Heart of Palm Nutrition & Calories - Complete data of all nutrients

Summary
Briefly, heart of palm is a low-calorie food with relatively high carbs (4.62g), low protein (2.52g), and fats (0.62g). Heart of palm is a great vitamin B9, copper, manganese, and iron source.
Heart of palm is a source of health-promoting dietary fiber and polyphenols with anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Introduction
Heart of palm is considered a vegetable. It is the stem cell of certain young palm trees. These trees include coconut palm, açaí palm, peach palm, and juçara palm. Heart of palm is also known as palm heart, palmito, or palm cabbage.
Palmito is a salad ingredient and substitute for gluten-free pasta.
This article provides information about heart of palm nutrition and everything you need to know about the food.
Nutrition
The infographics below are presented for 100g servings of the canned heart of palm, while one average serving size per person is considered to be one piece, weighing 33g, or one cup, equal to 146g.
Please note that the serving size listed is a typical amount and not a recommendation for your consumption.
Nutrient Density
Heart of palm is not very nutrient-dense as it contains 90.2% water and only 9.8% nutrients.
The majority of these nutrients are made up of carbohydrates - 4.62%.
Macronutrients chart
Calories
Heart of palm is a low-calorie food, providing only 28 calories per 100 grams.
Compared to all foods in our database, canned heart of palm is in the top 94% of foods low in calories.
Carbohydrates
Most of the heart of palm nutrients are carbs.
One hundred grams of heart of palm contains 4.62g of carbs, covering 2% of the daily need.
Net Carbs
48% (2.22g) of heart of palm carbs are net carbs, while the remaining 52% (2.4g) is dietary fiber.
Dietary Fiber
One hundred grams of heart of palm contains only 2.4g of dietary fiber, which is considered low.
2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend consuming 28g of dietary fiber daily for women and 34g for men (1).
Fiber content ratio for Heart of palm
Protein
Heart of palm is low in protein but contains essential amino acids. A 100-gram serving of heart of palm only covers 6% of daily protein needs, providing 2.52g of protein.
Fats
Hearts of palm is a food low in fat content, with only 0.62g of fat per 100g serving.
Fat type information
Vitamins
Heart of palm is not particularly rich in vitamins.
Heart of palm is a food that is high in vitamin B9, also known as folate. It is in the top 38% of foods that are rich in vitamin B9. Consuming 100g of heart of palm can provide approximately 10% of the daily value (DV) required for vitamin B9.
It is important for pregnant women to consume vitamin B9 to reduce the risk of neural tube defects in the fetus (2).
Heart of palm can also be a good source of vitamin C, falling in the top 26% of foods as a source.
Heart of palm contains insignificant levels of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, and B6.
Vitamin coverage chart
Minerals
Heart of palm is a great source of copper, manganese, and iron. One hundred grams of heart of palm covers 15% of the daily copper need, 61% of the daily manganese need, and 39% of the daily iron need.
Heart of palm falls in the top 39% of foods as a source of iron, being 1.2 times higher in this mineral than beef.
Heart of palm contains calcium, potassium, magnesium, zinc, phosphorus, and selenium at insignificant levels.
Consuming 100g of heart of palm can provide approximately 19% of the daily value (DV) required for sodium.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans suggest that one should consume no more than 2.3 grams of sodium in a day.
Mineral coverage chart
Ash
Technically, the ash content of foods is what’s left after heating it at very high temperatures, leaving only minerals and inorganic compounds. Thus, the ash content gives us an idea of the overall mineral content of the food.
The ash content of raw and canned heart of palm is very similar to each other - approximately 2g per 100g serving.
Phytochemicals
Polyphenols
Heart of palm is a source of polyphenols called chlorogenic acid. Chlorogenic acid is also the ester of caffeic acid and quinic acid, with potential antioxidant and anticancer effects and immune-strengthening abilities (3, 4).
Another health-promoting polyphenol found in heart of palm is protocatechuic acid. It has been shown to have anti-inflammatory, antihyperglycemic, and neuroprotective effects (5, 6).
Flavonoid myricetin has been found in heart of palm (5). Like other polyphenols, it has shown antioxidant, anticancer, antidiabetic, and anti-inflammatory effects (7).
Acidity
The pH value of heart of palm falls from 5 to 7, making it from acidic to neutral (8).
Potential Renal Acid Load or PRAL value is another way of looking at the acidity. The PRAL value measures how much acid or base is produced in the organism from the given food. The PRAL value of heart of palm is -31.9, making it alkaline or base-producing.
