in calories, containing 83 calories in every 100g serving. However, cooked crab meat has a similar caloric value to imitation crab, containing 95 calories per every hundred-gram serving.
Macronutrients chart
Carbohydrates
The predominant macronutrient of crab sticks is carbohydrates, consisting mainly of sugars: sucrose, glucose, and fructose. The rest of the carbohydrates comprise starch and some dietary fiber.
A 100g serving of crab sticks provides 15g of carbohydrates. Of this, 14.5g are net carbs, consisting of 6.25g of sugar and 8.25g of starch and other carbohydrates, and only 0.5g is dietary fiber.
The sugars consist of 47% sucrose, 43% of glucose, and only 10% of fructose.
Crab sticks contain 3.5g of starch in every hundred-gram serving.
Unlike imitation crab, real crab meat contains no notable carbohydrates, including sugars and starch.
Carbohydrate type breakdown
Protein
The fish meat in crab sticks makes up the protein content, about 8g in every 100g serving. This means that one average serving size of crab sticks contains 6.4g of protein.
The protein found in crab sticks is of high quality as it includes some amounts of all essential amino acids. Crab stick protein is rich in lysine, threonine, and tryptophan while relatively low in valine, isoleucine, and phenylalanine.
Crab stick is high in aspartic and glutamic acids, among the non-essential amino acids.
Real canned crab, on the other hand, contains over two times more protein, providing 18g per every 100g serving. At the same time, cooked fresh crab meat contains 19.35g of protein in a 100g serving.
Protein quality breakdown
Fats
Imitation crab contains minimal amounts of fats; however, it does contain some cholesterol and trans fats.
The fat composition is dominated by monounsaturated fatty acids, followed by saturated fatty acids, leaving polyunsaturated fatty acids in the last place.
A hundred-gram serving of crab sticks contains less than a gram of fats. However, the same serving size contains 20mg of cholesterol.
At the same time, real canned crab meat provides almost double the fat content but 97mg of cholesterol per 100g serving. However, while containing almost 2g of fats, real cooked crab meat has 53mg of cholesterol.
Fat type information
Vitamins
Crab sticks are rich in vitamins B12 and B6. It also contains moderate amounts of vitamins B1, B2, B3, E, and K.
However, crab sticks completely lack vitamin B5 and folic acid or vitamin B9 and vitamins A, C, and D.
Overall, imitation crab is not a great source of vitamins.
On the other hand, real crab meat is richer in almost all vitamins except for vitamins B1 and K.
Vitamin coverage chart
Minerals
Unlike vitamins, crab sticks contain some level of all essential minerals.
Crab sticks are very rich in selenium, phosphorus, and magnesium. Imitation crab is in the top 18% of foods as a source of phosphorus and in the top 24% as a source of magnesium.
Crab sticks also contain calcium, zinc, iron, choline, potassium, copper, and manganese.
However, crab sticks are also very high in sodium, being in the top 19% of foods as a source of sodium.
@foodMineralCoverag
Glycemic Index
Fish generally have a glycemic index close to zero; however, the added carbohydrates to imitation crab make the glycemic index of this food higher than most seafood products.
An exact number for the glycemic index of crab sticks has not yet been researched. However, as imitation crab contains added carbohydrates, such as sugar and starch, its glycemic index can be assumed to fall in the moderate category.
On the other hand, real crab meat contains no carbohydrates and has a glycemic index of 0.
Acidity
Surimi is the main ingredient found in imitation crab and has an average pH of 7, making this food’s acidity fall in the neutral category (2).
The acidity of foods can also be evaluated by looking at the potential renal acid load of the given food. The potential renal acid load or the PRAL value of the food demonstrates how much acid or base the given food produces inside the organism.
Based on the Potential Renal Acid Load (PRAL), the acidity of imitation crab meat is 11 due to its protein and micronutrient composition, making the crab stick an acid-forming food.
Health Impact
Health Benefits
Diabetes
Real crab meat is a much better choice for people with diabetes because imitation crab contains added carbohydrates, both starch and sugars. In contrast, crab meat does not contain carbohydrates at all. There are not enough studies concerning the effect of imitation crab meat on the diabetic profile.
