Crab meat vs. Salmon — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Crabmeat is richer in minerals and has lower saturated fats and cholesterol. The level of zinc in crab meat is 17 times higher than in salmon. On the other hand, salmon contains less sodium and has a higher amount of Vitamin B complex.
Introduction
In general, fish and crabs are the most popular marine food consumed by humans. In this article, we will discuss the main differences in the nutrition of crab meat and salmon. Salmons are long fishes; they can change their coloring from silver to pink. Crabs typically have a very short tail. They can live in fresh and land water.
Varieties
Salmons are a group of fish that belong to the family of Salmonidae. This family includes chars and whitefishes. There are many different types of salmon, but the most common species are Atlantic salmon, Chum salmon, and Masu salmon. Crabs belong to the Brachyura family, which contains 93 different families. The most common crabs to eat are Soft-Shell crab, Maryland Blue crab, and Dungeness crab [1].
Uses
Salmons and crabmeat are often interchangeably used in the kitchen. They are delicious and cooked. Both have entirely different tastes and are used in different dishes. In Charlotte, Island salmon is one of the significant sources of food. They are used in Salmon Pasta, Sesame-Crusted Salmon, and Salmon Tacos. Some species of crabs can be eaten whole, some with claws or legs [2].
Nutrition
Salmons and crab meat are rich in healthy compounds and macronutrients. However, to understand the difference between them, we created the nutritional infographic. Find it below.
Macronutrients and Glycemic Index
In general, the protein level of salmon and crab meat is equal. Besides, both contain no sugar or fiber and have the same glycemic index - 0. Crab meat contains more cholesterol.
Calories
Salmons contain more calories than crab meat. The calories level of salmon is almost two times higher. It contains 206 calories per 100 g, while crab meat contains 87 calories per 100 g [3].
Minerals
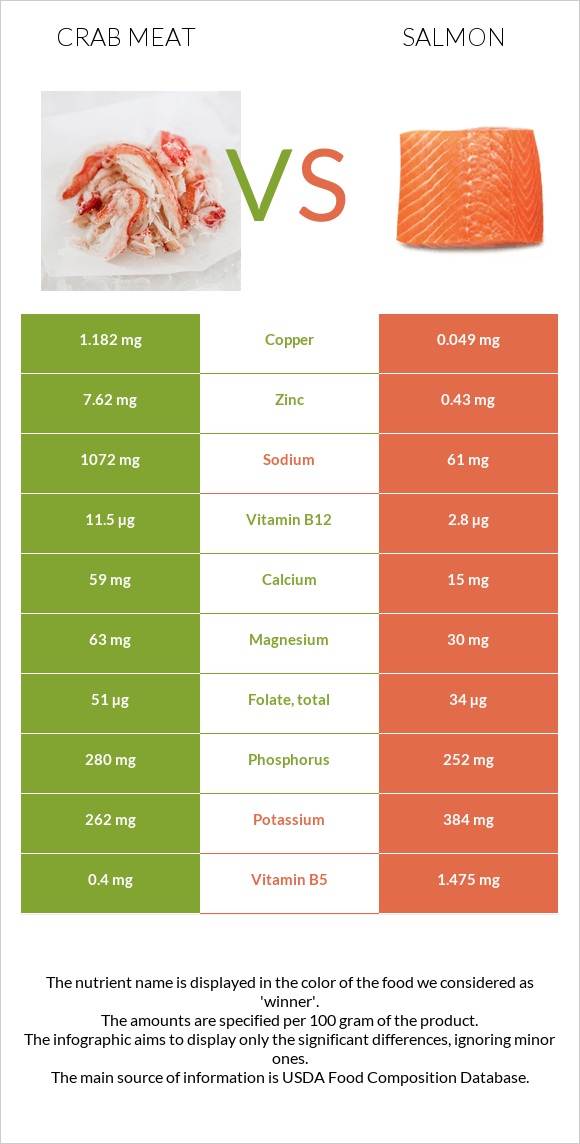
Overall, crab meat is richer in minerals than salmon. It contains more magnesium, copper, calcium, and iron. The level of zinc in crab meat is 17 times higher than in salmon. On the other hand, salmon contains more potassium and less sodium than crab meat. Both have an equal level of phosphorus [4] [5].
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+110%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+293.3%
Contains
more
IronIron
+123.5%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+2312.2%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+1672.1%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+150%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+46.6%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-94.3%
Vitamins
Salmon is higher in vitamins than crab meat. It is richer in Vitamin A, Vitamin B1, Vitamin B2, Vitamin B3, B5, and B6. Vitamin B6 in salmon is two times higher than in crab meat.
However, crab meat contains more Vitamin B12, C, and Folate. Vitamin B12 is three times higher in crab meat than in salmon; besides, just 2-3 ounces of crab meat contains an adult's daily B12 requirement [4] [5].
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+105.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+310.7%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+50%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+666.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+541.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+145.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+500.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+268.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+259.4%
HEALTH IMPACT
Cardiovascular Health
According to one study, omega-3 fatty acids may lower triglycerides, and blood pressure and reduce the risk of developing heart disease. In this case, salmon is a good source of omega-3 fatty acids. They have more alpha-linoleic acid (ALA) and DHA than crabmeat.
Salmon contains bioactive PLs with antithrombotic cardioprotective activities [6].
One study showed that 0.45-4.5 grams daily omega-3 fatty acids might improve arterial function [7].
