Herring vs. Sardine. What's The Difference?


Summary
Herring is richer in omega-3, monounsaturated fats, vitamin B3, vitamin D, and vitamin E. Herring is also lower in sodium. In comparison, sardine is higher in saturated fats and richer in polyunsaturated fats, calcium, selenium, iron, phosphorus, copper, and most B complex vitamins. Herring is higher in mercury.
Introduction
Herring and sardines are oily fish that are highly popular worldwide. They are part of different cuisines worldwide and can be eaten in various ways, from canned, fried, or baked.
This article will compare both fish according to general differences, nutritional content, and health impacts.
General differences
Size
Sardines are smaller than herring. Herring can be found in smaller sizes aswell, but they are almost twice the size of sardines.
Taste
It is essential to mention that both fish are oily and have a strong taste. Herring has a more pungent taste, often described as salty and “fishy.” Sardine, on the other hand, has a milder taste.
Texture
Herring has a meatier bite than sardines. Sardines taste moist and oiler than herring.
Price
Canned sardines are cheaper than herring. Overall, during their season, sardines are cheaper than herring.
Nutritional content comparison
This section will compare 100g of sardine oil drained to 100g of dry heat-cooked herring.
Calories
They have similar amounts of calories.
Carbs
Their carb content is negligible.
Protein
Herring and sardines are protein-rich foods. However, it is essential to mention that they are rich in protein but have similar amounts.
Fats
Their total fat content is similar. However, sardines are higher in saturated fats and polyunsaturated fats. In comparison, herring is richer in monounsaturated fats.
Below, we can see their fat distributions.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-41.6%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+88.2%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+23.8%
Cholesterol
Sardine contains twice the amount of dietary cholesterol compared to herring.
Minerals
Sardine is richer in calcium, selenium, iron, phosphorus, and copper.
However, sardines are very high in sodium. Herrings have a low sodium profile.
Below are the mineral distributions.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+416.2%
Contains
more
IronIron
+107.1%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+57.6%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+61.7%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+170%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+12.6%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-62.5%
Vitamins
Herring is richer in vitamins B1, B2, B5, B6, and B12. Sardines are richer in vitamins B3, D, and E.
Below are their vitamin distributions.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+48.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+27.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+2500%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+12.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+12.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+40%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+31.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+15.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+108.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+47%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+20%
Health impacts
In this section, we will dig deep into the differences in health impacts each type of fish provides, the negatives and the positives.
Insulin resistance
Individuals with type 2 diabetes who consume a diet enriched with sardines have been shown to have decreased markers of insulin resistance.
This is shown by a decrease in the HOMA-IR marker. This was exclusive to a sardine-rich diet (1).
Mercury levels
Herring is higher in mercury levels than sardine.
The levels of mercury in herring are almost 6 times higher compared to the level of mercury in sardine.
Herring increases the risks of mercury poisoning compared to sardines. Mercury poisoning affects the gastrointestinal system, the nervous system, the kidneys, and the lungs (2)(3).
Consumption of mercury over a consecutive amount of days leads to mercury poisoning. It is important to consider the amount of mercury we consume when consuming different types of fish.
In this article, you can read about the comparison between sardine vs tuna.
Omega-3 fats
Herring is richer in omega-3 fats, specifically EPA and DHA. Although sardines are also rich in these fats, comparatively, herring is richer. Herring richer in omega-3 fats are essential to our diet as they are necessary for our cardiovascular, endocrine, and immune systems (4).
Cardiovascular health
Sardines higher in dietary cholesterol in a balanced diet, such as the Mediterranean diet, do not increase blood cholesterol levels since the body can adapt to these changes metabolically. However, it was shown that the Western diet that contains high amounts of saturated fats and processed foods associated with dietary cholesterol increases blood cholesterol levels. So, having a balanced diet is necessary to maintain optimal health (5)(6)(7).
Sardines are also higher in saturated fats, and this increases the risks of cardiovascular diseases. In comparison, herring is richer in monounsaturated fats, which is associated with decreased cardiovascular disease risks (8)(9).
In this comparison, high sodium, such as in sardines, is linked with increased risks of hypertension (10).
Overall, sardines are associated with increased risks of cardiovascular diseases.
Bone health
Sardine is richer in calcium, necessary to prevent bone resorption and reduce osteoporosis risks. In addition to that, vitamin D is also necessary for this process. Sardines contain a rich amount of vitamin D, but in comparison, herring is richer in vitamin D.
Sardines are a better option for bone health than herring (11).
