Lima beans vs. Edamame — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Lima beans have more fiber and selenium, while edamame has higher folate, manganese, vitamin K, copper, phosphorus, vitamin B2, and vitamin C. Edamame has 57% more folate than lima beans. Lima beans, however, offer more selenium than edamame, with 4.5g compared to 0.8g.
Introduction
This article discusses the critical nutritional differences between two legume family members, lima beans and edamame, and their health benefits and risk factors.
Nutrition
The nutritional infographics below are presented for 100-gram servings of prepared frozen edamame and lima beans, boiled without salt.
The average portion size of these dishes is one cup, roughly 155 grams for edamame and 188 grams for lima beans.
Macronutrients and Calories
Lima beans comprise 70% water and 30% nutrients, while edamame comprises 73% water and 27% nutrients.
The primary macronutrient in edamame is protein, followed by carbohydrates and fats; lean beans are carbs, followed by protein and fats.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+134.3%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+52.7%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+1268.4%
Calories
They are both high-calorie foods. However, edamame is higher in calories, containing 121 calories per 100g, whereas lima beans have 115 calories in the same serving.
Protein
Edamame is significantly richer in protein, containing 12g in every 100g serving. A 100-gram serving of edamame covers 28% of the daily needed value for this nutrient. The same serving of lima beans covers 16%.
100g of lima beans and 100g of edamame beans provide 7.8 and 12g of protein, respectively. These beans contain some essential amino acids; however, edamame is more prosperous in all of these.
Fats
Edamame is also higher in fat, containing 5g more per 100g serving. In this serving size, edamame provides 5.2 g, while lima beans contain 0.38g of fat. Lima beans have less saturated fat (0.089g) than edamame (0.62g). Edamame has higher monounsaturated fat (1.282g) and polyunsaturated fat (2.156g) compared to lima beans (0.034g and 0.171g, respectively). Like all plant products, lima beans and edamame beans do not contain cholesterol.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-85.6%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+3670.6%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+1160.8%
Carbohydrates
While lima beans contain two times more carbohydrates, these edamame beans are relatively low in carbs: 100g contains 20.88g of total carbs, whereas edamame contains 8.91g.
Lima beans contain 6 grams more net carbs than edamame and nearly the same amount of sugar.
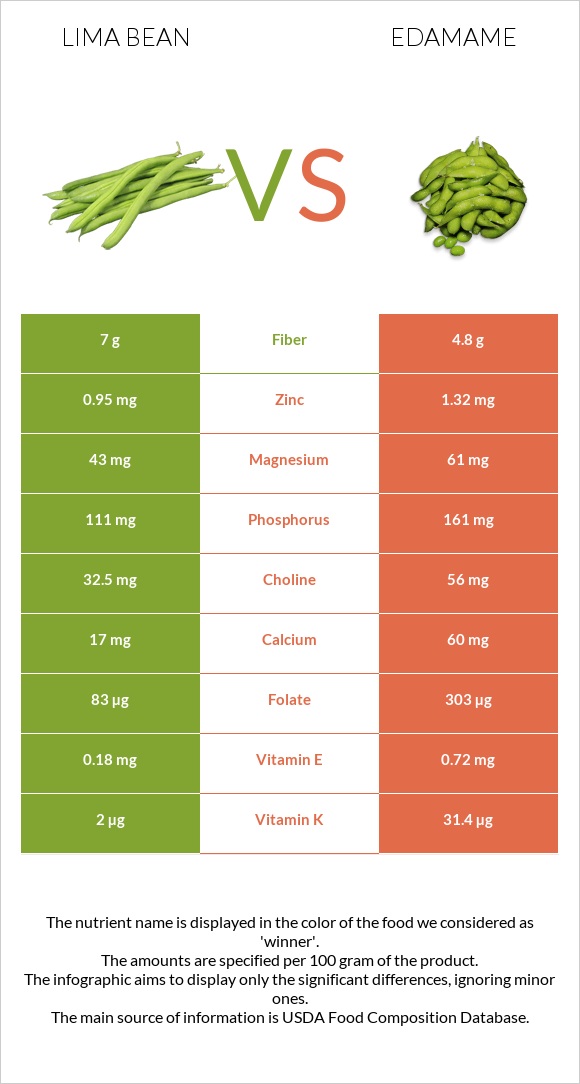
Fiber
Lima beans contain 1.8g more dietary fiber: a 100g serving of lima beans contains 7g of dietary fiber, whereas edamame contains 5.2g.
