Pinto beans vs. White beans — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
In summary, pinto beans and white beans are good sources of carbs and protein. Pinto beans are high in phosphorus, selenium, folate, and vitamin C. White beans, on the other hand, provide more potassium, calcium, and magnesium. Moreover, white beans are slightly high in protein content. They also contain more net carbs and less saturated fats, whereas pinto beans are high in fiber, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated fats. Pinto beans provide more calories and lower sodium content.
Introduction
Pinto beans and white beans are legumes. Both are part of the Phaseolus vulgaris species and belong to the family Fabaceae.
The inside of white beans is often ivory or pale yellow, while the outside skin is off-white. Pinto beans have reddish-brown backgrounds with dark-brown flecks.
Appearance
Pinto beans are medium-sized, whereas white beans can range in size from small to large.
Pinto beans are native to Mexico. Depending on the type and the area, white beans might have different origins and methods of growing.
Taste and Use
White beans have a milder flavor and a creamy, buttery texture, whereas pinto beans have a slightly earthy and nutty flavor. You can use white beans in salads, soups, stews, and side dishes. Pinto beans, on the other hand, may use for burritos.
Varieties
Navy beans, Great Northern beans, Cannellini beans, and Lima beans are common varieties of white beans. They are different in size, shape, and taste.
The most common varieties of pinto beans are Álava, Burke, Grand Mesa, Kodiak, and Othello.
Nutrition
In this part of the article, we will compare the nutritional values of pinto beans and white beans.
Macronutrients and Calories
Pinto beans are high in calories, fats, and fiber. White beans, on the other hand, are slightly high in net carbs and protein content.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+85.7%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+49.6%
Calories
Pinto beans provide more calories per 100 g compared to white beans. Pinto beans provide 143 calories, whereas white beans contain 139 calories.
Protein
Pinto beans contain 9.01g of protein per hundred grams, whereas the same amount of white beans provides 9.73g. Both contain all essential amino acids in small amounts.
Fats
Pinto beans and white beans contain less than 1g of fat. A hundred grams of pinto beans contain 0.65g of fat, whereas white beans provide only 0.35g. Pinto beans contain more monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, whereas white beans provide less saturated fats.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+329%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+54.6%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-33.1%
Carbohydrates
A hundred grams of pinto beans contain 26.22g of carbs, of which 9g are dietary fiber and 17.22g are net carbs.
A hundred grams of white beans contain 25.09g of carbohydrates, of which 6.3g are dietary fiber and 18.79g are net carbs.
Pinto beans are high in fiber content, whereas white beans are high in net carbs.
Pinto beans and white beans are cholesterol-free.
Vitamins
Pinto and white beans are not good sources of vitamins. Pinto beans provide more vitamins C, B2, B3, B6, and folate. Both have equal amounts of vitamins E, and K. Pinto beans and white beans do not contain vitamins A, D, and B12.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+63.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+34.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+127.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+146.2%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+112.3%
Minerals
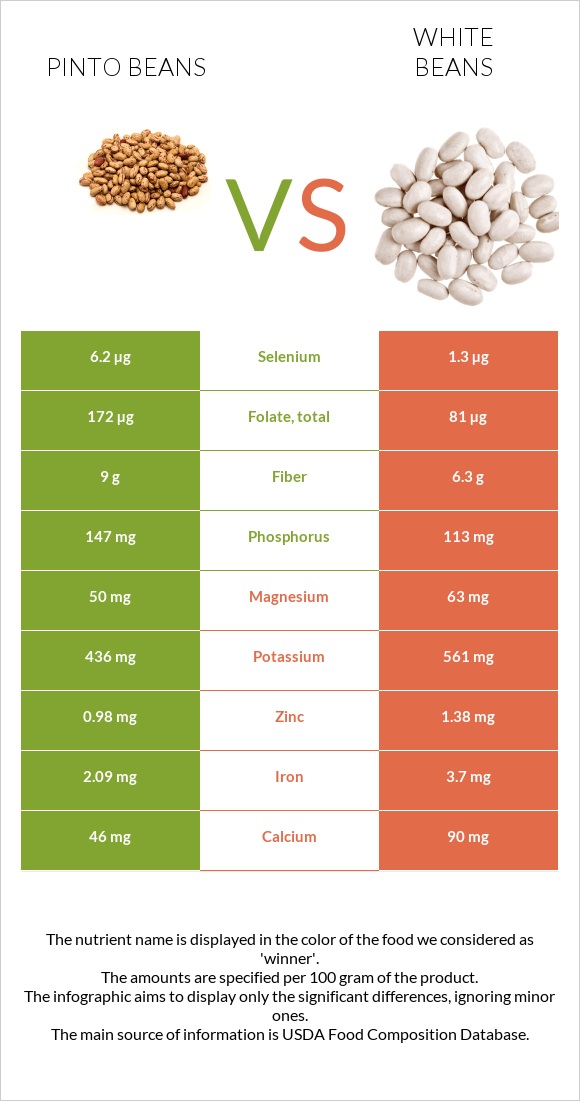
Pinto beans are high in phosphorus and selenium. White beans, on the other hand, contain more potassium, calcium, magnesium, iron, and zinc. Moreover, compared to white beans, pinto beans contain six times less sodium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+30.1%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-83.3%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+376.9%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+26%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+95.7%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+28.7%
Contains
more
IronIron
+77%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+31.1%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+40.8%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+40.4%
Acidity
The potential renal acid load, or PRAL, determines how much acid or base a food produces inside the body.
