Perch vs. Sunfish — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Perch provides more Vitamin C, B2, and B3 and less sodium than sunfish. On the other hand, sunfish is relatively richer in Folate, copper, and Vitamin A. Also, it contains less cholesterol than perch.
Introduction
We'll discuss the main nutritional differences between perch and sunfish and their impact on human health.
What's The Actual Difference?
The ocean sunfish, known as the common mola, is the world's heaviest bony fish. While sunfish belongs to the Molidae family, perch belong to the Percidae family.
Sunfish is bigger than perch, has a crisp and mild taste, and its skin may hint at bitterness, whereas the flavor of perch is sweet, and the texture is firm and crumbly.
NUTRITION
The food types discussed in this article are raw perch and raw sunfish with pumpkin seeds. You can look at nutrition infographics at the bottom of the page to better understand their differences.
Calories
Both perch and sunfish are considered moderate-calories foods and have almost equal numbers of calories.
Perch has 117 calories per 100g, and sunfish has 114 calories per 100g.
Minerals
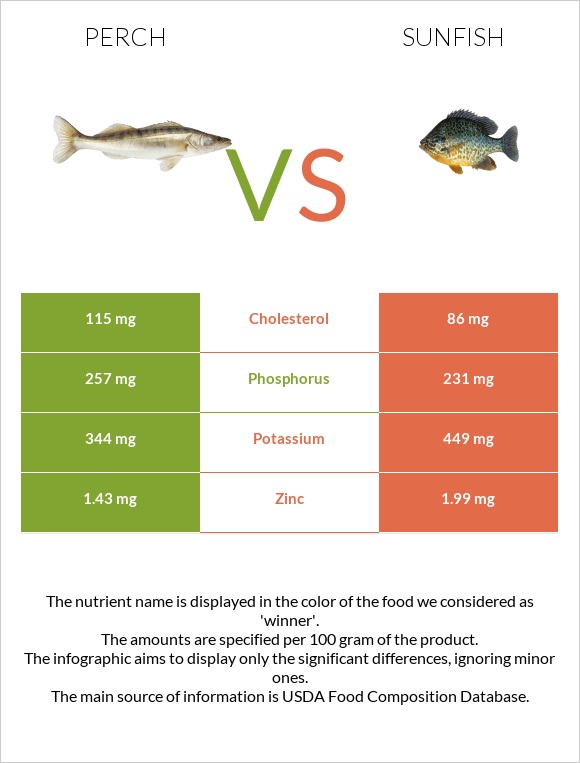
Sunfish is relatively richer in minerals than perch. It is richer in zinc and iron, potassium, and copper.
On the other hand, perch contains less sodium and more phosphorus.
Both fiches contain equal amounts of calcium and magnesium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+11.3%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-23.3%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+30.5%
Contains
more
IronIron
+32.8%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+100.5%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+39.2%
Vitamins
Perch provides more Vitamin C, Vitamin B2, and Vitamin B3.
Nevertheless, sunfish has more Folate, Vitamin B1, and Vitamin A.
Both fishes have an equal amount of Vitamin B5, Vitamin B6, and Vitamin B12.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+70%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+41.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+30%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+70%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+15%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+183.3%
Fats
Both perch and sunfish have tiny amounts of fat.
Protein
The amounts of protein in perch and sunfish are equal: 25 g. Both are rich in essential amino acids, such as tryptophan, lysine, histidine, and threonine.
Cholesterol
Perch provides more cholesterol than sunfish. It has 115 mg of cholesterol per 100g, while sunfish contains 86 mg per 100g.
HEALTH IMPACT
Health Benefits
Both perch and sunfish are high in omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-triglyceridemic, hemostatic, and anti-atherogenic properties and can help improve the heart's structure and function [1].
Also, perch is rich in gamma-tocopherol (gT), which has anti-inflammatory properties and benefits the cardiovascular system. Its antioxidant also may help reduce LDL cholesterol oxidation and increases HDL cholesterol levels [2]. Sunfish also has decent levels of Folate and potassium, which can help to regulate the heartbeat, ensure proper muscle and nerve function, and are required for protein synthesis and carbohydrate metabolism [3].
Side Effects
Sunfish contains a high amount of mercury. Excessive mercury intake is toxic and can result in neurological, cardiovascular, and behavioral issues. It could be unsafe for children. As a result, it is best to consume sunfish in moderation [4].
Perch is high in purines, which can cause kidney stones. A high purine intake causes increased uric acid production, and this concentration promotes the formation of uric acid stones [5].
Besides, if consumed in high amounts, these fish can cause gas and bloat. These fishes also contain salicylates and a compound known as amygdalin, which may cause allergic reactions in some people [6].
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6742725/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3712371/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8614638/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6923298/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18589026/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9397527/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Copper | 0.192mg | 0.385mg | 21% |
| Cholesterol | 115mg | 86mg | 10% |
| Iron | 1.16mg | 1.54mg | 5% |
| Zinc | 1.43mg | 1.99mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B12 | 2.2µg | 2.31µg | 5% |
| Phosphorus | 257mg | 231mg | 4% |
| Potassium | 344mg | 449mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.12mg | 0.085mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B3 | 1.9mg | 1.462mg | 3% |
| Folate | 6µg | 17µg | 3% |
| Vitamin C | 1.7mg | 1mg | 1% |
| Sodium | 79mg | 103mg | 1% |
| Vitamin A | 10µg | 17µg | 1% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.08mg | 0.092mg | 1% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.472g | 0.315g | 1% |
| Calories | 117kcal | 114kcal | 0% |
| Protein | 24.86g | 24.87g | 0% |
| Fats | 1.18g | 0.9g | 0% |
| Magnesium | 38mg | 38mg | 0% |
| Calcium | 102mg | 103mg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.9mg | 0.897mg | 0% |
| Selenium | 16.1µg | 16.2µg | 0% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.87mg | 0.865mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.14mg | 0.138mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.237g | 0.178g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.195g | 0.15g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.278mg | 0.279mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 1.09mg | 1.09mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 1.145mg | 1.146mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 2.02mg | 2.022mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 2.283mg | 2.284mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.736mg | 0.736mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.97mg | 0.971mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.281mg | 1.281mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.732mg | 0.732mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.101g | 0.047g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.223g | 0.092g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.036g | 0.042g | N/A |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more FatsFats | +31.1% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +39.2% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +30% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +49.8% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -24.9% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Perch - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173679/nutrients
- Sunfish - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172003/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






