Cream of Wheat vs. Cream of Rice — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Cream of Wheat is slightly higher in calories, proteins, dietary fiber, net carbs, B complex vitamins, and most minerals.
A cup of Cream of Wheat and Cream of Rice contain 12mg and 9.66g of iron, respectively.
According to the Cream of Wheat data source, their products are enriched with vitamin D and calcium and may cover 20-30% of the daily need.
The health effects of cereals are associated with the presence of several vitamins and minerals, ultra-processing, and gluten proteins.
Introduction
Cream of Wheat and Cream of Rice are breakfast cereals produced by the Cream of Wheat company. The company has many flavored cereals, such as Cinnabon, banana, mixed berry, etc.
This article will look into the nutrition and health impact of instant Cream of Wheat and Cream of Rice.
Nutrition
This article compares 100g of Cream of Wheat (without salt) and Cream of Rice (with salt), both cooked with water.
The nutritional values somewhat differ comparing the USDA and Cream of Wheat data sources (1, 2); this article primarily compares the nutritional values provided by the USDA’s data source.
Macronutrients and Calories
Cream of Wheat and Cream of Rice are not nutrient-dense; however, Cream of Wheat is slightly higher in proteins, dietary fiber, and net carbs.
In 100g of Cream of Wheat and Cream of Rice, the water content is approximately 84.5% and 87.5%, respectively.
The cereals have a serving size of one cup, which equals ~242g.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+104.4%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+140%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+13.7%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+∞%
Calories
A 100g of Cream of Wheat provides 62 calories, whereas Cream of Rice provides 52.
One serving of Cream of Wheat and Cream of Rice provide 149 and 127 calories, respectively.
Protein
Both cereals are low in proteins.
A cup of Cream of Wheat contains 4.43g of proteins, whereas a Cream of Rice contains 2.2g.
Fats
Cream of Wheat and Cream of Rice are also very low in fats, containing less than 1g per serving.
Carbohydrates
Carbs are the predominant energy source in cereals.
A 100g of Cream of Wheat contains 13.1g of total carbs, 0.6g of which is dietary fiber and 11.5g are net carbs.
A 100g of Cream of Rice contains 11.5g of total carbs, 0.1g of which is dietary fiber and 11.4g are net carbs.
One cup of Cream of Wheat contains 31.6g of total carbs and 1.45g of dietary fiber, whereas Cream of Rice contains 28.1g of total carbs and 0.244g of dietary fiber.
Vitamins
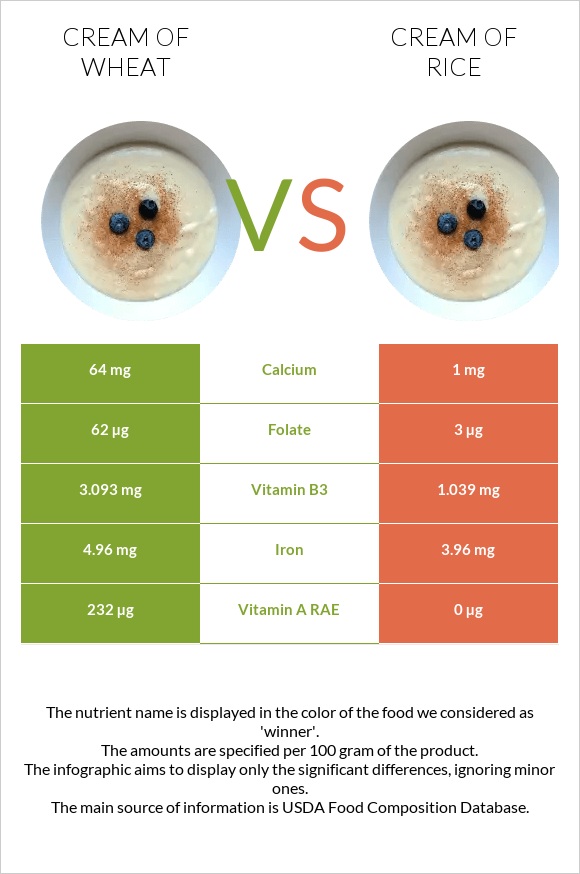
According to the USDA’s data source, Cream of Wheat is significantly richer in all B complex vitamins and vitamin A than Cream of Rice.
Nonetheless, according to the Cream of Wheat data source, they contain similar amounts of all vitamins and are enriched with vitamin D.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+226.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+1066.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+197.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+1044.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+1966.7%
Minerals
Cream of Wheat and Cream of Rice are not rich in most minerals; nonetheless, they’re great iron sources. Cream of Wheat is comparably higher in most minerals, but the difference is insignificant.
A 100g of Cream of Wheat and Cream of Rice contain 4.96mg and 3.96mg of iron, respectively.
One cup of Cream of Wheat and Cream of Rice contain 12mg and 9.66g of iron, respectively. The recommended daily iron intake is 8mg for men and 18mg for women aged 15-50 (3).
According to the Cream of Wheat data source, their products are enriched with calcium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+100%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+6300%
Contains
more
IronIron
+25.3%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+26.5%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-41%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+16.7%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+∞%
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index (GI) value of Cream of Wheat is 67, considered medium, whereas the GI value of instant Cream of Wheat is 75, considered high.
The glycemic index of Cream of Rice is yet to be calculated.
