Pizza Sauce vs. Marinara Sauce — Nutrition Comparison and Health Impact


Summary
Pizza sauce has a thicker consistency and tends to have relatively more ingredients, but it is mainly used for pizzas. In contrast, marinara sauce is more versatile and may be used as a dipping sauce, pasta sauce, spaghetti sauce, or topping.
Pizza sauce is slightly higher in total carbs, dietary fiber, and proteins. Marinara sauce is slightly higher in fats. Pizza sauce is 5.5 times richer in vitamin C; it is also richer in vitamin B1. In contrast, marinara sauce is 2.7 times richer in vitamin B3.
Introduction
Pizza and marinara sauces are tomato-based sauces - similar but not the same. Both are Italian sauces first mentioned in the 16th century. Pizza sauce originated in Naples, whereas the exact location where marinara sauce originated is uncertain; however, it’s most likely either Naples or Sicily in Northern Italy.
In this article, we will compare the two sauces and learn about their differences.
General Differences
Ingredients
Pizza sauce is usually well-seasoned to provide a strong flavor and taste. It mainly contains chopped tomatoes, garlic ( or garlic powder), onions ( or onion powder), cheese, oil, sugar, salt, capers, olives, herbs, spices, such as basil, thyme, oregano, and black pepper.
Marinara sauce is another type of tomato sauce. It is commonly made with tomatoes, garlic (also garlic cloves or powder), onions, red pepper flakes or crushed red pepper, and herbs, such as fresh basil leaves and oregano, black pepper, and olive oil.
Whether the tomatoes may be in the form of crushed tomatoes, canned tomatoes, tomato sauce, or tomato paste is a matter of preference.
The ingredients vary depending on the recipe and dish; thus, either sauce can have a more complex flavor.
Consistency & Usage
Pizza sauce has a thicker consistency than marinara sauce. Its thick consistency is great for the pizza dough as it doesn’t make the pizza crust soggy.
Marinara sauce is served as a dipping sauce, pasta sauce, spaghetti sauce, or topping. It may be served with mozzarella sticks, pasta dishes, homemade pizzas, meatballs, ground beef, and Italian sausage.
Despite having different ingredients and textures, they can still be substituted for each other.
Nutrition
In this section, we will compare the nutritional content of both these foods based on 100g.
The marinara sauce used in this article is low in sodium.
The nutritional profile of pizza sauce and marinara sauce will change depending on the ingredients.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+54.6%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+28.7%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+27.7%
Calories
Both sauces provide similar amounts of calories. They are categorized as low-calorie foods since they provide nearly 50 calories per 100g.
Carbs
Carbs are the predominant macronutrient in sauces, with pizza sauce being slightly higher in total carbs and dietary fiber.
Pizza sauce contains 8.7g of total carbs, of which 2g is dietary fiber. Comparably, marinara sauce contains 8g of total carbs, of which 1.8g is dietary fiber.
Protein
Pizza sauce is richer in protein; however, the protein content of pizza sauce and marinara is not very relevant, as it is 2.18g in pizza sauce and 1.41g in marinara sauce.
Fat
They have similar amounts of fats and are categorized as low, containing less than 2g of fats per 100g.
Minerals
Pizza sauce has a richer mineral profile than marinara sauce. Pizza sauce is richer in iron, copper, calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, zinc, and copper. Marinara sauce contains some amounts of selenium.
Below we can see the comparative diagram of their mineral profiles. As mentioned above, the marinara sauce used in this article is low-sodium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+16.7%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+100%
Contains
more
IronIron
+15.4%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+69.1%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+25%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+47.1%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+61.3%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-91.4%
Vitamins
Pizza and marinara sauces are good sources of vitamin A and vitamin B6. Pizza sauce is 5.5 times richer in vitamin C, while marinara sauce is 2.7 times richer in vitamin B3.
Pizza sauce is also richer in vitamin B1, while marinara sauce is a good source of fat-soluble vitamin K and vitamin E, the contents of which are unknown for pizza sauce.
We can see the comparative diagram of their vitamin profiles.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+465%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+154.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+15.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+175.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+27.2%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+30%
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index values of pizza sauce and marinara sauce are not calculated. However, you can learn about the glycemic indices of most ingredients by visiting our “Glycemic index chart” page.
You may also visit our “Insulin index chart of 140+ foods” page for additional information.
