Great northern beans vs. Navy beans — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Great Northern beans are high in selenium, phosphorus, vitamins C, A, and B3. On the other hand, navy beans are high in choline, zinc, vitamins B1, B6, and folate. Moreover, navy beans contain less sodium, whereas great Northern beans have fewer calories. While great Northern beans have fewer saturated fats, navy beans contain more monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. Navy beans are also high in net carbs and dietary fiber. Compared to Great Northern beans, Navy beans provide 14% more of your daily needs for dietary fiber.
Introduction
Navy beans and Great Northern beans are frequently confused, and their differences might be subtle. In this article, we will discuss some general distinctions.
Classification
Great Northern and navy beans are legumes and belong to the family Phaseolus. Navy beans are native to the U.S. Navy. Great Northern beans, on the other hand, are native to North Dakota. Navy beans are also known as pea beans or haricot. Great Northern beans are known as large white beans.
Appearance
Great Northern and navy beans are types of white beans. Great Northern beans are kidney-shaped and larger. Unlike them, navy beans are round-shaped and smaller. They are around the size of a pea.
Both have smooth surfaces but vary in texture. Navy beans have a creamy texture, whereas great Northern beans are firmer.
Taste and Use
Navy beans are mild and slightly sweet, whereas great Northern beans taste earthy.
While navy beans take 90 to 120 minutes to cook, great northern beans take 45 to 60 minutes.
Great Northern beans are perfect for salads and side dishes, whereas navy beans are good for soups and purees.
Nutrition
In this part of the article, we will compare the nutritional values of great Northern and navy beans, concentrating on differences.
Macronutrients and Calories
Great Northern Beans' average serving size is one cup, equal to 177g. The serving size of navy beans is 182g.
Great Northern and navy beans have similar nutritional densities, but navy beans are a little denser. Navy beans contain 64% water, whereas great Northern beans contain 69% water.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+37.8%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+23.5%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+14.2%
Calories
Compared to navy beans, great Northern beans have fewer calories. A hundred grams of great Northern beans provide 118 calories, whereas navy beans contain 140 calories.
Protein
Great Northern and navy beans are equal in protein content. A hundred grams of great Northern beans contain 8.33g of protein. Navy beans contain 8.23g of protein per hundred grams.
Fats
Compared to navy beans, great northern beans contain more fats. A hundred grams of navy beans contain 0.62g, whereas great northern beans provide 0.45g. Navy beans are high in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, whereas great northern beans provide more saturated fats.
Navy beans contain more omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Navy beans provide 0.18g and 0,14g of omega-3 and omega-6, respectively.
Great Northern beans, on the other hand, have 0,09g omega-3 and 0,1g omega-6.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-30%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+576.2%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+162%
Carbohydrates
Compared to great Northern beans, navy beans are high in net carbs and dietary fiber.
100g of great northern beans contain 21.09g of carbohydrates, of which 7g are dietary fiber and 14.09g are net carbs.
100g of navy beans contain 26.05g of carbohydrates, of which 10.5g are dietary fiber and 15.55g are net carbs.
Vitamins
Great Northern beans are high in vitamins C and A. Navy beans, on the other hand, are high in vitamins B1, B6, and folate.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+44.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+50%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+11.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+17.9%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+37.3%
Minerals
Great Northern beans are high in phosphorus and selenium. Navy beans, on the other hand, are slightly higher in iron and zinc.
Moreover, navy beans contain more choline and less sodium. The choline content in navy beans per hundred grams is 44.7mg. Great Northern beans provide 2mg of sodium, whereas navy beans 0mg.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+17.6%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+14.6%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+41.4%
Contains
more
IronIron
+10.8%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+17%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-100%
Acidity
The quantity of acid or base created by foods inside the body is known as the PRAL or potential renal acid load. Great Northern beans have a PRAL level of -0.2. The PRAL level of navy beans is -1.1. Both are alkaline.
Weight Loss & Diets
Plant-based dietary patterns that contain beans and legumes enhance body weight control, potentially lowering the impacts of obesity(1). Both contain dietary fiber that may aid in losing weight(2).
Great Northern and navy beans are vegan.
Plant-based foods such as Great Northern and navy beans can be part of the Mediterranean diet.
Due to their high carb content, great Northern and Navy beans are not good options for the Keto diet.
Both are low-fat and low-sodium foods and can be part of the DASH diet.
Great Northern and navy beans are not good options for the Paleo diet.
