Bass vs. Cod — Nutrition & Health Comparison


Summary
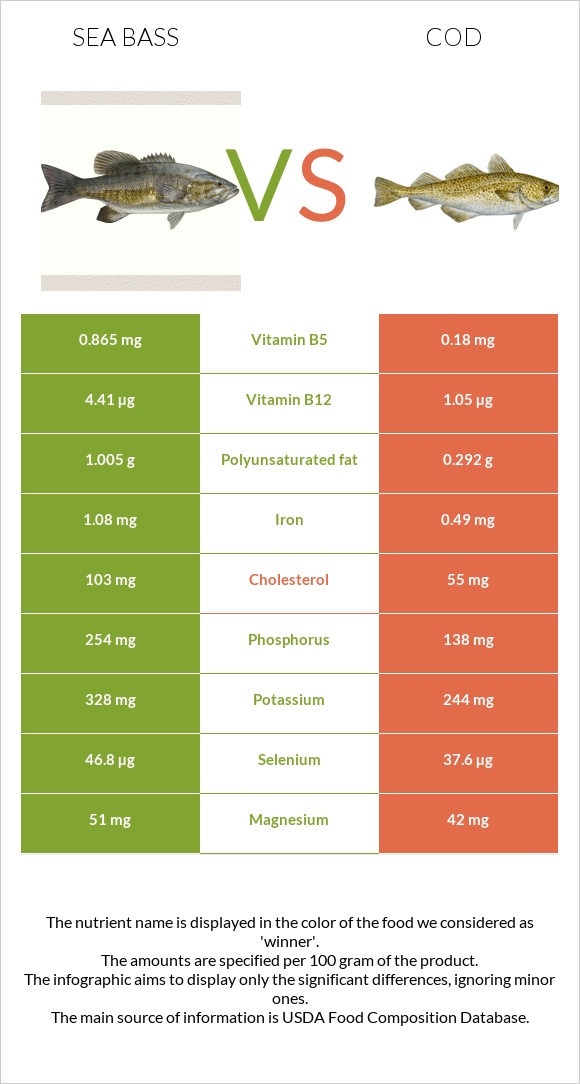
Cod is lower than bass in several critical elements, including iron, polyunsaturated fat, phosphorus, vitamin B5, selenium, and vitamin B12. Bass's daily coverage of Vitamin B12 is noticeably 140% more than cod's. The concentration of vitamin B5 in bass is five times higher than in cod, indicating a significant variation in vitamin B5. Cod has 0.18 mg of vitamin B5, compared to 0.865 mg in bass. Furthermore, cod has less cholesterol than bass does.
Introduction
This article discusses the key nutritional differences between bass and cod and their influence on human health.
Nutrition
This article discusses two food types: cooked cod and cooked bass. To better understand the differences between these two fish species, you may view the nutrition infographics included at the bottom of the page.
Calories
Bass and cod are both considered low-calorie foods. Cod and bass have 105 and 124 calories per 100g, respectively.
Protein
Protein contents in bass and cod are nearly equal: bass has 22.73g, and cod has 22.83g per 100g. High concentrations of essential amino acids, including valine, methionine, threonine, isoleucine, leucine, tryptophan, lysine, histidine, and phenylalanine, are found in both fish species. Completeness proteins, like those found in cod and perch, are those the human body cannot produce independently and include all nine necessary amino acids.
Fats
The fat content of bass is more than 3.4 times that of cod, with 2.99g per 100g vs. 0.86g for the same serving of cod. Bass contains twice the amount of cholesterol as cod, with 103mg per 100g compared to 55mg per 100g for cod.
There is a greater concentration of omega-3, monounsaturated, and saturated fats in bass than in cod.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+582.3%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+244.2%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-74.2%
Carbohydrates
Cod and bass have no carbohydrates.
Vitamins
Bass has twice as much vitamin A and RAE as cod and is high in vitamins B1, B5, B12, and folate. Compared to bass, cod contains more vitamins B2, C, and D.