Weight Loss & Diets
Vegan
Vegans can eat both marinara sauce and pizza sauce. In addition, vegan cheeses are available to make pizzas and pasta.
Several pizza sauces are not vegan; thus, the vegan option should be labeled as such on the packaging.
Keto
The sauces are allowed on the keto diet in low amounts.
The main concern comes with the dough in the case of pizza or pasta. There are alternatives to wheat flour dough low in carbs for keto diets.
Weight Loss
Pizza sauce and marinara can be used during weight loss diets as they are low in calories and consumed in low amounts. It is important to mention that while undergoing a diet, the food that the person eats must make one happy or give a good feeling of satisfaction; otherwise, the diet won't work long.
Health Impact
Since these foods are sauces, it would be more relevant to consider their health impacts in their usages. It is more relevant to speak about pizzas and pasta and compare their health impacts when it comes to that.
Here is linked our article related to the comparison of pizza vs. pasta.
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin E | 2.4mg | 16% | |
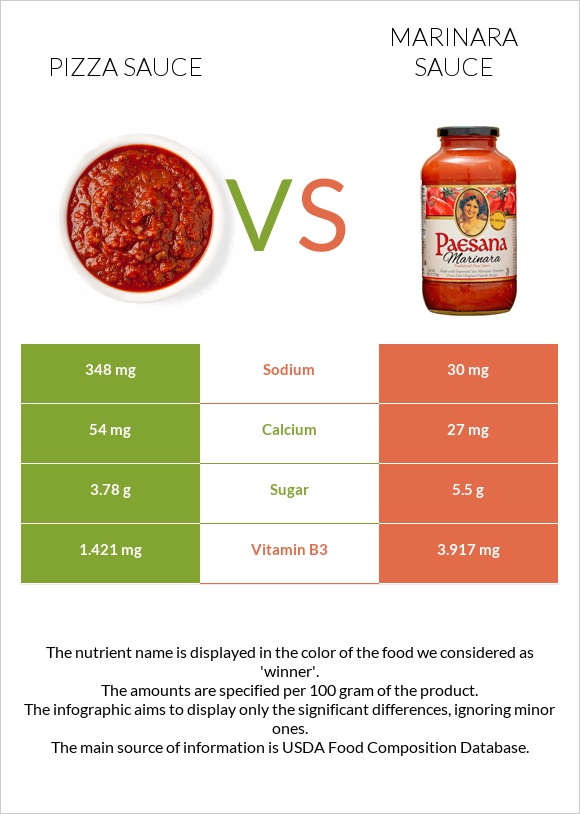
| Vitamin B3 | 1.421mg | 3.917mg | 16% |
| Sodium | 348mg | 30mg | 14% |
| Vitamin K | 13.9µg | 12% | |
| Vitamin C | 11.3mg | 2mg | 10% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.374mg | 7% | |
| Copper | 0.137mg | 0.081mg | 6% |
| Vitamin A | 33µg | 4% | |
| Manganese | 0.221mg | 0.137mg | 4% |
| Calcium | 54mg | 27mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.061mg | 0.024mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.136mg | 0.173mg | 3% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.099g | 0.508g | 3% |
| Protein | 2.18g | 1.41g | 2% |
| Iron | 0.9mg | 0.78mg | 2% |
| Phosphorus | 50mg | 34mg | 2% |
| Selenium | 1.1µg | 2% | |
| Choline | 13.7mg | 2% | |
| Fats | 1.15g | 1.48g | 1% |
| Cholesterol | 0mg | 2mg | 1% |
| Magnesium | 21mg | 18mg | 1% |
| Potassium | 354mg | 319mg | 1% |
| Fiber | 2g | 1.8g | 1% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.053mg | 0.061mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.02µg | 0µg | 1% |
| Folate | 10µg | 13µg | 1% |
| Saturated fat | 0.46g | 0.17g | 1% |
| Calories | 54kcal | 51kcal | 0% |
| Net carbs | 6.66g | 6.26g | N/A |
| Carbs | 8.66g | 8.06g | 0% |
| Sugar | 3.78g | 5.5g | N/A |
| Zinc | 0.25mg | 0.2mg | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.461g | 0.377g | 0% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +22.3% |
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -63% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +413.1% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Pizza sauce - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/172880/nutrients
- Marinara sauce - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171597/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





