Ground chicken vs. Ground turkey — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Ground turkey is richer in protein, including all essential amino acids, and slightly lower in calories. Ground turkey is also higher in unsaturated but lower in saturated fats and cholesterol.
Ground chicken is 4 times richer in vitamin E and 2 times richer in potassium, while the ground turkey is 4 times richer in folate (vitamin B9) and 3 times richer in vitamin B12. Ground turkey is also overall a better source of minerals, such as calcium, zinc, copper, and iron.
Overall, based on this information, ground turkey can be considered a somewhat preferable choice over ground chicken nutritionally, despite all their similarities.
Introduction
Ground turkey and ground chicken are both minced types of meat that can be used in a variety of recipes. They have similar nutritional profiles, but there are still some differences in taste and texture, as well as nutrition and health impact.
If interested, you can also read about the differences and similarities between roasted whole chicken and turkey.
Classification
Chicken is widely known as white meat, but is turkey meat white or red? White meat is lighter in color as it is lower in the iron-containing compound myoglobin. Both chicken and turkey are poultry and are, therefore, considered to be white meat.
Ground chicken and turkey are not processed meats. Processed meat is defined as meat that has undergone salting, curing, fermentation, smoking, or other processes to enhance flavor or improve preservation (1).
Appearance, Taste, and Use
Ground turkey has a slightly milder flavor compared to ground chicken. It also tends to be drier and can have a crumbly texture.
Ground chicken, on the other hand, has a slightly sweeter taste and a juicier texture. It can also be fattier than ground turkey, which some people prefer as it can make the meat more flavorful and moist.
In terms of cooking, both can be used interchangeably in recipes. The choice between ground turkey and ground chicken often comes down to personal preference and the desired outcome of the dish.
Nutrition
The infographics below are presented for 100g of cooked ground turkey and pan-browned ground chicken crumbles.
The average serving size of cooked ground chicken and turkey per person is considered to be one patty equal to 82g.
Macronutrients and Calories
Ground turkey and chicken are nearly identical in their macronutrient compositions, consisting of 62% and 65% water, respectively.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
OtherOther
+450%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+17.6%
Calories
These two types of meat provide a similar number of calories, with ground turkey containing only 14 more calories per 100g serving. Ground chicken has 189 calories per 100g serving.
Protein
While both these foods are good sources of protein, ground turkey is somewhat richer in protein compared to ground chicken. Ground turkey provides about 27g of protein per 100g serving, while ground chicken contains 23g.
The protein found in ground turkey and chicken is of high quality as they contain good amounts of all essential amino acids. Turkey is naturally richer in all these amino acids.
Fats
These two types of meat are similar in their fat contents, with ground chicken containing slightly more fat.
Per 100g serving sizes, ground chicken and ground turkey provide 10.92g and 10.4g of fats, respectively.
However, these two differ in their fat compositions.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+41.1%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-14.2%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+40.2%
As can be seen in the infographic above, ground turkey has a more favorable fat composition, being richer in polyunsaturated and lower in saturated fats.
At the same time, ground chicken is higher in monounsaturated fats.
Ground turkey is also lower in cholesterol (93mg per 100g) compared to ground chicken (107mg per 100g).
Carbohydrates
Like most other meat, ground turkey and ground chicken do not contain notable amounts of carbohydrates.
Vitamins
Ground turkey is 4 times richer in folate (vitamin B9) and 3 times richer in vitamin B12. It also contains vitamin A, which ground chicken lacks entirely, and is higher in vitamins B3 and B6.
On the other hand, ground chicken is 4 times richer in vitamin E, somewhat richer in vitamins B1, B2, and B5, and provides vitamin K, which ground turkey does not contain.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+254.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+57.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+43.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+11.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+22.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+17.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+162.7%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+250%
Minerals
Ground turkey can be considered the winner in the mineral category, being 4 richer in calcium and higher in zinc, copper, and iron.
Nevertheless, ground chicken contains 2 times more potassium.
Without added salt, these two types of meat provide nearly the same amount of sodium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+130.3%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+45.5%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+250%
Contains
more
IronIron
+63.4%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+143.5%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+62%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+117.5%
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index of foods with no carbohydrates, such as ground chicken and turkey, is considered to be 0, as these foods do not raise blood glucose levels after consumption.
Insulin Index
The insulin index is useful for foods with no glycemic index values, as it demonstrates how much the blood insulin levels rise after intake.
The insulin index of turkey has not yet been researched, but chicken is known to have a low insulin index, falling in the range of 17 to 23 (2, 3).
Health Impact
Both ground turkey and ground chicken are excellent protein sources and can be part of a healthy diet. In this section, we will look at the scientific evidence of how chicken and turkey negatively or positively affect health.
Cardiovascular Health
A large study has concluded that choosing poultry, such as chicken and turkey, can be a healthier alternative to red or processed meat, decreasing cardiovascular risk (4).
The decrease in salt, heme iron, and saturated fat intake may account for these variations between red meat and poultry. Ground turkey is richer in unsaturated fats and lower in cholesterol, but it is also higher in iron.
Even if eating poultry is better for your heart than eating red meat, you might be better off choosing fish or vegetables. There is evidence that consuming these foods rather than poultry, such as chicken and turkey, lowers the risk of cardiovascular disease (5).
Diabetes
Ground turkey and chicken, due to their glycemic and insulin index values, do not raise blood glucose levels after consumption, while raising insulin levels only a little.