Pinto beans have a PRAL rating of -1.2, whereas white beans have a PRAL value of -5.6. Pinto beans and white beans are alkaline.
Weight Loss & Diets
Pinto beans and white beans are good choices for DASH diets due to their low fat and high protein content.
Pinto beans and white beans are not good options for paleo and keto diets because of their high carb content.
Moreover, pinto beans and white beans are excellent choices for the Mediterranean diet.
Health Benefits
Obesity
White kidney bean extract may inhibit the enzyme α-amylase, limiting carbohydrate absorption and digestion(1). So it has metabolic effects. Regular intake of white beans may induce weight loss(2). The high dietary fiber content in pinto beans may lower the risk of obesity(3).
Diabetes
White kidney bean extract may also decrease complications of diabetes(4). According to the research, pinto beans and rice consumption reduces the glycemic response(5).
Cardiovascular Health
Pinto beans are a good source of dietary fiber, which has some advantageous health impacts. A high dietary fiber intake decreases the risk of coronary heart disease, hypertension, and stroke(3).
Furthermore, white and pinto beans are also known to decrease LDL cholesterol(6)(7).
Digestive Health
Pinto beans and white beans have a protective impact on gut microbiota and gut inflammatory indicators(7)(8). Pinto beans also have prebiotic effects(7).
Cancer
People who use a lot of beans have a lower risk of cancer and chronic degenerative disorders. Bean intake is related to a lower risk of cancer in human populations. In animal models, bean consumption reduces carcinogenesis and induces apoptosis(9).
Sources
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32414090/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32180941/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19335713/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36303868/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22494488/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17951475/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6574449/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7915747/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5302293/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Folate | 172µg | 81µg | 23% |
| Iron | 2.09mg | 3.7mg | 20% |
| Fiber | 9g | 6.3g | 11% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.229mg | 0.093mg | 10% |
| Selenium | 6.2µg | 1.3µg | 9% |
| Copper | 0.219mg | 0.287mg | 8% |
| Manganese | 0.453mg | 0.636mg | 8% |
| Starch | 15.15g | 6% | |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.193mg | 0.118mg | 6% |
| Phosphorus | 147mg | 113mg | 5% |
| Calcium | 46mg | 90mg | 4% |
| Potassium | 436mg | 561mg | 4% |
| Zinc | 0.98mg | 1.38mg | 4% |
| Magnesium | 50mg | 63mg | 3% |
| Protein | 9.01g | 9.73g | 1% |
| Vitamin C | 0.8mg | 0mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.062mg | 0.046mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.318mg | 0.14mg | 1% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.235g | 0.152g | 1% |
| Calories | 143kcal | 139kcal | 0% |
| Fats | 0.65g | 0.35g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 17.22g | 18.79g | N/A |
| Carbs | 26.22g | 25.09g | 0% |
| Sugar | 0.34g | 0.34g | N/A |
| Sodium | 1mg | 6mg | 0% |
| Vitamin E | 0.94mg | 0.94mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.21mg | 0.229mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 3.5µg | 3.5µg | 0% |
| Choline | 35.3mg | 35.1mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.136g | 0.091g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.133g | 0.031g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.108mg | 0.115mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.331mg | 0.409mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.426mg | 0.429mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.765mg | 0.776mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.63mg | 0.668mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.117mg | 0.146mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.531mg | 0.526mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.519mg | 0.509mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.247mg | 0.271mg | 0% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Pinto beans - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/175200/nutrients
- White beans - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/175203/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.