There is hope in the future of processing and the development of surimi meat to use cryoprotectants other than sugars, such as amino acids, methylamines, carbohydrate polymers, synthetic polymers (polyethylene glycol), other proteins (bovine serum albumin), and even inorganic salts (potassium phosphate and ammonium sulfate) (3). This will, naturally, decrease the sugar concentration and, consequently, the glycemic index of crab sticks.
Cancer
There is some limited suggestive evidence that fish, in general, can decrease the risk of cancer (4). Some studies linked higher fish consumption with a reduced risk of developing liver, breast, and colon cancers in particular (5).
Most of the anticancer quality of fish is related to the omega-3 fatty acid content. Imitation crab meat contains some polyunsaturated fatty acids. However, fortifying surimi meat with omega-3 fatty acids could significantly improve its anticarcinogenic abilities. Fortifying surimi-based seafood products with omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids without affecting the taste or texture of the meat has been proven possible (6).
Cardiovascular Health
Fortifying surimi-based seafood products with omega-3 fatty acids not only improves the anticarcinogenic qualities of the products but also improves their potential to protect against arrhythmias, reduce blood pressure, and generally benefit cardiovascular and diabetic conditions (7).
While consuming dishes with imitation crab meat, people with cardiovascular conditions must remember that it is high in salt and sugar.
Downsides and Risks
Allergy
Fish allergies are one of the most common allergies among adults. Even after thorough processing, surimi can retain the allergens found in the fish since approximately 75% of the fish’s original protein content remains. Therefore, consuming crab sticks can severely threaten people allergic to certain types of fish, particularly pollock (8).
The codfish from which surimi can be made usually contains several allergic proteins, whereas the surimi contains only one allergic protein (9). Thus, surimi is generally less allergenic than the fish from which it has been made.
The symptoms of a crab stick allergy are the same as most food allergy symptoms: oral allergy syndrome (an itching, tingling, or swelling feeling in the mouth), nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and, in some rare cases, anaphylactic shock.
Crab sticks do not contain crab meat; however, some added proteins may come from the aqueous extract of crabs, so for people allergic to shellfish and crab, it is better to read the label or avoid it as a whole.
In the production of crab sticks, egg whites, and wheat starch are sometimes added, so it is usually not gluten-free. People who are allergic to egg whites or gluten intolerant should avoid crab sticks.
Diabetes
Even though imitation crab meat has a relatively low glycemic index, there is a possibility that some of its dietary proteins react with the pancreatic islet cells, among other low glycemic index seafood proteins, potentially causing an immune response harming the pancreatic beta cells. This may lead to latent autoimmune diabetes in adulthood in people predisposed to it or with prior sensitization (10).
Pregnancy
Imitation crab meat is cooked during production, so it is usually safe for pregnant women. However, it is best to ask whether there are other raw products in foods containing crab sticks to avoid potential poisoning.
Listeria monocytogenes contamination of ready-to-eat foods, especially seafood, is a potential risk. However, the bacteria are inactivated by thermal treatment in crab stick production (11). Using starfish gelatin film containing vanillin in crab stick packaging with its antimicrobial qualities also decreases the risk of Listeria monocytogenes contamination (12).
Crab Stick in Diets
Crab sticks are very low in fats and calories. Crab sticks can fit into a weight-loss diet. However, crab sticks are a highly processed food with a high content of salt, starch, and sugars; therefore, they should be used with caution.
Real crab meat, although higher in fats, is a better option for healthy weight loss diets, as it is richer in beneficial nutrients and contains no carbohydrates.