Antioxidative Stress
Salmon is red because of astaxanthin, which belongs to the carotenoid family. That family has a strong antioxidant effect. Astaxanthin has many health benefits, such as a lower risk of heart disease, and a lower cholesterol level in the body. Moreover, according to one study, astaxanthin may work with omega-3 fatty and protect the brain and nervous system from inflammation. Besides, salmons contain 0.4–3.8 mg of astaxanthin per 100 g, making them a good source of this antioxidant [8] [9].
Bone Health
We all know that calcium is an essential mineral for bone health. The second mineral, which is also essential for bone health, is phosphors. In this case, crabmeat is an excellent source of both minerals. As a result, eating crab meat can lower the risk of developing osteoporosis, especially getting older [10].
Diabetes
Including fish oil in your diet may improve metabolic features associated with type 2 diabetes. According to studies, a high-fat diet supplemented with fish oil may reduce the risk of impaired glucose tolerance and hepatic steatosis. Besides, salmons are an excellent source of magnesium, which deficiency has been associated with chronic diseases such as diabetes mellitus [11].
Diet
Crabmeat is low in calories and high in protein, making it a great choice if you are on a diet. Cooked crab meat contains 17 grams of protein, 40% of recommended daily intake for adults. Protein can help you feel full for longer and may reduce the total number of calories you eat. On the other hand, salmons and crabs are both excellent sources of omega-3 fats. According to studies, omega-3 fats may promote weight loss and decrease belly fat in overweight individuals [12].
Other health benefits
Salmons are rich in B vitamins, especially Vitamin B1 (thiamin). Studies show that the human body needs B vitamins to provide energy for properly functioning your brain, nerves, muscles, skin, and every cell in your body. Vitamin B1 also helps prevent heart, nerves, and digestive system diseases. Salmons are also a good source of Vitamin B3 (niacin), which may help to lower LDL "bad" cholesterol and prevent heart disease [13] [14].
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 has an essential role in the human body. It may boost your energy, support the normal function of your nerve cells and improve your memory. Besides, Vitamin B12 may prevent significant congenital disabilities and support bone health. The daily intake of Vitamin B12 for adults is 2.4 micrograms. The amount of Vitamin B12 in salmon is about six micrograms per 100g [15].
Side Effects
Allergy
According to studies, 0.4% of adults in the USA have an allergy to shellfish. Protein parvalbumin in the muscle of most fish can cause an allergy, which symptoms include hives, skin ras, headaches, diarrhea, and breathing difficulty. Salmons and crabmeat contain omega-3 fatty acids, which may have potential side effects, including a fishy aftertaste and gastrointestinal disturbances. However, it is dose-dependent and should be chosen carefully [16].
Sodium
Sodium is an essential mineral that is needed by the body. However, it is better to limit sodium intake to less than 2,3 mg per day. Too much salt may cause swollen hands and feet or a swollen face. Crabmeat contains a high amount of sodium, so adjust your daily intake [17].
References
- http://etd.auburn.edu/handle/10415/6069
- https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s13280-018-1060-9.pdf
- https://udspace.udel.edu/bitstream/handle/19716/189/SeafoodIsGood.pdf?sequence=1
- https://sci-hub.se/10.1093/jn/62.2.225
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1365-2621.1981.tb04890.x
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6357043/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22317966/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24955642/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24402174/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0009912012002391
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0899900713001044
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17502874/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27488863/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18375237/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15619681/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27613460/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2589537021000304
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B12 | 11.5µg | 2.8µg | 363% |
| Copper | 1.182mg | 0.049mg | 126% |
| Vitamin D | 526 IU | 66% | |
| Vitamin D | 13.1µg | 66% | |
| Zinc | 7.62mg | 0.43mg | 65% |
| Sodium | 1072mg | 61mg | 44% |
| Vitamin B3 | 1.34mg | 8.045mg | 42% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.18mg | 0.647mg | 36% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.536g | 4.553g | 27% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.053mg | 0.34mg | 24% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.4mg | 1.475mg | 22% |
| Fats | 1.54g | 12.35g | 17% |
| Choline | 90.5mg | 16% | |
| Saturated fat | 0.133g | 2.397g | 10% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.185g | 4.181g | 10% |
| Magnesium | 63mg | 30mg | 8% |
| Vitamin E | 1.14mg | 8% | |
| Vitamin A | 9µg | 69µg | 7% |
| Protein | 19.35g | 22.1g | 6% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.055mg | 0.135mg | 6% |
| Calories | 97kcal | 206kcal | 5% |
| Iron | 0.76mg | 0.34mg | 5% |
| Vitamin C | 7.6mg | 3.7mg | 4% |
| Calcium | 59mg | 15mg | 4% |
| Potassium | 262mg | 384mg | 4% |
| Phosphorus | 280mg | 252mg | 4% |
| Folate | 51µg | 34µg | 4% |
| Cholesterol | 53mg | 63mg | 3% |
| Selenium | 40µg | 41.4µg | 3% |
| Manganese | 0.04mg | 0.016mg | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 0.1µg | 0% | |
| Tryptophan | 0.269mg | 0.248mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.783mg | 0.969mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.938mg | 1.018mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.536mg | 1.796mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 1.684mg | 2.03mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.545mg | 0.654mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.817mg | 0.863mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.91mg | 1.139mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.393mg | 0.651mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.295g | 0.69g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.118g | 1.457g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.031g | 0.17g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more WaterWater | +19.8% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +95% |
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +14.2% |
| Contains more FatsFats | +701.9% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -94.5% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +2160% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +749.4% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Crab meat - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174202/nutrients
- Salmon - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/175168/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






