Ground turkey vs Ground Beef: Nutrition comparison & Health impact


Summary
Ground beef is red meat and has higher mortality rates than ground turkey. Ground turkey is richer in protein, selenium, phosphorus, copper, and most B complex vitamins. Comparatively, ground beef is richer in zinc, iron, and vitamin B12.
Introduction
This article is a comparison between 2 types of animal products; ground turkey and ground beef. We will compare these two foods according to general differences, nutritional content, and health impacts.
By ground beef, we are considering ground beef 70/30 in this article. We will compare them both in their cooked states.
By the end of the article, we will understand their nutritional differences and how they impact our health.
General differences
Ground turkey is white meat, and ground beef is red meat.
Price
Now which one is a cheaper protein? Ground turkey or ground beef
By the global average, ground turkey is a cheaper food compared to ground beef.
Taste and flavor
Turkey meat is leaner meat and has less fat. Ground turkey is comparatively milder in taste. Some people say that turkey meat is bland aswell.
Culinary World
Ground meats are usually used in different recipes and dishes, such as burgers, sandwiches, etc. Ground turkey is used to make turkey burgers, turkey meatballs, and turkey-stuffed peppers, and ground beef is used in all types of beef burgers, tacos, taco pizzas, and so on.
Nutrition
In this section, we will compare 100g of each food based on cooked forms of both.
Calories
Ground turkey is lower in calories compared to ground beef. Ground turkey contains 203 calories, and ground beef contains 241 calories.
Fats
The fat contents of ground turkey are lower than that of ground beef. Ground turkey contains 10g of fats, and ground beef contains 15g of fats.
Considering the different types of fats, ground turkey contains higher amounts of polyunsaturated fats, whereas ground beef contains higher amounts of saturated and monounsaturated fats.
Below we can visualize their fat-type distributions
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+111.7%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-56.1%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+615%
Carbs
Their carb contents are negligible.
Protein
Ground turkey is richer in protein compared to ground beef.
Ground turkey contains 27.4g of protein; ground beef contains 24g of protein.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+47.8%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+1393.8%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+14.7%
Minerals
Ground turkey is richer in selenium, phosphorus, and copper. In comparison, ground beef is richer in zinc and iron.
Here we can visualize their mineral distributions.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+17.9%
Contains
more
IronIron
+49.3%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+87.8%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+76.5%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+22%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+91.1%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+53%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+22.2%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+62.8%
Vitamins
Ground turkey is richer in vitamins B2, B3, B5, and B6. In comparison, ground beef is richer in vitamin B12.
Here we can visualize their vitamin distributions.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+85.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+700%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+51%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+23.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+116.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+133%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+103.5%
Cholesterol
Ground beef contains more cholesterol than ground turkey. It has 93 mg of cholesterol per 100 g, while ground turkey has 88 mg.
Health Impacts
Ground beef and ground turkey are rich in nutrients that can be added to our diets. In this section, we will discuss the health benefits and negative impacts of each in detail.
You can also read a comparative text between steak and ground beef.
Anemias
Ground beef is a richer source of vitamin B12 and iron. A diet with moderate red meat has decreased iron deficiency and vitamin B12 anemia risks. Here we must mention that iron derived from heme protein has a very high bioavailability and is efficiently absorbed. Ground beef has an advantage over ground turkey over anemias since it is richer in iron and vitamin B12. (1)(2)
Muscle mass loss
With old age comes sarcopenia, which is muscle mass loss due to normal physiological processes related to aging. However, a diet rich in red meat, such as ground beef, has been associated with lower risks of muscle mass loss in elderly people. This is mainly associated with decreased rates of muscle mass loss provided by ground beef by this reference. (3)
Zinc benefits
Zinc is a catalyst in several metabolic pathways in the body and is essential in immune and reproductive physiology. Zinc is an essential mineral that must be consumed in our diets, and ground beef is an excellent source of zinc compared to ground turkey. (4)
Calories and weight loss
Overall, ground turkey is lean meat; it's leaner than ground beef. Ground turkey is richer in proteins and has lower calories. It is a great food to be added to weight loss diets, even in healthy diets not focused on weight loss. (5)
Vitamin B6 benefits
Similar to the benefits of zinc in ground beef, ground turkey is richer in vitamin B6, a catalyst in multiple metabolic pathways, and essential in the body's physiological and biochemical maintenance. (6)
Infections
It is important not to eat ground beef and ground turkey raw and even medium rare states. Cook them well because they get mixed with all sorts of bacteria, especially E.coli, which causes severe diarrhea and diseases such as hemolytic uremic syndrome while getting ground. (7)
Heart health
Ground turkey is lower in total fats; to be more specific, ground turkey contains half the amount of fats compared to ground beef. This, in turn, can show that ground turkey is a better alternative to ground beef regarding heart health and a decrease in mortality rates from heart diseases. (8)
It is also worth mentioning that ground turkey is richer in polyunsaturated fats, and ground beef is richer in monounsaturated fats. However, the double amount of saturated fats in ground beef is more significant.