| Keto | Imitation crab stick is not ideal for this diet due to the carbohydrates added during processing. One serving of crab sticks contains 15g of carbohydrates, while keto allows for an average of 20 to 30g of carbohydrates per day. Real crab meat is a better choice since it has no carbs. |
| DASH | Both imitation crab and crab meat, as most seafood products are very high in salt. For this reason, crab meat, both real and imitation, is not recommended for individuals with high blood pressure. |
| Atkins | During the Induction phase, you can only have 20 to 25g of carbohydrates a day (13), so imitation crab meat is not advised in this phase. You can add crab sticks to your diet starting from the third Fine-tuning phase and use them throughout the Maintenance phase. |
| Mediterranean | Seafood is a staple part of the Mediterranean diet; however, imitation crab is a highly processed food with added sugars, so if available, real crab meat is the correct alternative. |
| Paleo | Imitation crab meat, being a highly processed food with additives, does not fit this diet. |
| Vegan/ Vegetarian/ Pescetarian | Even though imitation crab doesn’t contain actual crab meat, it is still made of fish, so it does not fit a vegetarian or a vegan diet. Crab sticks also often contain eggs and a natural dye called carmine that is made using insects (14). Crab sticks do suit the pescetarian diet. However, in rare cases, the surimi in imitation crab can be made from deboned chicken, pork, or beef. |
| Gluten-free | Wheat starch is often used as a stabilizing ingredient in the production of imitation crab. Whilst wheat starch is wheat’s carbohydrate fraction and should contain no protein or gluten, it is still not considered entirely safe for people with gluten intolerance. However, gluten-free imitation crab can also be found in the market. |
| Dukan | Although imitation crab is rich in protein, it also contains 15g of sugars in a 100g serving. For this reason, imitation crab does not fit in the first two phases of the Dukan diet - the Attack and Cruise phases (15). You can start eating crab sticks starting from the Consolidation phase or the third phase, but only in strict moderation. |
| Intermittent Fasting | As with most foods, you can eat imitation crab during eating periods but refrain during fasting. |
| Low Fat & Low Calorie | Crab sticks fit a low fat and a low-calorie diet, containing only 95 calories and less than a gram of fats in a single serving. |
| Low Carb | Crab sticks contain 15g of carbohydrates per serving, which is not ideal for a low-carb diet. Real crab meat is the better alternative for this. |
| Anti Inflammatory | Real crab meat may have anti-inflammatory qualities due to its omega-3 fatty acid content (16). However, there is not enough research on this topic regarding imitation crab. |
| BRAT | Seafood products full of proteins are advised to be avoided on a BRAT diet (17), so imitation crab is unsuitable for this diet. |
Food additives
Food additives are unique compounds added to different foods to increase their quality. They help the particular food to taste, smell, or look better than usual.
Food gum, carmine, sodium benzoate, and MSG are the additives used to prepare crab sticks. Carrageenan is a type of food gum that increases the stability of the crab stick.
Carmine is an additive that gives the stick an extra red color, making it more attractive. MSG, or monosodium glutamate, is a chemical that enhances the taste and promotes an attraction to food flavor. Lastly, sodium benzoate is a preservative that increases the shelf life of the crab stick.
High consumption of foods with high amounts of artificial additives may cause some health conditions. Thus, everyone should consider the chemical content of processed foods before eating them.
Comparison to Crab Meat
Real crab meat is much richer in protein compared to crab sticks. It also tends to have fewer calories since it contains no carbohydrates, unlike crab sticks, which are high in sugars and starch.
Real crab meat is low in fats but still contains more than crab sticks; therefore, it has a higher cholesterol level. However, the predominant fats found in crab meat are polyunsaturated fats with a high concentration of omega-3 fatty acids.
Compared to crab sticks, crab meat contains vitamins A, C, and B5. It is also higher in vitamins B12, B2, B3, B6, and E. However, crab sticks contain higher levels of vitamin B1 and vitamin K.
Real crab meat is richer in iron, calcium, potassium, copper, and zinc, whereas crab sticks are higher in magnesium and phosphorus. The sodium concentration is lower in imitation crabs.
Environmental Impact
Many seafood products cause significant environmental damage as some sea creatures are overfished and endangered due to high demand.
While Alaska pollock is not at risk of endangerment, surimi made from Alaska pollock has been researched to have a high carbon footprint due to the energy used to produce products such as crab sticks (20).
Other environmental issues that arise during surimi processing include the high use of water. The minced meat used to make surimi is washed multiple times. This requires much freshwater while creating more wastewater (21).
However, surimi production can also have a beneficial impact on the environment. As surimi is made from minced meat, it provides an opportunity to use various ingredients as its source of protein, including the underutilized species with little or no commercial value. This could be a way of using abundant resources that would otherwise have been neglected (21).
Storing, Keeping & Conservation
Freezing imitation crab meat is not recommended. It is supposed to be refrigerated at a temperature between 32°F (0°C) and 38°F (3°C). Imitation crab meat should be discarded if kept at room temperature for 2 hours (19).
