Chicken meat vs. Rabbit Meat — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Rabbit meat is higher in protein while being lower in calories and fats compared to chicken meat. Rabbit meat is also nearly 22 times richer in vitamin B12 and a better source of most minerals, while chicken is richer in most other B-group vitamins.
It should be noted that skinless chicken meat is lower in fats and calories than chicken with skin.
Chicken meat is cheaper and more available.
Introduction
In this article, we are going to discuss the difference between rabbit meat and chicken meat according to their general differences, nutritional content, weight loss and diet, and health impacts.
General Differences
The general differences between rabbit meat and chicken meat are based on numerous things like price and distribution, taste, culinary world usage, and classification.
Growing Conditions
The consumption of rabbit meat is not as common as other types of meat. Rabbit meat is often considered game meat, meaning that it’s a hunt. However, nowadays, they are mostly raised on farms as livestock. Farm-raised rabbits are raised in ways that are optimal for consumption when it comes to their nutritional content since they are fed highly nutritious foods and are away from danger, such as prey which reduces stress on them and keeps their meat more tender than the wild types.
Chicken meat is common because it is easy to raise chicken without requiring much space. The lifespan of a chicken is between 8-12 weeks, depending on what type of food the chicken will be used for.
Price and Distribution
Chicken meat is cheaper than rabbit meat and is more available worldwide. Thus, the production and consumption of chicken is also higher than that of turkey.
Taste
Although these two different animals belong to two different families, they have somewhat similar tastes. The difference is in the intensity of the taste and texture. Rabbit meat is dryer and has a gamier, stronger taste, while the taste of chicken meat is milder and slightly umami.
Culinary Use
Chicken meat is one of the most commonly used meats all around the world. Chicken meat can be grilled, boiled, added to stews, barbecued, and fried.
Rabbit meat also has versatility in the culinary world. In fact, the two types of meat are nearly interchangeable in the kitchen. Rabbit is commonly roasted whole or in pieces, similar to chicken. It is also excellent for grilling, stews, braises, etc.
Classification
Chicken meat is the most commonly consumed poultry in the world. Poultry is white meat due to a low content of myoglobin - an iron-containing protein that gives red meat its dark color.
Rabbit meat is also qualified as poultry and white meat; however, it is darker, as it has a higher content of myoglobin and iron. Still, it is used as white meat in the culinary world.
Nutritional Content
In this section, we will compare the nutritional content of 100g servings of stewed wild-caught rabbit meat and roasted chicken meat with the skin on.
Rabbit and chicken meat both consist of nearly 60% water and 40% nutrients. Of these nutrients, rabbit meat is considerably higher in protein, while chicken contains more fats.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+287.5%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+21%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+∞%
Calories
Chicken meat contains 1.4 times more calories than rabbit meat. However, this high value is mostly due to the chicken skin; the same 100g serving of roasted skinless chicken provides 49 fewer calories than chicken with skin on (1).
A 100g serving of rabbit meat provides 173 calories, while the same serving of chicken with skin and skinless chicken contains 239 and 190 calories, respectively.
Protein
Rabbit meat and chicken meat are both very high in protein and have rich essential amino acid profiles. However, rabbit meat is 1.2 times richer in proteins compared to chicken meat.
A 100g serving of rabbit meat consists of 33% protein, while this number for chicken meat is 27%.
As expected, rabbit is richer in all of the essential amino acids.
Fats
One of the most important characteristics of rabbit meat is it is a lean meat, low in fat. It contains nearly 4 times less fat than chicken. A 100g serving of stewed rabbit meat has 3.5g of fats, while roasted chicken with skin contains 13.6g.
However, it is important to note that chicken skin contains a high content of fats; thus, skinless chicken is considerably lower in this nutrient. A 100g serving of skinless chicken provides 7.4g of fat.
The fat content found in chicken and rabbit meat is similar, consisting of 25% saturated fats and 75% of unsaturated fats.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+462.1%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+336.8%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-72.3%
The high-protein/low-fat relationship in rabbit meat will be discussed in the health impact section.
Cholesterol
Despite the lower fat content, rabbit meat contains 35mg more cholesterol per 100g serving than chicken meat.
Carbohydrates
Like other types of meat, chicken meat and rabbit meat have 0g of carbs; their calories are based on fats and proteins. This information can be important for people on certain diets.
Minerals
They both have rich mineral profiles; however, rabbit meat is richer in almost all minerals compared to chicken meat. Rabbit meat is 4 times higher in iron and 3 times higher in copper. It is also a better source of phosphorus, zinc, magnesium, potassium, and calcium.
Rabbit meat is also lower in sodium.
It is important to note that chicken contains most of these minerals in high amounts, just comparatively not as high as rabbit meat. Chicken is richer in selenium.
