Pomegranate vs. Passion fruit — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Passion fruit is higher in calories, minerals, fiber, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, Vitamin A, and vitamin C, while pomegranate is richer in zinc and vitamin K. Pomegranates also have less sodium.
Introduction
This article will compare Passion fruit and Pomegranate, focusing on their nutritional content and health impact. Here we will discuss the differences between raw passion fruits and raw pomegranates.
Macronutrients
Although Passion fruit and Pomegranate have more than 70% water, they differ in the distribution of various macronutrients. The quantities of nutrients they provide are shown and described below.
Calories
Passion fruits are higher in calories than pomegranates.
Carbs
In terms of carbs, Passion fruit is higher compared to Pomegranate.
Passion fruit provides 10.4g of dietary fiber per 100g, while the same serving of Pomegranate contains only 4g of it.
Passion fruits are especially rich in soluble fiber. Pomegranate is higher in net carbs: 100g has 14.7g of net carbs, while the same amount of Passion fruit contains 13g.
Protein
Passion fruit and Pomegranates are not animal food products. Hence, they are not supposed to contain much protein. Still, Passion fruit is higher in proteins than Pomegranate, but this difference is insignificant.
Vitamins
The two fruits are rich in different vitamins.
Passion fruit is an excellent source of vitamin C: it is three times higher in vitamin C (30mg per 100g) than Pomegranate (10mg per 100g).
Pomegranate is richer in vitamins B1, E, and K, while Passion fruit provides more vitamins B2, B3, B6, and A.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+2900%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+2242.9%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+171.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+194.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+145.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+411.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+33.3%
Minerals
Passion fruit is the winner in this section. It is higher in calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, iron, and potassium.
Pomegranate is higher in zinc and is lower in sodium.
You can check the mineral composition of these two fruits in the chart below.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+83.7%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+250%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-89.3%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+∞%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+141.7%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+20%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+47.5%
Contains
more
IronIron
+433.3%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+88.9%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+20%
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index of pomegranate is unknown, but existing research allows us to infer its impact on blood glucose levels. According to The International Tables of Glycemic Index, pomegranate juice from Australia has a glycemic index of 53, classifying it as low on the glycemic index scale (1) (2).
The glycemic index of passion fruit is equal to 16, which is classified as low GI.
Health Impact
Antioxidants
Antioxidants are chemicals that fight against oxidative stress, a process that causes cellular damage, various diseases, and premature aging (3).
Both Passion fruit and Pomegranate contain antioxidants, but the two fruits' antioxidant capacities are linked to different chemicals.
Pomegranates provide anthocyanins, hydrolyzable tannins, and punicalagin (4) (5).
Passion fruit contains other antioxidants: vitamin C, beta carotene, and polyphenols. Polyphenols have anti-inflammatory effects (6), and vitamin C supports the immune system (7).
Cancer
According to a study, pomegranate fruit, juice, and extract can kill cancer cells or inhibit their spread in the body (8). Pomegranate juice showed the property of reducing the risk of death from prostate cancer (9).
Due to their beta-carotene content, passion fruits are involved in lowering the risk of stomach, prostate, colon, and breast cancers (10) (11) (12) (13).
Cardiovascular Health
Passion fruit and pomegranate may decrease the risk of coronary heart disease by lowering endothelial dysfunction. They contain polyphenols, which have antiatherosclerotic effects because they reduce the concentration of free active radicals, which can damage vascular endothelial cells (14).
Passion fruit contains piceatannol, which may decrease the concentration of total cholesterol and triglyceride levels (15). Pomegranate juice consumption may lower LDL (bad cholesterol) levels in the blood (16,17).
Regularly incorporating these fruits into your diet may help reduce cardiovascular risk.