Vitamins
Edamame is a better source of most vitamins, four times richer in folate or vitamin B9 and covering the DV by 78%, and two times richer in vitamin B3.
Edamame beans also contain more vitamins C, B1, B2, A, E, and K.
At the same time, lima beans are richer in vitamins B5 and B6.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+61%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+277.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+24.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+181.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+117.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+1235%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+274.7%
Minerals
Lima beans contain more potassium and selenium. Edamame is four times higher in calcium, three times higher in sodium, and 1.5 times higher in phosphorus, magnesium, and copper.
Edamame beans are also somewhat richer in zinc, manganese, and magnesium. Both contain nearly the same amount of iron.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+16.5%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-66.7%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+462.5%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+48.8%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+270.6%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+46.8%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+44.2%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+52.3%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+98.4%
Oxalates
The oxalate content of lima beans is 20mg per 100 grams, and the oxalate content of edamame is 44mg per 100 grams. Both are considered to be low in oxalates.
Glycemic Index
Lima beans have an average glycemic index of 32, a deficient glycemic index number.
The glycemic index value of edamame beans is currently unknown. While this score may be higher due to more net carbohydrates and reduced fiber content, it will still be in the low glycemic index group.
Low glycemic index foods may enhance blood sugar levels, glucose utilization, lipid profile, fibrinolysis capability (which prevents blood clot formation), and body weight in type 2 diabetes (1, 2).
Acidity
Lima beans have a PRAL value of -4.1, making them base-producing, whereas the PRAL value of edamame is 0.4, making them acidic-producing.
Weight Loss and Diets
Edamame may be preferred for keto and low-carb diets due to its lower carb content. Both legumes align well with the DASH, Mediterranean, vegan/vegetarian, and pescetarian diets, providing plant-based protein and fiber. Lima beans, being minimally processed, may be suitable for paleo diets. Edamame might be favored in intermittent fasting due to its nutrient profile. Both are relatively low in fat and calories, making them suitable for low-fat, low-calorie diets. In anti-inflammatory diets, both legumes can contribute to overall health. However, edamame might be considered for its gentle nature during BRAT diets, while lima beans are not a typical choice.
Health Benefits
Cardiovascular Health
Soy protein is high in edamame, and studies indicate that a daily intake of soy protein may modestly reduce LDL cholesterol, a factor linked to heart disease (3, 4). Additionally, edamame provides fiber, antioxidants, and vitamin K, which can contribute to heart health (5). Lima beans, on the other hand, excel at providing 9 grams of heart-healthy fiber per cup. The soluble fiber in lima beans has been shown to lower cholesterol, inflammation, and blood pressure, lowering the risk of heart disease (6, 7, 8).
Diabetes
Both lima beans and edamame offer potential benefits for blood sugar levels. The glycemic index of lima beans is low, and they are high in fiber, which helps slow sugar absorption and promote stable blood sugar (9, 10). Studies suggest that including legumes like lima beans in your diet may reduce fasting blood sugar and lessen the incidence of type 2 diabetes (11, 12). Similarly, edamame is low in carbs, making it suitable for people with diabetes. Its low glycemic index indicates it won't cause rapid spikes in blood sugar (13).
Cancer
Lima beans stand out as a rich source of fiber, promoting digestive health, reducing the risk of colorectal cancer, and enhancing the gut microbiome (14, 15). The high fiber content aids in bowel movements and lowers the chances of diverticular disease (16). On the other hand, the impact of soy consumption, as seen in edamame, on cancer risk, particularly breast and prostate cancer, is not firmly established. While some studies suggest potential risks, others in Asian populations hint at protective effects (17, 18, 19, 20). Further research, especially long-term studies, is needed to determine the link between soy intake and cancer risk conclusively.