Below, we can see the mineral coverage chart comparing both of these foods.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+∞%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+57.2%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+34.8%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+20%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+53.8%
Contains
more
IronIron
+284.9%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+166.7%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+22.7%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+31.9%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-45.1%
Vitamins
When it comes to comparing their vitamin profiles, chicken has a more versatile and richer vitamin profile. Chicken is richer in vitamins B1, B2, B3, and B6. It is also higher in vitamins A and K.
However, rabbit meat provides almost 22 times more vitamin B12 while also being richer in vitamins E and B9 or folate.
In the infographics below, you can see the vitamin chart comparisons.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+215%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+140%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+32.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+17.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+60%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+51.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+2070%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+60%
Glycemic index
Rabbit and chicken meat have glycemic index values equal to 0.
Insulin Index
Foods' insulin index value shows how much its intake raises insulin blood levels within the first two hours after eating.
While the insulin index of rabbit meat has not yet been calculated, chicken has a low insulin index of 23 (2).
Diet and Weight Loss
Chicken meat and rabbit meat can fit well in some weight loss diets, although it is important to mention the cooking method of both these foods has to be taken into consideration. For example, boiled chicken and rabbit meat is a healthier alternative to deep-fried.
In addition to that, it is important to mention that consuming chicken without its skin significantly changes the nutrition of chicken. Skinless chicken is considerably lower in calories and fats.
Keto
Rabbit meat and chicken meat are ideal in the keto diet. They contain 0 carbs and have glycemic index values of 0. They are also excellent sources of proteins.
Bodybuilding
Both these foods are perfect for bodybuilding. Chicken breast is one of the main foods for bodybuilders for their high protein content, easy preparation, and low price.
Rabbit meat is also a good option for those trying to gain muscle; however, relying on rabbit meat as the only protein source for a long duration is not advised. Although protein poisoning is extremely uncommon, it is crucial to remember that the body needs a balance of all nutrients, including fats and carbohydrates, when following "high protein diets."
Vegan, Vegeterian, and Pescetarian
Rabbit and chicken meat naturally cannot be consumed in vegan, vegetarian, or pescatarian diets.
Health Impacts
Cardiovascular Health
Rabbit meat and chicken meat are white meats. White meat has been researched to be a good alternative to red meat when it comes to its overall effect on cardiovascular health (3). The substitution of a daily serving of red meat with one daily serving of poultry, such as rabbit and chicken meat, can reduce cardiovascular risk by 19% (4).
The decrease in sodium, heme iron, and saturated fat intake may account for these variations between red meat and poultry. Between chicken and rabbit, rabbit meat is significantly lower in fats and sodium but higher in heme iron.
Farm-raised rabbits can be raised as functional foods - fed a balanced diet rich in polyunsaturated fats, which can help decrease the risk of cardiovascular diseases (5).
Chicken meat extract has been proven to have anti-hypertensive and anti-atherosclerotic properties in experimental animals (6).
In summary, both rabbit meat and chicken meat can be part of a heart-healthy diet when consumed in moderation and prepared in a healthy manner. Rabbit meat may have a slight edge in terms of leanness and omega-3 fatty acid content, but both types of meat provide valuable nutrients and protein. Incorporating a variety of lean protein sources, including rabbit and chicken, along with plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, can help reduce the risk of CVD and promote overall heart health.
Diabetes and Metabolism
Gout
Avoiding meat is one of the main dietary restrictions for people with gout to avoid aggravation of the disease. This is because meats are high in purine, and the metabolite of purine generates uric acid causing gout attacks.
Chicken meat has been researched to contain higher levels of purines compared to rabbit meat, pork, beef, and mutton (7).
Diabetes and Obesity
Rabbit meat and chicken meat have 0g of carbs and glycemic index values of 0. Carbohydrate-restricted diets with low glycemic index values have been researched to prevent the development of type 2 diabetes (8). Thus, rabbit and chicken meat can be eaten for diets modified and catered for diabetic patients to control blood glucose and insulin levels.
The benefits of using chicken meat as a source of protein in the dietary management of diabetic individuals have been researched and reported (9).
The conjugate linoleic acid present in rabbit meat has been studied to have anti-obesity qualities that can ameliorate diabetes (10).
Protein Poisoning
Protein poisoning is an acute form of malnutrition that happens when the body consumes too much protein and insufficient amounts of fats and carbs, as the name implies. This phenomenon is also known as "rabbit malaise" and "rabbit starvation."
The symptoms include nausea, headaches, fatigue, diarrhea, and low blood pressure.
While this is a rare occurrence, it is important to remember about balanced nutrition when discussing the health benefits of certain foods.
Unlike rabbit meat, chicken, especially with chicken skin, offers more fats.
Cancer
The linoleic acid present in rabbit meat has anti-carcinogenic properties (10).
White meat intake, including rabbit and chicken meat, has been associated with a decreased risk of gastric cancer risk (11).
