Navy beans vs. White beans — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Navy beans are higher in selenium, choline, and vitamin B9. They are also higher in dietary fiber, while white beans are higher in net carbs, vitamin E, and iron.
White beans contain over six times more vitamin K, while navy beans contain two times more vitamin B1.
Introduction
Navy beans and white beans belong to the family Phaseolus. Navy beans are one of the most popular types of small white beans. Navy beans are oval-shaped, small, and have a smooth surface. They're about the size of a pea.
The color of white beans is white, while navy beans are closer to ivory than white.
Taste
White beans have a mellow, somewhat nutty flavor, whereas navy beans have a mild taste and a soft texture. It is most common to use navy beans in American cuisine. They go well with soups and stews, while white beans are the best choices for salads.
Nutrition
We will compare the nutritional information of navy beans and white beans in this part of the article.
Macronutrients and Calories
Navy beans contain slightly more carbs and fats, while white beans contain more protein.
Navy beans are over 1.5 times richer in dietary fiber, while white beans are higher in net carbs.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+18.2%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+35.7%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+77.1%
Calories
Navy beans and white beans are both providing a similar amount of calories. A hundred grams of navy beans contain 140 calories, while the same amount of white beans has 139 calories.
Protein
A hundred grams of navy beans contain 8.23g of protein, while same-size white beans have 9.73 g.
Although navy beans and white beans contain all essential amino acids, white beans are richer in all essential amino acids.
Fats
White beans and navy beans have very little fat content. Navy beans contain slightly more monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, while white beans contain less saturated fats. Navy beans and white beans do not contain trans fats.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+358.1%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+222.4%
Carbohydrates
Navy beans and white beans have about the same amount of carbohydrates.
100g of navy beans contain 26g of carbohydrates, of which 10.5g are dietary fiber and 15.5g are net carbs.
100g of white beans contain 25g of carbohydrates, of which 6g are dietary fiber and 19g are net carbs.
The main carbohydrate found in navy beans is starch. It contains 15.4 g of starch.
However, navy beans are richer in dietary fiber, while white beans are higher in net carbs.
Vitamins
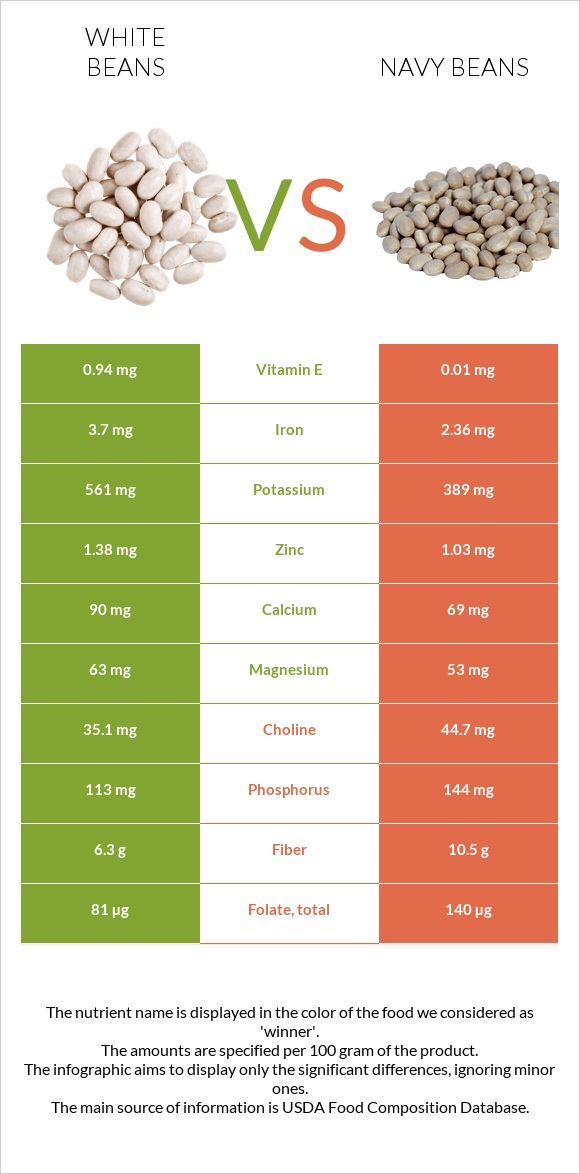
Navy beans are richer in vitamin B1 and folate (vitamin B9). Navy beans have 140 µg of folate, whereas white beans only have 81µg. White beans, on the other hand, contain higher levels of vitamin E and vitamin K.