Downsides and Risks
Lima beans may cause allergy reactions in certain people (21). Raw lime beans, similar to other types of beans, contain antinutrients. These compounds can potentially hinder the absorption of minerals in the body (22). Additionally, raw lima beans contain linamarin, a cyanogenic compound some consider toxic to humans (23). However, these can be reduced through proper cooking, soaking, and processing. Rapidly increasing fiber intake in lima beans may lead to digestive side effects (24). There is no available information on specific side effects related to edamame.
Classification
Lima beans (Phaseolus lunatus) and edamame belong to the Fabaceae family, commonly known as the legume family. Lima beans, also called butter beans, belong to the Phaseolus genus. Edamame, however, comes from young, green soybeans and belongs to the same family but falls under the Glycine genus. The Fabaceae family is extensive and includes various legumes such as soybeans, chickpeas, peanuts, lentils, and alfalfa.
Appearance, taste, and use
Lima beans, often known as butter beans, are more significant, flatter, and have a buttery texture with a mild, somewhat sweet flavor. They are versatile and used in various global cuisines, absorbing the flavors of the dishes they're in. On the other hand, edamame, or vegetable soybeans, are small, plump pods with bright green beans inside, typically served in Japanese cuisine. Edamame has a mild, nutty flavor with a hint of sweetness and a slightly crunchy texture when cooked. While both legumes have unique qualities, lima beans are more common in diverse culinary traditions, while edamame is closely associated with Japanese dishes.
Sources
- https://diabetesjournals.org/care/article/27/8/1866/23355/Improved-Plasma-Glucose-Control-Whole-Body-Glucose
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31374573/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6543199/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11010706/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8071044/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27807734/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24871476/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4072837/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6213615/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559033/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7400945/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28392166/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32093020/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6560290/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8153313/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31037341/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29300347/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30956643/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27038352/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29277346/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6213573/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7070695/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7402084/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33208922/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Folate | 83µg | 311µg | 57% |
| Manganese | 0.516mg | 1.024mg | 22% |
| Vitamin K | 2µg | 26.7µg | 21% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.171g | 2.156g | 13% |
| Copper | 0.235mg | 0.345mg | 12% |
| Protein | 7.8g | 11.91g | 8% |
| Phosphorus | 111mg | 169mg | 8% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.055mg | 0.155mg | 8% |
| Fats | 0.38g | 5.2g | 7% |
| Vitamin C | 0mg | 6.1mg | 7% |
| Fiber | 7g | 5.2g | 7% |
| Selenium | 4.5µg | 0.8µg | 7% |
| Magnesium | 43mg | 64mg | 5% |
| Calcium | 17mg | 63mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.161mg | 0.1mg | 5% |
| Carbs | 20.88g | 8.91g | 4% |
| Zinc | 0.95mg | 1.37mg | 4% |
| Choline | 32.5mg | 56.3mg | 4% |
| Vitamin E | 0.18mg | 0.68mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.161mg | 0.2mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.421mg | 0.915mg | 3% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.034g | 1.282g | 3% |
| Potassium | 508mg | 436mg | 2% |
| Iron | 2.39mg | 2.27mg | 2% |
| Vitamin A | 0µg | 15µg | 2% |
| Saturated fat | 0.089g | 0.62g | 2% |
| Starch | 1.51g | 1% | |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.422mg | 0.395mg | 1% |
| Calories | 115kcal | 121kcal | 0% |
| Net carbs | 13.88g | 3.71g | N/A |
| Sugar | 2.9g | 2.18g | N/A |
| Sodium | 2mg | 6mg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0g | 0.009g | N/A |
| Tryptophan | 0.092mg | 0.126mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.337mg | 0.331mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.411mg | 0.3mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.673mg | 0.745mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.523mg | 0.745mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.099mg | 0.141mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.449mg | 0.488mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.469mg | 0.324mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.238mg | 0.267mg | 0% |
| Fructose | 0.12g | 0% | |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0g | 0.003g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.358g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.002g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 1.789g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Lima beans - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174253/nutrients
- Edamame - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168411/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