Vacuum-sealed, pasteurized crab sticks can be kept in the refrigerator for two months if the packaging is unopened. It should be used within three days after opening.
Imitation crab sold in loose forms in trays in fish cases should be kept for three to five days. If frozen, it can be kept for up to six months.
It is not recommended to refreeze imitation crab.
Consumption & Production
Originating in Japan in the seventies, imitation crab quickly spread to the West and became a trendy food in the United States.
Imitation crab meat is the most common product in the world made from surimi. Crab sticks usually contain about 35 to 40 percent fish meat. However, some crab sticks’ fish content can be up to 85 percent (22).
Countries that produce a significant percentage of the world’s surimi-based products are Japan, the Republic of Korea, France, Spain, Italy, and the USA. Thailand, China, Lithuania, and India produce surimi-based products mainly for export. The Russian Federation is also becoming a significant market for surimi-based products (22).
Eighty percent of the surimi-based products in France are imitation crab sticks.
From 2000 to 2004, the export of imitation crab meat from South Korea decreased by double; however, seafood consumption in the Republic of Korea is increasing. This may be due to the depletion of near and deep-sea resources (22).
References
- https://repository.library.noaa.gov/view/noaa/5681/noaa_5681_DS1.pdf
- https://juniperpublishers.com/nfsij/pdf/NFSIJ.MS.ID.555672.pdf
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/257653670
- https://www.wcrf-uk.org/sites/default/files/Meat-Fish-and-Dairy-products.pdf
- https://www.aicr.org/news/fish-and-cancer-risk-4-things-you-need-to-know/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25212318/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/281761053
- https://www.jacionline.org/article/S0091-6749(96)70104-5/fulltext#
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7521143/
- https://dash.harvard.edu/bitstream/handle/1/34375135/5551512.pdf?sequence=1
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11307883/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6049121/
- https://www.atkins.com/how-it-works/atkins-20
- https://idl-bnc-idrc.dspacedirect.org/bitstream/handle/10625/21568/116551.pdf
- https://www.dukandiet.com/low-carb-diet/4-phases
- https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2014/06/140624105235.htm
- https://www.oregonclinic.com/diets-BRAT
- https://www.osakisuisan.com/global/
- https://www.louiskemp.com/faq/
- https://online.ucpress.edu/elementa/article/doi/10.1525/elementa.386/112512/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/229734276
- http://www.fao.org/3/a-bb244e.pdf
Top nutrition facts for Crab stick

| Calories ⓘ Calories for selected serving | 95 kcal |
| Glycemic index ⓘ Gi values are taken from various scientific sources. GI values less than 55 are considered as low. Values above 70 are considered as high. | 50 (low) |
| Glycemic load | 6 (low) |
| Net Carbs ⓘ Net Carbs = Total Carbohydrates – Fiber – Sugar Alcohols | 15 grams |
| Default serving size ⓘ Serving sizes are mostly taken from FDA's Reference Amounts Customarily Consumed (RACCs) | 3 oz (85 grams) |
| Acidity (Based on PRAL) ⓘ PRAL (Potential renal acid load) is calculated using a formula. On the PRAL scale the higher the positive value, the more is the acidifying effect on the body. The lower the negative value, the higher the alkalinity of the food. 0 is neutral. | 11 (acidic) |
Crab stick calories (kcal)
| Calories for different serving sizes of crab stick | Calories | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Calories in 100 grams | 95 | |
| Calories in 3 oz | 81 | 85 g |
Crab stick Glycemic index (GI)
Crab stick Glycemic load (GL)
Mineral coverage chart
Mineral chart - relative view
Vitamin chart - relative view
Fiber content ratio for Crab stick
All nutrients for Crab stick per 100g
