Strawberry vs. Banana — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Introduction
Strawberries and bananas are two delicious and healthy fruits that are popular worldwide. Everything you need to know about their differences can be found in this article.
Table of contents
Classification
Strawberries were first cultivated in Europe in the 18th century, while bananas, which are members of the Musa family of plants, are native to Southeast Asia.
Both fruits are grown in warmer sections of the world, although strawberries are able to endure a wider range of climatic conditions, while bananas are mainly found in tropical areas.
Appearance
The texture and form of the strawberries and bananas are two key differences. Strawberry flesh is small and slightly rough, while the flesh of a banana is lengthy and creamy.
Bananas come in a wide variety of shapes and sizes, with colors that typically vary from green to yellow, though some might be red. On the other hand, strawberries are known for their bright red color and unique shape.
Taste and use
The flavors of strawberries and bananas also differ. Strawberries have a tangy and slightly sweet flavor, but bananas have a sweet, almost creamy flavor.
Compared to strawberries, which are frequently used in desserts, jams, and sauces but can also be eaten fresh, bananas are typically eaten on their own or used in cooking and baking.
Nutrition
The banana and the strawberry are great providers of fiber, vitamins, and minerals, making them a nutritious addition to any diet.
Macronutrients and calories
In comparison to strawberries, bananas contain more protein, more carbohydrates, and more "other" nutrients. Strawberries, on the other hand, contain more water than bananas. The 0.3 g of fat in each of the two fruits is the same.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
WaterWater
+21.4%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+62.7%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+197.4%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+107.5%
Calories
100 grams of a strawberry normally have 32 calories, while 100 grams of a banana typically have 89 calories.
As a result, a banana has 2.8 times the calories of a strawberry in 100 grams.
Protein
Protein content per 100 grams is roughly 1.6 times higher in bananas than in strawberries.
Fats
Bananas have nearly no saturated fat and just a small amount of polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fat. They are extremely low in fat. While strawberries also have a very low-fat content, they do so with a higher concentration of polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats and even less saturated fat. In particular, strawberries have roughly twice the amount of polyunsaturated fat and one-third more monounsaturated fat than bananas, yet strawberries have approximately seven times less saturated fat. Because of this, despite the fact that both fruits are low in fat, strawberries have a larger percentage of good fats than bananas.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-86.6%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+34.4%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+112.3%
Carbohydrates
While a 100-gram serving of strawberry has 7.68 grams of carbohydrates, a 100-gram serving of banana has 22.84 grams. Compared to strawberries' single form of carbs, bananas have five different types.
Strawberries have no measurable levels of maltose, lactose, or galactose, but bananas have significantly larger amounts of starch, sucrose, glucose, and fructose.
More specifically, compared to strawberries, bananas have 140 times the starch, 5 times the sucrose, and 2 times the glucose and fructose.
Carbohydrate type comparison
Contains
more
StarchStarch
+13350%
Contains
more
SucroseSucrose
+408.5%
Contains
more
GlucoseGlucose
+150.3%
Contains
more
FructoseFructose
+98.8%
Contains
more
MaltoseMaltose
+∞%
Vitamins
Strawberries are higher in vitamin K (4 times more), folate, and C (7 times more). Compared to strawberries, bananas are higher in vitamin B6 (8 times more), vitamin B5 (3 times more), vitamin B2 (2 times more), vitamin B3 (2 times more), vitamin B1, and vitamin A (5 times more). Both fruits lack vitamin B12 and vitamin D.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+575.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+190%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+340%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+20%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+200%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+29.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+231.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+72.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+167.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+680.9%
Fibers and other plant compounds
Both strawberries and bananas are good sources of dietary fiber, with bananas having higher concentrations of resistant starch and pectin. Strawberries contain soluble and insoluble fiber. Strawberries' carbohydrate content is primarily made up of fiber and simple sugars, whereas bananas have a higher proportion of total carbohydrates.
Bananas have dopamine and catechin as their prominent plant chemicals, while strawberries are rich in anthocyanins, ellagic acid, ellagitannins, and procyanidins.