Related articles:
Cream of Wheat and Diabetes - Is It Good For Diabetics
Acidity
Cooked Cream of Wheat is calculated to have a pH value from 6.06 to 6.16. There is no calculated pH value for Cream of Rice.
The PRAL value shows how much acid or base is produced by the organism from the consumed food. The PRAL value of Cream of Wheat is -1.7, making it base-producing, whereas the PRAL value of Cream of Rice is 4, making it acid-producing.
Diets
Cream of Wheat and Cream of Rice can be consumed during low-fat and low-calorie diets. Cream of Wheat can be consumed during high-fiber diets as well.
These cereals are not included in the Mediterranean and low-carb diets such as keto or Atkins.
The Cream of Wheat products may be consumed during the gastroparesis liquid diet as well.
Related article: Gastroparesis Liquid Diet: Food List & Guide
Health Impact
Although Cream of Wheat and Cream of Rice are rich in iron, calcium, vitamin D, and B-complex vitamins, they are also ultra-processed, which may adversely affect health.
Iron on Health
Cream of Wheat and Cream of Rice are great iron sources; they may prevent microcytic anemia and restore the iron supply when needed.
Microcytic anemia is caused by iron deficiency, which may be due to physiologically increased iron requirement (children, adolescents, pregnant people), several diets, chronic blood loss, pathological absorption, and chronic inflammatory diseases (4, 5).
Keeping iron levels in the normal range is important, as iron excess can cause tissue injury, cell death, and oxidative stress (6).
B-complex Vitamins on Health
Cream of Wheat company’s products are a source of B-complex vitamins: B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, and folate.
B-complex vitamins are needed for energy metabolism, DNA synthesis and repair, methylation, healthy immune and nervous systems, and synthesis of numerous neurochemicals and signaling molecules (7, 8).
Calcium and Vitamin D on Health
According to the Cream of Wheat data source, their products are enriched with vitamin D and calcium. One serving of each cereal may cover 20-30% of the daily vitamin D and calcium need.
Calcium and vitamin D are essential factors for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is a bone disorder causing progressive bone density and mass loss, which results in thin, weakened, fragile, and easily fractured bones (9).
Gluten in Cream of Wheat
Cream of Wheat is made from wheat; thus, it contains gluten proteins. Consumption of Cream of Wheat should be avoided for people with gluten-related disorders such as Coeliac disease, non-coeliac gluten sensitivity, wheat allergy, dermatitis herpetiformis, and gluten ataxia, as it will likely trigger the disease (10).
Cream of Rice is gluten-free and can be safely consumed by people with gluten-related disorders.
Ultra-processing on Health
Cream of Wheat and Cream of Rice are highly processed or ultra-processed foods. Consumption of highly processed foods is associated with an increased risk of overall and breast cancer. Available evidence suggests that ultra-processed foods may increase cancer risks by obesity-promoting properties or carcinogenic compounds; however, further research is required (11, 12).
The consumption of ultra-processed foods is also associated with higher risks of obesity, metabolic syndrome, irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease, heart disease, depression, cancer, and all-cause mortality (13, 14, 15, 16).
Similar articles:
Oatmeal vs Cream of Wheat - Health impact and Nutrition Comparison
Corn Grits vs Cream of Wheat - Health impact and Nutrition Comparison
References
- https://creamofwheat.com/product/stove-top-cream-of-rice/
- https://creamofwheat.com/product/original-2-minute/
- Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020-2025
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30401704/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34755596/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31446062/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30779018/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4772032/
- Calcium and vitamin D for bone health (Beyond the Basics) - UpToDate
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538505/
- https://acsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cncr.31655
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35236935/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32792031/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32819372/
- https://www.bmj.com/content/374/bmj.n1554
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7399967/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin A | 232µg | 0µg | 26% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.309mg | 0.027mg | 22% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.21mg | 0.018mg | 15% |
| Folate | 62µg | 3µg | 15% |
| Iron | 4.96mg | 3.96mg | 13% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.232mg | 0.071mg | 13% |
| Vitamin B3 | 3.093mg | 1.039mg | 13% |
| Calcium | 64mg | 1mg | 6% |
| Manganese | 0mg | 0.144mg | 6% |
| Sodium | 102mg | 173mg | 3% |
| Protein | 1.84g | 0.9g | 2% |
| Fiber | 0.6g | 0.1g | 2% |
| Calories | 62kcal | 52kcal | 1% |
| Carbs | 13.08g | 11.5g | 1% |
| Magnesium | 6mg | 3mg | 1% |
| Copper | 0.043mg | 0.034mg | 1% |
| Selenium | 3.5µg | 3µg | 1% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.134g | 0.027g | 1% |
| Fats | 0.24g | 0.1g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 12.48g | 11.4g | N/A |
| Potassium | 20mg | 20mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 0.07g | 0.04g | N/A |
| Zinc | 0.17mg | 0.16mg | 0% |
| Phosphorus | 18mg | 17mg | 0% |
| Vitamin E | 0.02mg | 0.02mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.082mg | 0.076mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 0.1µg | 0µg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.038g | 0.02g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.033g | 0.031g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.025mg | 0.013mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.058mg | 0.044mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.08mg | 0.015mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.139mg | 0.073mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.047mg | 0.037mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.034mg | 0.026mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.099mg | 0.037mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.089mg | 0.057mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.042mg | 0.026mg | 0% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +396.3% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -47.4% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Cream of Wheat - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173902/nutrients
- Cream of Rice - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173914/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.