Negative impacts
The culprit is processed red meats that cause significant health problems, and we need to differentiate between red meat and processed red meat. This article discusses some negative impacts of red meat that are based on dietary guidelines concerning the negative impacts of red meat.
Comparatively, ground turkey has a lower risk mortality rate than red meat consumption. In this article, you can read about turkey meat in depth.
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12643357/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24280989/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26946103/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2820120/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4462824/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34579110/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30068886/
- https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/eat-smart/fats/saturated-fats
Infographic
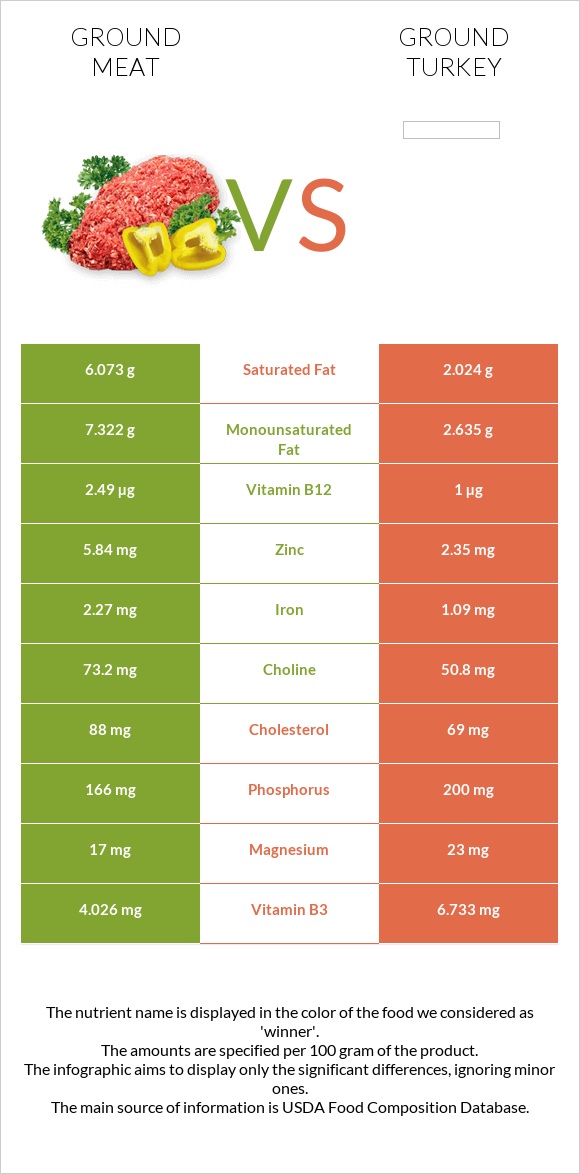
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B12 | 2.49µg | 1.34µg | 48% |
| Vitamin B3 | 4.026mg | 8.724mg | 29% |
| Zinc | 5.84mg | 3.11mg | 25% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.311mg | 0.633mg | 25% |
| Selenium | 19.1µg | 31.1µg | 22% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.408g | 2.917g | 17% |
| Saturated fat | 6.073g | 2.669g | 15% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.512mg | 1.193mg | 14% |
| Phosphorus | 166mg | 254mg | 13% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 7.322g | 3.458g | 10% |
| Iron | 2.27mg | 1.52mg | 9% |
| Fats | 15.37g | 10.4g | 8% |
| Copper | 0.079mg | 0.151mg | 8% |
| Protein | 23.87g | 27.37g | 7% |
| Magnesium | 17mg | 30mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.171mg | 0.211mg | 3% |
| Calories | 241kcal | 203kcal | 2% |
| Cholesterol | 88mg | 93mg | 2% |
| Potassium | 241mg | 294mg | 2% |
| Vitamin A | 3µg | 24µg | 2% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.051mg | 0.077mg | 2% |
| Vitamin K | 2.9µg | 0µg | 2% |
| Vitamin D | 2 IU | 8 IU | 1% |
| Calcium | 33mg | 28mg | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 0µg | 0.2µg | 1% |
| Choline | 73.2mg | 78.2mg | 1% |
| Sodium | 73mg | 78mg | 0% |
| Vitamin E | 0.12mg | 0.11mg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.009mg | 0.011mg | 0% |
| Folate | 7µg | 7µg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 1.173g | 0.134g | N/A |
| Tryptophan | 0.121mg | 0.312mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.923mg | 1.258mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 1.055mg | 1.227mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.861mg | 2.262mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 1.976mg | 2.452mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.614mg | 0.806mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.931mg | 1.068mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.172mg | 1.27mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.775mg | 0.811mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0g | 0.01g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0g | 0.009g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.136g | N/A | |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0g | 0.012g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - Eicosatrienoic acid | 0.001g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.008g | 0.008g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Dihomo-gamma-linoleic acid | 0.011g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.019g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 2.508g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Ground beef - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169474/nutrients
- Ground turkey - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171506/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