Minerals
Bananas are substantially richer in magnesium, potassium (twice as much), and copper than strawberries, which have a greater calcium and iron concentration. But phosphorus, sodium, and zinc are equal.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+220%
Contains
more
IronIron
+57.7%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+43%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+107.7%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+134%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+62.5%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+150%
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index of a banana is around 48. Strawberries have a relatively low glycemic index, around 40.
Glycemic Load
100 grams of strawberries have approximately a 3 glycemic load. The glycemic load of a medium-sized banana is approximately 15.
Insulin Index
The insulin index of bananas is 82. Information about the insulin index of strawberries is unknown.
Acidity
Bananas have a slightly higher alkaline effect (-6.9) compared to strawberries (-2.5).
Weight Loss and Diets
As strawberries and bananas are low in fat and calories, they are great for weight loss. The fiber in bananas and strawberries can help you feel fuller for longer and reduce cravings. Resistant starch found in bananas can help boost your metabolism and burn fat.
Health Impact
Both fruits have special health benefits, with bananas popular for their nutrient content and potential effects on weight management, digestion, and heart health, and strawberries being known specifically for their anti-inflammatory characteristics.
Cardiovascular Health
Due to their nutrient contents, strawberries and bananas can both be advantageous for heart health. Potassium, an essential mineral that helps control blood pressure and heart function, is found in bananas insignificantly (1). Strawberries are rich in antioxidants, especially anthocyanins, which have been found to lower inflammation and enhance heart health (2). In addition, bananas contain antioxidant flavonoids, which are also associated with a significant decrease in heart disease risk (3). Strawberries may also reduce the risk of atherosclerosis since they drastically reduce total and LDL (bad) cholesterol levels in the blood (4).
Bananas, which contain potassium and antioxidant flavonoids, and strawberries, which are abundant in anthocyanins that reduce inflammation and cholesterol levels, both have benefits for heart health.
Blood sugar regulation
Both strawberries and bananas have potential advantages for controlling blood sugar levels. Bananas include resistant starch, which is not digested by the body, and soluble fiber, which can gel during digestion. These two fibers may normalize blood sugar levels after meals and control hunger by delaying the stomach (5).
Similarly, strawberries have been shown to lower rises in insulin and glucose levels after a meal high in carbohydrates, suggesting potential advantages for reducing metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes (6).
Digestive Health
Bananas and strawberries contain dietary fiber, which is helpful for digestion by avoiding constipation and allowing regular bowel movements.
In addition to being an excellent source of resistant starch, which is prebiotic that feeds the good bacteria in your gut, bananas are a wonderful source of soluble fiber (7).
Pectin, another kind of fiber included in bananas, may aid in preventing constipation and may even have anti-cancer properties (8).
In a similar vein, strawberries contain polyphenols, which help support healthy gut flora and have prebiotic effects. They are also a rich source of dietary fiber (9). Strawberries may even have anti-inflammatory effects in the gut, perhaps aiding in the treatment of digestive diseases, according to certain animal research.
Cancer
Bananas and strawberries contain minerals and substances that have been researched for their potential ability to prevent cancer.
Bananas include lectins, which are active proteins that interact with cancer cells and inhibit their proliferation. This, in turn, slows the spread and metastasis of cancer (10). On the other side, strawberries have been discovered to possess anti-cancer effects possibly. They include ellagitannins and ellagic acid, which have been demonstrated to inhibit the proliferation of cancer cells and prevent the development of tumors (11). Studies on human liver cancer cells and oral cancer models in animals have shown these effects.
Downsides and Risks
People who are allergic to latex may also be allergic to bananas due to cross-reactivity (12). Although allergies to strawberries are quite prevalent, especially in young children, strawberries are often well tolerated. Both allergies frequently cause mouth tingling or itching, hives, headaches, swelling of the lips, face, tongue, or throat, as well as potentially serious breathing difficulties (13). Strawberries also contain goitrogens, which may interfere with thyroid function in people who already have thyroid issues (14).