| Nutrient | Value | DV% | In TOP % of foods | Comparison |
| Vitamin A | 0µg | 0% | 100% | |
| Calories | 95kcal | 5% | 74% |
2 times more than Orange
|
| Protein | 7.6g | 18% | 51% |
2.7 times more than Broccoli
|
| Fats | 0.46g | 1% | 81% |
72.4 times less than Cheese
|
| Vitamin C | 0mg | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Net carbs | 15g | N/A | 38% |
3.7 times less than Chocolate
|
| Carbs | 15g | 5% | 41% |
1.9 times less than Rice
|
| Cholesterol | 20mg | 7% | 43% |
18.7 times less than Egg
|
| Vitamin D | 0µg | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Magnesium | 43mg | 10% | 24% |
3.3 times less than Almonds
|
| Calcium | 13mg | 1% | 68% |
9.6 times less than Milk
|
| Potassium | 90mg | 3% | 85% |
1.6 times less than Cucumber
|
| Iron | 0.39mg | 5% | 81% |
6.7 times less than Beef broiled
|
| Sugar | 6.3g | N/A | 46% |
1.4 times less than Coca-Cola
|
| Fiber | 0.5g | 2% | 56% |
4.8 times less than Orange
|
| Copper | 0.03mg | 4% | 88% |
4.4 times less than Shiitake
|
| Zinc | 0.33mg | 3% | 78% |
19.1 times less than Beef broiled
|
| Starch | 3.5g | 1% | 95% |
4.4 times less than Potato
|
| Phosphorus | 282mg | 40% | 18% |
1.5 times more than Chicken meat
|
| Sodium | 529mg | 23% | 19% |
1.1 times more than White bread
|
| Vitamin E | 0.17mg | 1% | 79% |
8.6 times less than Kiwi
|
| Manganese | 0.01mg | 0% | 89% | |
| Selenium | 22µg | 41% | 42% | |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.03mg | 3% | 82% |
8.9 times less than Pea raw
|
| Vitamin B2 | 0.08mg | 6% | 73% |
1.6 times less than Avocado
|
| Vitamin B3 | 0.62mg | 4% | 75% |
15.4 times less than Turkey meat
|
| Vitamin B5 | 0mg | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Vitamin B6 | 0.13mg | 10% | 59% |
1.1 times more than Oats
|
| Vitamin B12 | 0.57µg | 24% | 47% |
1.2 times less than Pork
|
| Vitamin K | 0.4µg | 0% | 82% |
254 times less than Broccoli
|
| Trans fat | 0.01g | N/A | 71% |
1861.3 times less than Margarine
|
| Folate | 0µg | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Choline | 13mg | 2% | 82% | |
| Saturated fat | 0.22g | 1% | 76% |
27.3 times less than Beef broiled
|
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.28g | N/A | 76% |
35.6 times less than Avocado
|
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.14g | N/A | 82% |
329.9 times less than Walnut
|
| Tryptophan | 0.08mg | 0% | 82% |
4.1 times less than Chicken meat
|
| Threonine | 0.29mg | 0% | 79% |
2.5 times less than Beef broiled
|
| Isoleucine | 0.23mg | 0% | 84% |
4 times less than Salmon raw
|
| Leucine | 0.61mg | 0% | 80% |
4 times less than Tuna Bluefin
|
| Lysine | 0.71mg | 0% | 74% |
1.6 times more than Tofu
|
| Methionine | 0.26mg | 0% | 73% |
2.7 times more than Quinoa
|
| Phenylalanine | 0.26mg | 0% | 84% |
2.6 times less than Egg
|
| Valine | 0.29mg | 0% | 83% |
7.1 times less than Soybean raw
|
| Histidine | 0.16mg | 0% | 82% |
4.8 times less than Turkey meat
|
| Fructose | 0.62g | 1% | 88% |
9.5 times less than Apple
|
| Caffeine | 0mg | 0% | 100% | |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0g | N/A | 100% |
N/A
|
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.03g | N/A | 38% |
52.1 times less than Salmon
|
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.01g | N/A | 98% |
1142.5 times less than Canola oil
|
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0g | N/A | 52% |
170 times less than Salmon
|
| Omega-3 - Eicosatrienoic acid | 0g | N/A | 100% | |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0g | N/A | 100% | |
| Omega-6 - Dihomo-gamma-linoleic acid | 0g | N/A | 100% | |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0g | N/A | 100% | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 0.09g | N/A | 98% |
138.4 times less than Almonds
|
Check out similar food or compare with current
NUTRITION FACTS LABEL
Serving Size ______________
Health checks
Crab stick nutrition infographic
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.



