Pollock vs. Haddock — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Pollock is overall denser in nutrients than haddock, being higher in calories, protein, and fats. More importantly, pollock is nearly 2 times richer in vitamins B12, D, and B1 and 3 times richer in vitamin B2. Pollock is also a better source of most minerals, especially calcium, magnesium, iron, and copper.
That being said, haddock provides 4 times more vitamin B9 or folate and 2 times more vitamin E.
Despite the nutritional advantage, pollock is cheaper and more available; therefore, it is often used in processed fish products, while haddock is served as fillets.
When it comes to health, the focus should not be on whether to eat pollock or haddock but on how to cook the chosen fish.
Introduction
Pollock and haddock have many similarities, both being white fish with a mild taste and a low fat content and belonging to the Gadidae or cod family. However, there are things that set these two apart, which will be discussed in this article.
There are two main commercial varieties of pollock, namely Atlantic and Alaska, while there is one popular commercial variety for haddock. Atlantic pollock is darker and has a stronger taste, while Alaska pollock is flakier.
When looking at fresh fish fillets, haddock is usually white, while pollock is slightly darker, mostly due to a higher content of the iron-containing protein myoglobin.
Taste and Use
Haddock tends to have a more distinct taste, whereas pollock is milder. However, Atlantic pollock has a stronger taste compared to Alaska pollock.
Regarding price, pollock tends to be cheaper than haddock as it is easier to find. Due to its availability, pollock is more often used for producing processed fish products, while haddock is served as a meal.
Pollock usually has a softer texture, while haddock is slightly firmer.
Nutrition
In this section, we are comparing the nutritional values of 100g serving sizes of Alaska pollock and haddock, both cooked using dry heat.
One average serving size per person of pollock and haddock, like all fish, is considered 3 ounces or 85g. If interested, you can choose your preferred serving size in different sections.
You can also choose the type of fish and your preferred cooking method for a more specific nutritional comparison.
Macronutrients and Calories
Overall, pollock is slightly denser in nutrients, consisting of 74% water and 23% protein, whereas haddock is made up of 70% water and 20% protein.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+17.5%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+114.5%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+∞%
Calories
Both of these fishes are considered medium-to-low-calorie foods; however, pollock is somewhat higher in calories compared to haddock. A hundred-gram serving of pollock and haddock provide 111 and 90 calories, respectively.
Protein
Pollock contains about 3.5g more protein per every 100g serving. That being said, both of these foods are excellent sources of protein, with a 100g serving providing about 50% of the protein needed daily.
Additionally, the protein found in pollock and haddock is of high quality, containing some level of all essential amino acids, particularly lysine, histidine, threonine, and tryptophan. Pollock is somewhat richer in all essential amino acids.
Fats
Pollock is also 2 times higher in fats; however, this does not mean much, as both pollock and haddock are lean meats with low-fat content.
A hundred-gram serving of pollock and haddock provide 1.18g and 0.55g of fats, respectively. Most of these fats are polyunsaturated fatty acids, such as omega-3 and omega-6.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+81.1%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+185.8%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-30.2%
Carbohydrates
Pollock and haddock, like most types of meat, do not contain carbohydrates.
Vitamins
The vitamin and mineral sections are where we get to the real nutritional differences between these fish.
Both pollock and haddock are excellent sources of vitamin B12; however, pollock is nearly 2 times higher, providing more than the required daily value per 100g serving.
Pollock is also 2 times richer in vitamin D and vitamin B1 and 3 times richer in vitamin B2.
At the same time, haddock provides over 4 times more folate or vitamin B9 and 2 times more vitamin E. Haddock is also somewhat higher in vitamin A and vitamin B5.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+116.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+134.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+223.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+71.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+23.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+96.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+14.4%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+333.3%
Minerals
Pollock easily wins in this category, being richer in nearly all minerals. Pollock provides 5 times more calcium, nearly 3 times more magnesium and iron, and 2 times more copper, as well as being higher in zinc, manganese, selenium, and potassium.
Haddock is somewhat lower in sodium; however, the sodium content will naturally depend on the cooking method and the amount of salt added.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+211.5%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+414.3%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+22.5%
Contains
more
IronIron
+166.7%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+130.8%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+42.5%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+38.5%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+39.1%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-37.7%
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index values of haddock and pollock are 0 since they contain no carbohydrates.