Summary
Strawberries are richer in vitamin C and manganese, while bananas are richer in potassium and vitamin B6. In comparison to bananas, strawberries have a 56% higher daily need for vitamin C. Bananas contain eight times as much vitamin B6 as strawberries do. Strawberries have less sugar than bananas.
Sources.
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21403995/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22211184/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23953879/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0271531710001296
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2898027/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19930765/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32040399/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33357885/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24876314/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6272006/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20626254/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12440950/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19940506/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6198931/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
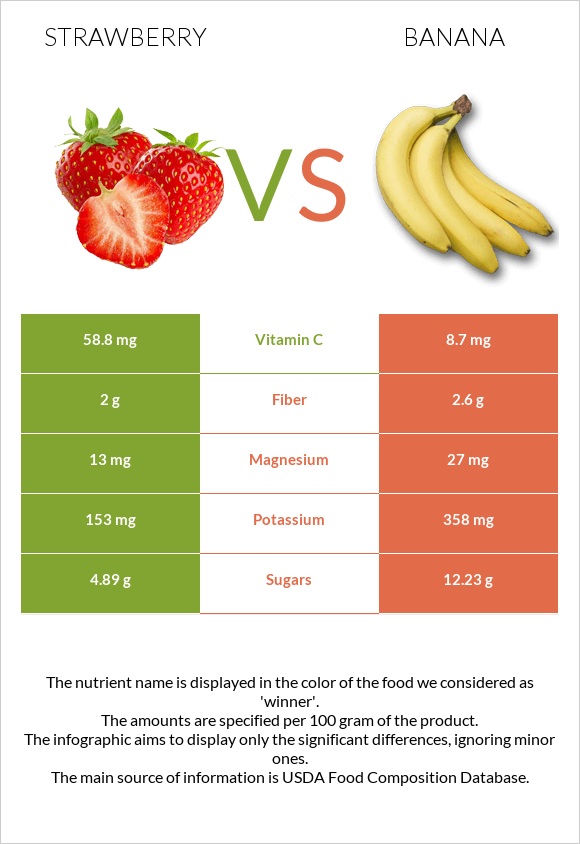
| Vitamin C | 58.8mg | 8.7mg | 56% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.047mg | 0.367mg | 25% |
| Potassium | 153mg | 358mg | 6% |
| Carbs | 7.68g | 22.84g | 5% |
| Manganese | 0.386mg | 0.27mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.022mg | 0.073mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.125mg | 0.334mg | 4% |
| Calories | 32kcal | 89kcal | 3% |
| Magnesium | 13mg | 27mg | 3% |
| Copper | 0.048mg | 0.078mg | 3% |
| Fructose | 2.44g | 4.85g | 3% |
| Iron | 0.41mg | 0.26mg | 2% |
| Fiber | 2g | 2.6g | 2% |
| Starch | 0.04g | 5.38g | 2% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.386mg | 0.665mg | 2% |
| Protein | 0.67g | 1.09g | 1% |
| Calcium | 16mg | 5mg | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 0.29mg | 0.1mg | 1% |
| Selenium | 0.4µg | 1µg | 1% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.024mg | 0.031mg | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 2.2µg | 0.5µg | 1% |
| Folate | 24µg | 20µg | 1% |
| Choline | 5.7mg | 9.8mg | 1% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.155g | 0.073g | 1% |
| Fats | 0.3g | 0.33g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 5.68g | 20.24g | N/A |
| Sugar | 4.89g | 12.23g | N/A |
| Zinc | 0.14mg | 0.15mg | 0% |
| Phosphorus | 24mg | 22mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 1mg | 1mg | 0% |
| Vitamin A | 1µg | 3µg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.015g | 0.112g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.043g | 0.032g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.008mg | 0.009mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.02mg | 0.028mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.016mg | 0.028mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.034mg | 0.068mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.026mg | 0.05mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.002mg | 0.008mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.019mg | 0.049mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.019mg | 0.047mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.012mg | 0.077mg | 0% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Strawberry - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/167762/nutrients
- Banana - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173944/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.