Both fish contain the same amount of vitamins B3 and B6.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+121.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+30.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+380.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+22.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+320%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+25%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+113.5%
Minerals
Bass has more minerals than cod. Compared to cod, bass has 1.4 times the calcium, almost twice the iron, 1.8 times the phosphorus, and 1.4 times the potassium.
Both have almost comparable quantities of zinc, copper, manganese, magnesium, selenium, and sodium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+21.4%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+35.7%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+34.4%
Contains
more
IronIron
+120.4%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+84.1%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+24.5%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+13.7%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-11.4%
Weight Loss and Diets
Both fish can be effective protein sources with minimal carbs in ketogenic (Keto) diets. The lean protein level of cod and bass corresponds with the DASH diet's principles. Both fish are acceptable for the Atkins diet, which stresses low-carb intake. Incorporating cod or bass into the Mediterranean diet, which is noted for its concentration on fish, is consistent with the diet's fish-centric approach. Cod and bass are both acceptable in the Paleo diet, which promotes natural foods and lean proteins. Both fish can be included in the Dukan diet's protein-rich stages for protein consumption. Both fish are lean protein sources in low-fat and low-calorie diets.
Health Benefits
Cardiovascular Health
Including fish in your diet can significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, particularly if you consume bass and cod. These fish are rich in the essential omega-3 to omega-6 fatty acid ratio, which the human body cannot produce by itself. Studies have shown that an imbalanced ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 fatty acids can increase the risk of heart disease, making it crucial to maintain a well-balanced diet that includes fish (1, 2).
It is crucial to consume omega-3 fatty acids as they possess anti-triglyceridemic, hemostatic, antiarrhythmic, anti-atherogenic, and antithrombotic qualities, which significantly improve heart function and structure. Therefore, the American Heart Association strongly recommends the consumption of fatty fish twice a week.
Combining statins with omega-3 fats is effective and well-tolerated for dyslipidemia and may benefit recent myocardial infarction patients, according to research.
Diabetes
Considering that they contain many omega-3 fatty acids, people with diabetes may find cod and bass beneficial.
Consuming the high-omega-3 fatty acids in cod and bass liver oil has been linked to studies with several biochemical changes that may help manage diabetes, including reduced triglyceridemia, enhanced fatty acid oxidation, boosted HDL, and lowered LDL levels. Along with hyperlipidemia, there is a reduction in insulin resistance (3, 4).
Omega-3 fatty acids have been shown in another investigation to considerably lower fasting blood glucose levels (5).
Immune system
Studies have shown that by boosting the immune system, omega-3 fatty acids can lessen the symptoms of several illnesses, such as autoimmune hepatitis and sepsis. Acquiring comprehensive knowledge regarding the distinct direct impact of omega-3 fatty acids on various immune system cells will enable future investigators and medical professionals to enhance and implement omega-3-rich dietary supplements and meals (such as cod and bass) for the management of an extended array of ailments (6). Furthermore, bass, especially its Anti-Stress Bioactive (ASB), has encouraging immune-stimulating and wound-healing qualities. Through TLR4 signaling, ASB inhibits inflammatory mediators, indicating that it may promote cell migration and proliferation to improve wound healing. The in vivo results show how ASB promotes angiogenesis, re-epithelialization, and organized collagen deposition during the proliferative stage of wound healing. These results provide a solid basis for investigating sea bass's immunomodulatory potential in biological and medicinal studies (7).
Side Effects
Cod and bass, like most fish, contain mercury. Mercury ingestion is hazardous and can cause neurological and behavioral issues. It might be especially dangerous for youngsters. As a result, it is preferable to take fish and bass in moderation (8, 9).