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4836051/
- https://www.fda.gov/food/environmental-contaminants-food/mercury-levels-commercial-fish-and-shellfish-1990-2012
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499935/
- https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Omega3FattyAcids-HealthProfessional/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9143438/
- https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000743
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6129189/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30084105/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25274026/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34579105/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6683260/
Infographic
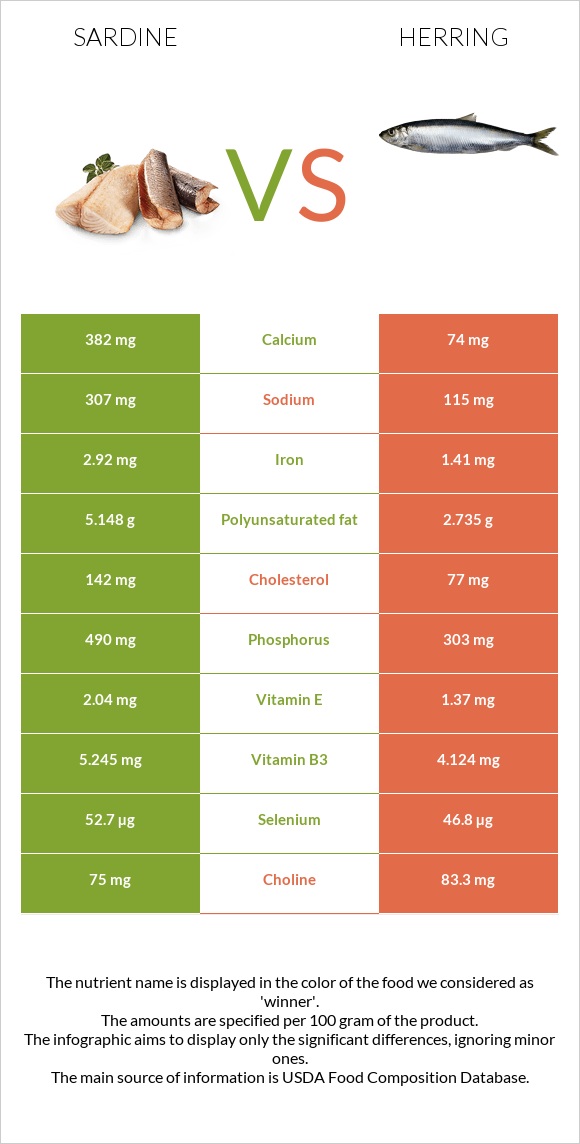
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B12 | 8.94µg | 13.14µg | 175% |
| Calcium | 382mg | 74mg | 31% |
| Phosphorus | 490mg | 303mg | 27% |
| Cholesterol | 142mg | 77mg | 22% |
| Iron | 2.92mg | 1.41mg | 19% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 5.148g | 2.735g | 16% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.167mg | 0.348mg | 14% |
| Selenium | 52.7µg | 46.8µg | 11% |
| Copper | 0.186mg | 0.118mg | 8% |
| Sodium | 307mg | 115mg | 8% |
| Vitamin B3 | 5.245mg | 4.124mg | 7% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.227mg | 0.299mg | 6% |
| Saturated fat | 1.528g | 2.615g | 5% |
| Vitamin E | 2.04mg | 1.37mg | 4% |
| Protein | 24.62g | 23.03g | 3% |
| Vitamin D | 193 IU | 214 IU | 3% |
| Vitamin D | 4.8µg | 5.4µg | 3% |
| Manganese | 0.108mg | 0.04mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.08mg | 0.112mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.642mg | 0.74mg | 2% |
| Vitamin K | 2.6µg | 0.1µg | 2% |
| Choline | 75mg | 83.3mg | 2% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 3.869g | 4.79g | 2% |
| Vitamin C | 0mg | 0.7mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 397mg | 419mg | 1% |
| Folate | 10µg | 12µg | 1% |
| Calories | 208kcal | 203kcal | 0% |
| Fats | 11.45g | 11.59g | 0% |
| Magnesium | 39mg | 41mg | 0% |
| Zinc | 1.31mg | 1.27mg | 0% |
| Vitamin A | 32µg | 36µg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.276mg | 0.258mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 1.079mg | 1.01mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 1.134mg | 1.061mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 2.001mg | 1.872mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 2.26mg | 2.115mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.729mg | 0.682mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.961mg | 0.899mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.268mg | 1.187mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.725mg | 0.678mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.473g | 0.909g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.509g | 1.105g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0g | 0.071g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more OtherOther | +254.1% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Sardines - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/175139/nutrients
- Herring - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/175117/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.