Navy beans and white beans are absent in vitamin A, vitamin B12, and vitamin D.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+9300%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+483.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+100.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+43.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+363.6%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+16.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+48.4%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+72.8%
Minerals
White beans are higher in potassium. Navy beans contain 389 mg of potassium, whereas white beans contain 561mg.
White beans are also higher in iron and copper. At the same time, navy beans contain more phosphorus, choline, and selenium. Compared to white beans, which have 1.3µg of selenium, navy beans have 2.9µg. Navy beans and white beans are also low in sodium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+18.9%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+30.4%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+44.2%
Contains
more
IronIron
+56.8%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+36.7%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+34%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+20.7%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+27.4%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-100%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+123.1%
Acidity
Calculating the potential renal acid load, or PRAL, reveals how much acid or base the given food produces inside the body and is an alternate approach to evaluating acidity. The PRAL value of navy beans is -1.1 (alkaline), and the PRAL value of white beans is -5.6(alkaline).
Weight Loss & Diets
Due to lower fat levels, less sodium, and high protein content, navy beans and white beans are excellent DASH diet choices.
Both are suitable for vegan and vegetarian diets.
Moreover, navy beans and white beans are plant-based foods, and you can use them in your Mediterranean diet.
According to the Paleo guidelines, people on the Paleo diet should avoid navy beans and white beans.
Because navy beans and white beans include a high amount of carbohydrates, they are not keto-friendly.
Health Benefits
As mentioned above, navy beans are rich in dietary fiber, which has several positive health effects. High consumption of dietary fiber is associated with a lower risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, hypertension, diabetes, and obesity(1).
Consuming navy beans, among other Phaseolus vulgaris bean varieties, may help prevent chronic diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Furthermore, P. vulgaris species are also known to decrease LDL cholesterol, which is one of the risk factors for CVD(2).
Navy beans are high in resistant starch. Resistant starch(RS) is a beneficial dietary ingredient with health benefits. A new study reveals that RS may help manage chronic renal disease and diabetes(3).
Similarities
Digestive Health
A plant-based diet that includes navy beans and white beans has protective effects on metabolism, body weight, gut microbiome environment, and low-grade inflammation(4).
Moreover, fiber consumption aids gastrointestinal problems, including gastroesophageal reflux disease, duodenal ulcer, diverticulitis, constipation, and hemorrhoids(1).
Cancer
Randomized controlled research discovered that a high-legume diet altered biomarkers for cancer risk(2).
Furthermore, research suggests that eating more legumes, such as navy beans, may lower the risk of colorectal cancer(5).
Sources
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19335713/
- https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/british-journal-of-nutrition/article/phaseolus-beans-impact-on-glycaemic-response-and-chronic-disease-risk-in-human-subjects/A9BA36BE08D2B4476D022C27AA22893D
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/nbu.12244
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7915747/#B21-nutrients-13-00519
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30583518/
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Iron | 3.7mg | 2.36mg | 17% |
| Fiber | 6.3g | 10.5g | 17% |
| Folate | 81µg | 140µg | 15% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.118mg | 0.237mg | 10% |
| Copper | 0.287mg | 0.21mg | 9% |
| Starch | 15.4g | 6% | |
| Vitamin E | 0.94mg | 0.01mg | 6% |
| Potassium | 561mg | 389mg | 5% |
| Manganese | 0.636mg | 0.527mg | 5% |
| Phosphorus | 113mg | 144mg | 4% |
| Protein | 9.73g | 8.23g | 3% |
| Zinc | 1.38mg | 1.03mg | 3% |
| Selenium | 1.3µg | 2.9µg | 3% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.14mg | 0.649mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.093mg | 0.138mg | 3% |
| Magnesium | 63mg | 53mg | 2% |
| Calcium | 90mg | 69mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.046mg | 0.066mg | 2% |
| Vitamin K | 3.5µg | 0.6µg | 2% |
| Choline | 35.1mg | 44.7mg | 2% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.152g | 0.49g | 2% |
| Vitamin C | 0mg | 0.9mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.229mg | 0.266mg | 1% |
| Calories | 139kcal | 140kcal | 0% |
| Fats | 0.35g | 0.62g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 18.79g | 15.55g | N/A |
| Carbs | 25.09g | 26.05g | 0% |
| Sugar | 0.34g | 0.37g | N/A |
| Sodium | 6mg | 0mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.091g | 0.098g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.031g | 0.142g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.115mg | 0.1mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.409mg | 0.289mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.429mg | 0.387mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.776mg | 0.7mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.668mg | 0.52mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.146mg | 0.111mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.526mg | 0.471mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.509mg | 0.504mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.271mg | 0.206mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.177g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- White beans - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/175203/nutrients
- Navy beans - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173746/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