Habitat
Cod may be found in the Northwest Atlantic from Greenland to Cape Hatteras, North Carolina, although it is most common in US waters along Georges Bank and the western Gulf of Maine. Cold waters between 30 and 500 feet deep are preferred by Atlantic cod, which live on rocky ledges and slopes close to the bottom. Conversely, bass are adaptable and may be found in various water bodies, such as ponds, rivers, lakes, and reservoirs. They favor places with shelter, including boulders, fallen trees, and submerged plants. A particular species of bass, the largemouth bass, inhabits areas of North America that stretch from the Mississippi River basin to the Great Lakes and the St. Lawrence River. They also inhabit areas of the Atlantic Ocean that drain from North Carolina to Florida and northern Mexico.
Longevity
Atlantic cod, noted for their longevity, may live for more than 20 years. They may reach lengths of 51 inches and weigh up to 77 pounds. Cods usually begin reproducing between the ages of 2 and 3, when they are between 12 and 16 inches long. Their age and size impact their breeding habits. In contrast, bass species such as largemouth bass have distinct biological traits. While particular specifics vary amongst bass species, they usually have a shorter lifetime than cod, frequently surviving approximately ten years. Bass achieve sexual maturity at a younger age and are smaller in size than Atlantic cod.
Appearance
Like a catfish's whiskers under the lower jaw, the unusual barbel structure is a feature of Atlantic cod, along with their big head and blunt snout. Their body, head, tail, and fins are speckled with deeper hues, while their colors range from pale yellowish-green to red and olive. Pacific fish are sometimes called gray cod due to their color, which is brown or grayish with darker areas or patterns on their flanks and a whiter belly. When it comes to basses, their bodies are typically grayish-black to dark brown, with a noticeably lighter belly. A bass's body often has a long, streamlined shape that tapers toward the tail. Furthermore, bass include a dorsal fin commonly separated between an anterior spiny portion and a posterior soft-rayed portion.
Taste and Use
Cod is praised for its flexibility, thanks to its mild, flaky white flesh. It's common in classic recipes like fish and chips and fish stews. It has a light taste. On the other hand, bass lends itself wonderfully to grilling, baking, or pan-searing because of its harder texture and somewhat stronger flavor.
Sources
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34371930/
- https://www.fayoum.edu.eg/scien/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12935323/
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/
- https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30862523/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B12 | 4.41µg | 1.05µg | 140% |
| Phosphorus | 254mg | 138mg | 17% |
| Selenium | 46.8µg | 37.6µg | 17% |
| Cholesterol | 103mg | 55mg | 16% |
| Choline | 83.7mg | 15% | |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.865mg | 0.18mg | 14% |
| Iron | 1.08mg | 0.49mg | 7% |
| Vitamin D | 46 IU | 6% | |
| Vitamin D | 1.2µg | 6% | |
| Vitamin E | 0.81mg | 5% | |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.346mg | 0.283mg | 5% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 1.005g | 0.292g | 5% |
| Fats | 2.99g | 0.86g | 3% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.037mg | 0.079mg | 3% |
| Magnesium | 51mg | 42mg | 2% |
| Potassium | 328mg | 244mg | 2% |
| Vitamin A | 31µg | 14µg | 2% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.115mg | 0.088mg | 2% |
| Saturated fat | 0.65g | 0.168g | 2% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.846g | 0.124g | 2% |
| Calories | 124kcal | 105kcal | 1% |
| Vitamin C | 0mg | 1mg | 1% |
| Calcium | 19mg | 14mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.51mg | 0.58mg | 1% |
| Folate | 10µg | 8µg | 1% |
| Protein | 22.73g | 22.83g | 0% |
| Copper | 0.04mg | 0.036mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 88mg | 78mg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.019mg | 0.02mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B3 | 2.558mg | 2.513mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 0.1µg | 0% | |
| Tryptophan | 0.255mg | 0.256mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.997mg | 1.001mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 1.047mg | 1.052mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.848mg | 1.856mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 2.088mg | 2.097mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.673mg | 0.676mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.887mg | 0.891mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.171mg | 1.176mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.669mg | 0.672mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.217g | 0.004g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.75g | 0.154g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.013g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more FatsFats | +247.7% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +135.9% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Sea bass - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174228/nutrients
- Cod - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171956/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