Health Benefits
Cardiovascular Health
Navy beans contain more fiber than great Northern beans. Fiber-enriched food consumption may lower the risk of coronary heart disease, hypertension, and stroke(2).
Great Northern and navy beans may also decrease LDL cholesterol(2). According to the study, great northern beans may lower plasma and liver cholesterol(3).
Diabetes
When ingested alone, as part of a low GI or fiber-rich diet, beans promote low-glycemic response and enhance postprandial glycemic response and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) outcomes in Type 2 diabetes. Great Northern and navy beans may aid in managing hyperglycemia and dyslipidemia(1).
Digestive Health
Great Northern and Navy beans are plant-based and provide some bioactive compounds. These phytochemicals may improve low-grade inflammation and gut microbiome(1).
In addition, high fiber consumption helps with gastrointestinal problems, including gastroesophageal reflux disease, duodenal ulcer, diverticulitis, constipation, and hemorrhoids(2).
Cancer
Increased daily consumption of common beans may lower the risk of colon cancer. Beans are high in bioactive compounds that exhibit anti-proliferative activity. They may induce apoptosis and cell cycle arrest(4).
Studies indicate that consuming more legumes, such as navy beans, may reduce the incidence of colorectal cancer(5).
Infographic
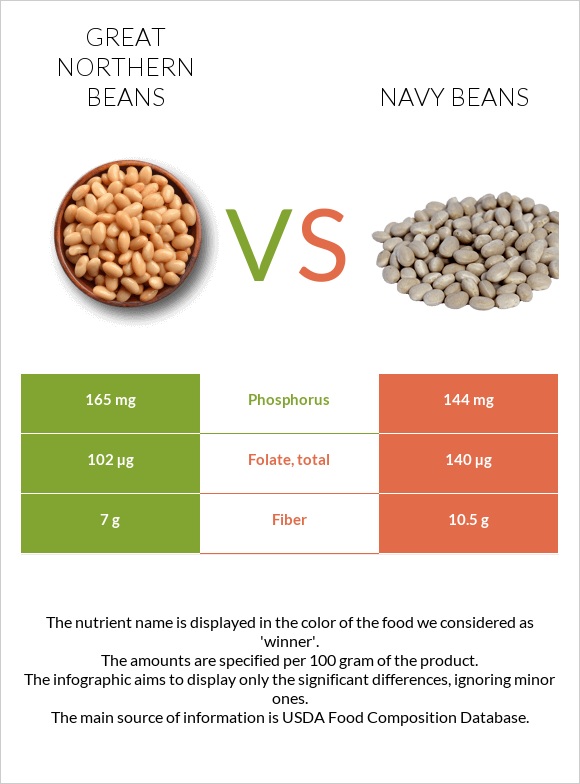
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Fiber | 7g | 10.5g | 14% |
| Folate | 102µg | 140µg | 10% |
| Choline | 44.7mg | 8% | |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.158mg | 0.237mg | 7% |
| Starch | 15.4g | 6% | |
| Copper | 0.247mg | 0.21mg | 4% |
| Iron | 2.13mg | 2.36mg | 3% |
| Phosphorus | 165mg | 144mg | 3% |
| Carbs | 21.09g | 26.05g | 2% |
| Selenium | 4.1µg | 2.9µg | 2% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.117mg | 0.138mg | 2% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.187g | 0.49g | 2% |
| Calories | 118kcal | 140kcal | 1% |
| Magnesium | 50mg | 53mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 0.88mg | 1.03mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.059mg | 0.066mg | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 0.6µg | 1% | |
| Protein | 8.33g | 8.23g | 0% |
| Fats | 0.45g | 0.62g | 0% |
| Vitamin C | 1.3mg | 0.9mg | 0% |
| Net carbs | 14.09g | 15.55g | N/A |
| Calcium | 68mg | 69mg | 0% |
| Potassium | 391mg | 389mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 0.37g | N/A | |
| Sodium | 2mg | 0mg | 0% |
| Vitamin E | 0.01mg | 0% | |
| Manganese | 0.518mg | 0.527mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.681mg | 0.649mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.266mg | 0.266mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.14g | 0.098g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.021g | 0.142g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.099mg | 0.1mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.351mg | 0.289mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.368mg | 0.387mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.665mg | 0.7mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.572mg | 0.52mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.125mg | 0.111mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.451mg | 0.471mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.436mg | 0.504mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.232mg | 0.206mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.177g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Great northern beans - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/175191/nutrients
- Navy beans - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173746/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