References
- https://glycemicindex.com/gi-search/ food_name=pomegranate%20juice
- The glycemic index (GI)
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6316255/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28125044/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28867799/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25616409/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16373990/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23359482/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16818701/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12010859/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14973107/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17284749/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10648274/
- https://researchmap.jp/7000012136/published_papers/33281381/attachment_file.pdf
- https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2016/fo/c6fo01067a/unauth
- https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2018.00544/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23908863/
Infographic
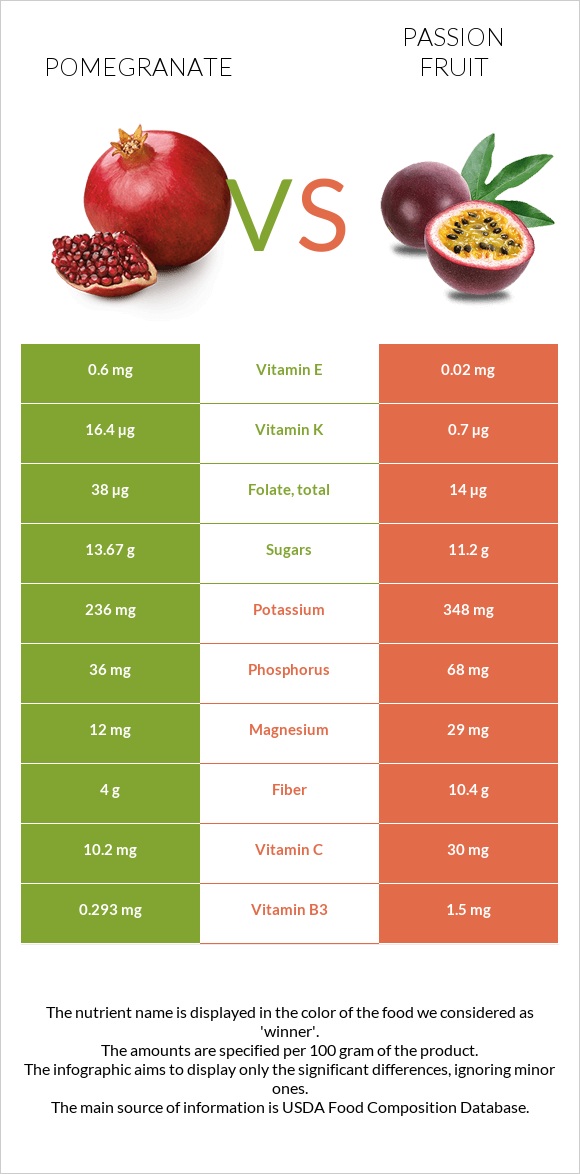
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Fiber | 4g | 10.4g | 26% |
| Vitamin C | 10.2mg | 30mg | 22% |
| Iron | 0.3mg | 1.6mg | 16% |
| Vitamin K | 16.4µg | 0.7µg | 13% |
| Copper | 0.158mg | 0.086mg | 8% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.293mg | 1.5mg | 8% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.377mg | 8% | |
| Vitamin A | 0µg | 64µg | 7% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.067mg | 0mg | 6% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.053mg | 0.13mg | 6% |
| Folate | 38µg | 14µg | 6% |
| Phosphorus | 36mg | 68mg | 5% |
| Manganese | 0.119mg | 5% | |
| Magnesium | 12mg | 29mg | 4% |
| Vitamin E | 0.6mg | 0.02mg | 4% |
| Potassium | 236mg | 348mg | 3% |
| Carbs | 18.7g | 23.38g | 2% |
| Zinc | 0.35mg | 0.1mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.075mg | 0.1mg | 2% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.079g | 0.411g | 2% |
| Calories | 83kcal | 97kcal | 1% |
| Protein | 1.67g | 2.2g | 1% |
| Fats | 1.17g | 0.7g | 1% |
| Sodium | 3mg | 28mg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 14.7g | 12.98g | N/A |
| Calcium | 10mg | 12mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 13.67g | 11.2g | N/A |
| Selenium | 0.5µg | 0.6µg | 0% |
| Choline | 7.6mg | 7.6mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.12g | 0.059g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.093g | 0.086g | 0% |
Macronutrient Comparison
| Contains more FatsFats | +67.1% |
| Contains more ProteinProtein | +31.7% |
| Contains more CarbsCarbs | +25% |
| Contains more OtherOther | +49.1% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -50.8% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +420.3% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Pomegranate - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169134/nutrients
- Passion fruit - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169108/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.