Consuming poultry meat as part of a diet high in vegetables is linked to a lower risk of developing cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and being overweight or obese (6).
However, research has found a connection between saturated fat consumption from animal sources and insulin resistance/ hyperinsulinemia (6).
When discussing factors that influence the likelihood of acquiring type 2 diabetes, the preparation process may be just as important as the product itself. Compared to cooking at moderate temperatures, such as boiling, steaming, and stir-frying, cooking meat at high temperatures, such as grilling and barbecuing, increases the risk of type 2 diabetes (7).
Cancer
White meat, especially chicken and turkey, is thought to have a somewhat preventive or neutral effect on the risk of cancer (6).
Sources.
- https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/cancer-carcinogenicity-of-the-consumption-of-red-meat-and-processed-meat
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/26770180
- https://ses.library.usyd.edu.au/handle/2123/11945
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34542332/
- https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/42/12/1136/6032616
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4462824/
- https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/2018/03/23/how-meat-is-cooked-may-affect-risk-of-type-2-diabetes/
Infographic
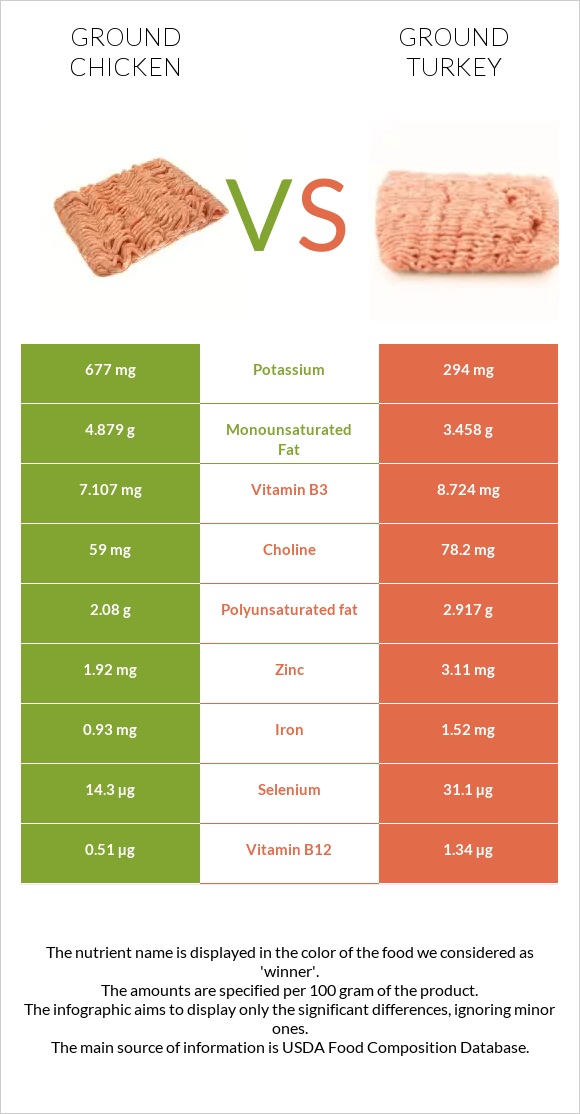
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.51µg | 1.34µg | 35% |
| Selenium | 14.3µg | 31.1µg | 31% |
| Potassium | 677mg | 294mg | 11% |
| Zinc | 1.92mg | 3.11mg | 11% |
| Copper | 0.062mg | 0.151mg | 10% |
| Vitamin B3 | 7.107mg | 8.724mg | 10% |
| Protein | 23.28g | 27.37g | 8% |
| Iron | 0.93mg | 1.52mg | 7% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.302mg | 0.211mg | 7% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.538mg | 0.633mg | 7% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 2.08g | 2.917g | 6% |
| Cholesterol | 107mg | 93mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.121mg | 0.077mg | 4% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 4.879g | 3.458g | 4% |
| Phosphorus | 234mg | 254mg | 3% |
| Vitamin A | 0µg | 24µg | 3% |
| Vitamin B5 | 1.327mg | 1.193mg | 3% |
| Choline | 59mg | 78.2mg | 3% |
| Calcium | 8mg | 28mg | 2% |
| Vitamin E | 0.39mg | 0.11mg | 2% |
| Vitamin K | 2.1µg | 0µg | 2% |
| Saturated fat | 3.11g | 2.669g | 2% |
| Calories | 189kcal | 203kcal | 1% |
| Fats | 10.92g | 10.4g | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 8 IU | 1% | |
| Vitamin D | 0.2µg | 1% | |
| Folate | 2µg | 7µg | 1% |
| Magnesium | 28mg | 30mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 75mg | 78mg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.016mg | 0.011mg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0.087g | 0.134g | N/A |
| Tryptophan | 0.196mg | 0.312mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.97mg | 1.258mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 1.06mg | 1.227mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.816mg | 2.262mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 2.014mg | 2.452mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.596mg | 0.806mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.912mg | 1.068mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.102mg | 1.27mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.706mg | 0.811mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.008g | 0.01g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.031g | 0.009g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.081g | 0.136g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.016g | 0.012g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - Eicosatrienoic acid | 0.001g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.02g | 0.008g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Dihomo-gamma-linoleic acid | 0.011g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.015g | 0.019g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 1.787g | 2.508g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Ground chicken - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171117/nutrients
- Ground turkey - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171506/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