Comparison to Similar Foods
“Heart of palm vs. Artichoke” Artichoke is much lower in fats, richer in proteins, and contains about 2 times more dietary fiber. Artichoke is a better source of folate and vitamin K, phosphorus, and magnesium; meanwhile, heart of palm is a better source of copper, manganese, and iron. Artichoke contains 4.5 times less sodium.
“Heart of palm vs. Asparagus” With about equal amounts of dietary fiber and protein, asparagus has five times less fat than heart of palm; as a result, it has fewer calories. Heart of palm has more iron, phosphorus, and zinc than asparagus, while asparagus has higher levels of vitamins K, A, E, B1, and folate.
References
- Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020-2025
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29777755/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24499380/
- Chlorogenic acid | C16H18O9 - PubChem
- Palm Hearts: Overlooked Healthy Vegetables
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22519395/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4772053/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6443711/
Top nutrition facts for Heart of palm

| Calories ⓘ Calories for selected serving | 115 kcal |
| Glycemic index ⓘ Gi values are taken from various scientific sources. GI values less than 55 are considered as low. Values above 70 are considered as high. | 32 (low) |
| Net Carbs ⓘ Net Carbs = Total Carbohydrates – Fiber – Sugar Alcohols | 24 grams |
| Acidity (Based on PRAL) ⓘ PRAL (Potential renal acid load) is calculated using a formula. On the PRAL scale the higher the positive value, the more is the acidifying effect on the body. The lower the negative value, the higher the alkalinity of the food. 0 is neutral. | -31.9 (alkaline) |
Heart of palm calories (kcal)
| Calories for different serving sizes of heart of palm | Calories | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Calories in 100 grams | 115 |
Heart of palm Glycemic index (GI)
Mineral chart - relative view
Vitamin chart - relative view
All nutrients for Heart of palm per 100g
| Nutrient | Value | DV% | In TOP % of foods | Comparison |
| Vitamin A | 3µg | 0% | 62% | |
| Calories | 115kcal | 6% | 70% |
2.4 times more than Orange
|
| Protein | 2.7g | 6% | 73% |
Equal to Broccoli
|
| Fats | 0.2g | 0% | 88% |
166.6 times less than Cheese
|
| Vitamin C | 8mg | 9% | 26% |