Unlike red meat consumption, chicken meat has been only mildly associated with the development of colorectal cancer (12).
Tularemia
Tularemia is a zoonotic infection caused by bacteria (Francisella tularensis) that is frequently associated with rabbit hunters and rabbit meat consumers. Infection can be due to contact with infected tissue during skinning of rabbits or by ingestion of infected meat. Transmission can also occur after a bite from a tick residing on the animal’s skin (13).
References
- https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171054/nutrients
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/26770180
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33672599/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7924043/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3257606/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11432770/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22611945/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19239633/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19966489/
- http://cuniculture.info/Docs/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6520977/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15342453/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430905/
Infographic
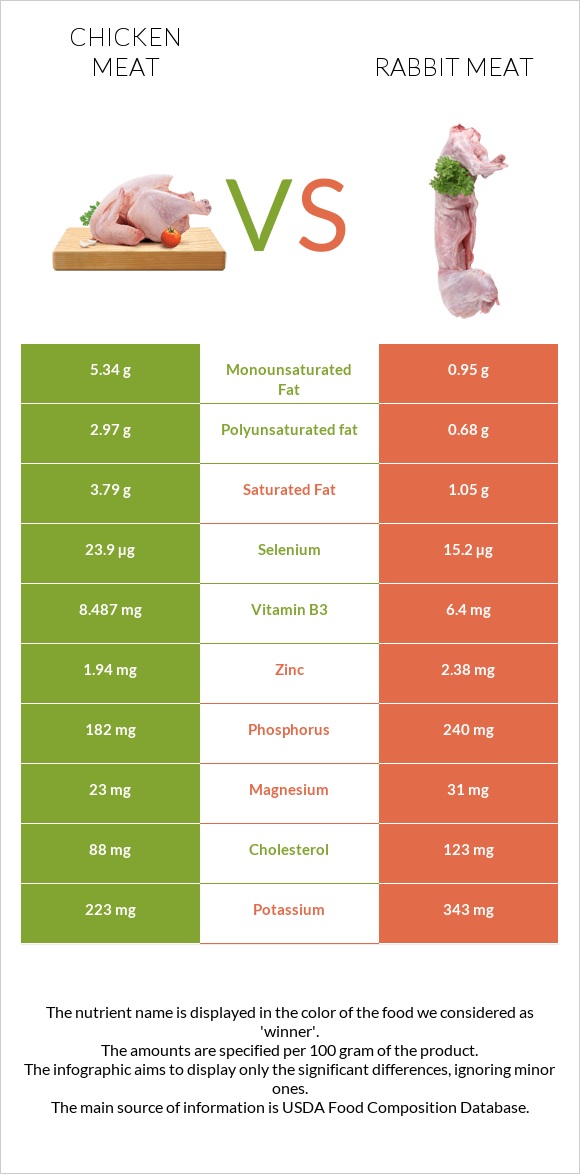
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.3µg | 6.51µg | 259% |
| Iron | 1.26mg | 4.85mg | 45% |
| Vitamin B5 | 1.03mg | 21% | |
| Fats | 13.6g | 3.51g | 16% |
| Selenium | 23.9µg | 15.2µg | 16% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 2.97g | 0.68g | 15% |
| Vitamin B3 | 8.487mg | 6.4mg | 13% |
| Cholesterol | 88mg | 123mg | 12% |
| Copper | 0.066mg | 0.176mg | 12% |
| Choline | 65.9mg | 129.9mg | 12% |
| Saturated fat | 3.79g | 1.05g | 12% |
| Protein | 27.3g | 33.02g | 11% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 5.34g | 0.95g | 11% |
| Phosphorus | 182mg | 240mg | 8% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.168mg | 0.07mg | 8% |
| Vitamin A | 48µg | 0µg | 5% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.4mg | 0.34mg | 5% |
| Potassium | 223mg | 343mg | 4% |
| Zinc | 1.94mg | 2.38mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.063mg | 0.02mg | 4% |
| Calories | 239kcal | 173kcal | 3% |
| Magnesium | 23mg | 31mg | 2% |
| Sodium | 82mg | 45mg | 2% |
| Vitamin E | 0.27mg | 0.41mg | 1% |
| Manganese | 0.02mg | 1% | |
| Vitamin K | 2.4µg | 1.5µg | 1% |
| Folate | 5µg | 8µg | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 2 IU | 0 IU | 0% |
| Calcium | 15mg | 18mg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.305mg | 0.436mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 1.128mg | 1.477mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 1.362mg | 1.567mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.986mg | 2.573mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 2.223mg | 2.891mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.726mg | 0.826mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 1.061mg | 1.355mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.325mg | 1.678mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.802mg | 0.926mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.01g | 0g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.04g | 0g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.02g | 0g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Chicken meat - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171450/nutrients
- Rabbit Meat - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174348/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.