6.6 times less than Lemon
|
| Net carbs | 24g | N/A | 28% |
2.2 times less than Chocolate
|
| Carbs | 26g | 9% | 29% |
1.1 times less than Rice
|
| Cholesterol | 0mg | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Vitamin D | 0µg | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Magnesium | 10mg | 2% | 84% |
14 times less than Almonds
|
| Calcium | 18mg | 2% | 57% |
6.9 times less than Milk
|
| Potassium | 1806mg | 53% | 6% |
12.3 times more than Cucumber
|
| Iron | 1.7mg | 21% | 44% |
1.5 times less than Beef broiled
|
| Sugar | 17g | N/A | 34% |
1.9 times more than Coca-Cola
|
| Fiber | 1.5g | 6% | 43% |
1.6 times less than Orange
|
| Copper | 0.64mg | 72% | 18% |
4.5 times more than Shiitake
|
| Zinc | 3.7mg | 34% | 25% |
1.7 times less than Beef broiled
|
| Phosphorus | 140mg | 20% | 54% |
1.3 times less than Chicken meat
|
| Sodium | 14mg | 1% | 83% |
35 times less than White bread
|
| Vitamin E | 0.5mg | 3% | 57% |
2.9 times less than Kiwi
|
| Selenium | 0.7µg | 1% | 86% | |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.05mg | 4% | 72% |
5.3 times less than Pea raw
|
| Vitamin B2 | 0.18mg | 14% | 51% |
1.4 times more than Avocado
|
| Vitamin B3 | 0.9mg | 6% | 70% |
10.6 times less than Turkey meat
|
| Vitamin B6 | 0.81mg | 62% | 15% |
6.8 times more than Oats
|
| Vitamin B12 | 0µg | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Vitamin K | 0µg | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Folate | 24µg | 6% | 45% |
2.5 times less than Brussels sprouts
|
| Trans fat | 0g | N/A | 100% |
N/A
|
| Choline | 0mg | 0% | 100% | |
| Saturated fat | 0.05g | 0% | 86% |
128.2 times less than Beef broiled
|
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.01g | N/A | 94% |
1959.8 times less than Avocado
|
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.09g | N/A | 86% |
530 times less than Walnut
|
| Caffeine | 0mg | 0% | 100% | |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0g | N/A | 100% |
N/A
|
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0g | N/A | 100% |
N/A
|
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0g | N/A | 100% |
N/A
|
Check out similar food or compare with current
NUTRITION FACTS LABEL
Serving Size ______________
Health checks
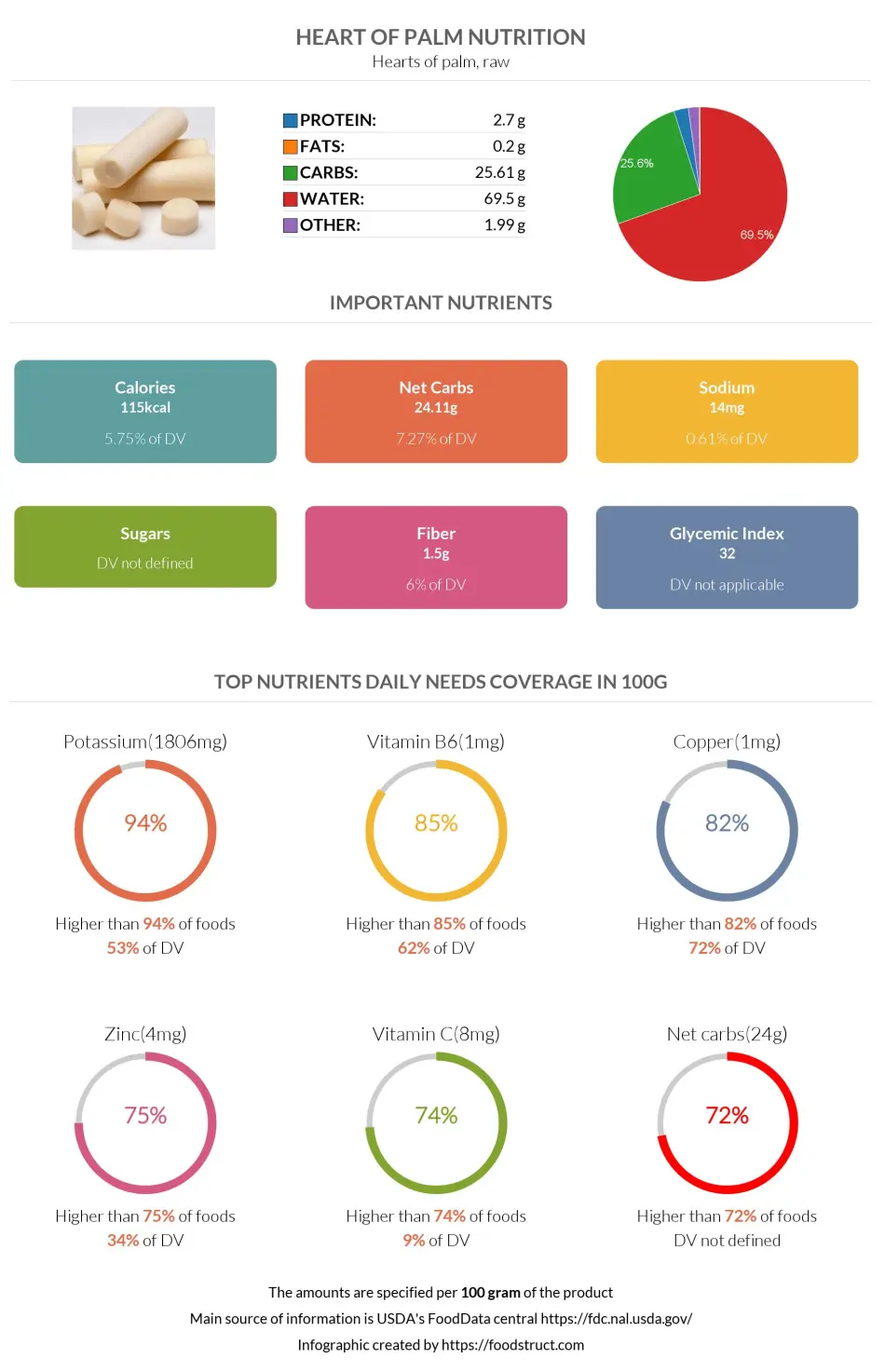
Heart of palm nutrition infographic
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.