Insulin Index
The insulin index value of both haddock and pollock is considered a moderate 59, as this is the calculated value for white fish (1).
Health Impact
Pollock and haddock are both white lean fish, generally impacting our health in similar ways. In this section, we will look into what research says about these fish.
Cardiovascular Health
A high-quality systematic review found that non-fried fish consumption is probably associated with a decreased risk of cardiovascular disease and heart attack, while a high intake of fried fish is conversely associated with an increased risk (2). Therefore, the health focus should not be on whether to eat pollock or haddock but on how to cook the chosen fish.
Another systematic review concluded that eating two portions of fish a week may reduce fatal and non-fatal outcomes of cardiovascular disease by about 10% (3). However, the recommended fish intake is mostly based on healthy cooking methods for fatty fish, such as salmon or mackerel, which are high in polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Diabetes
A cohort study by the American Diabetes Association found that both fatty and white fish consumption can be beneficial for reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes (4). Conversely, the findings of a prospective follow-up study by the same institution did not support the beneficial effect of fish consumption on the risk of type 2 diabetes, possibly due to the selenium and contaminants found in fish (5).
Thus, the impact of haddock and pollock on the development of type 2 diabetes is not conclusive.
Mercury Content
The FDA states that both pollock and haddock are low-mercury fish varieties and can even be eaten in amounts of 2 serving sizes a week during pregnancy and breastfeeding (6).
Sources.
- https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/66/5/1264/4655967
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33444594/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37960192/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2752921
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2768220/
- https://www.fda.gov/food/consumers/advice-about-eating-fish#choice
Infographic
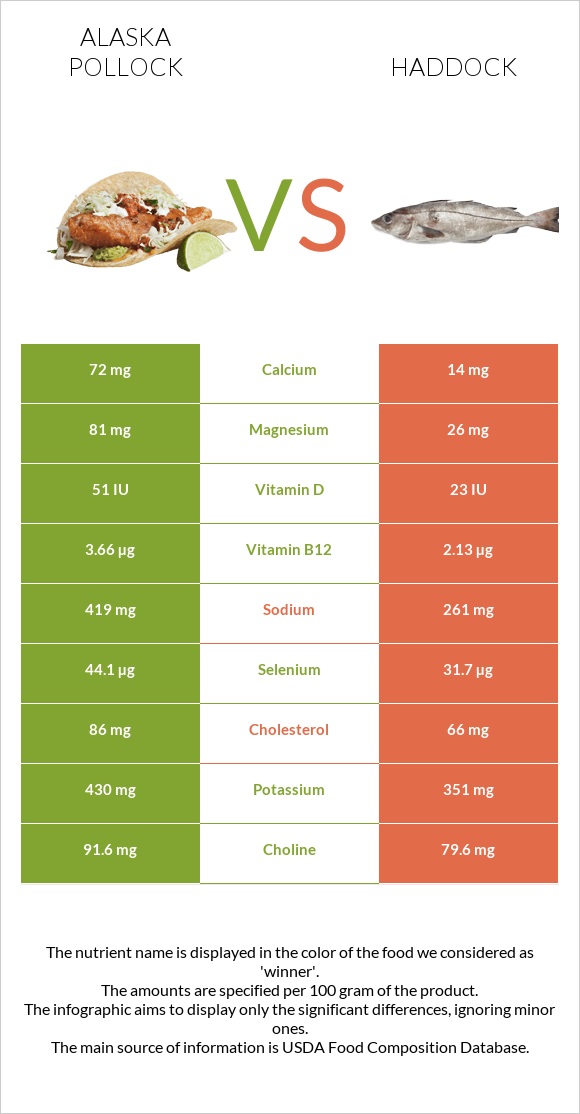
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B12 | 3.66µg | 2.13µg | 64% |
| Selenium | 44.1µg | 31.7µg | 23% |
| Magnesium | 81mg | 26mg | 13% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.223mg | 0.069mg | 12% |
| Protein | 23.48g | 19.99g | 7% |
| Cholesterol | 86mg | 66mg | 7% |
| Sodium | 419mg | 261mg | 7% |
| Calcium | 72mg | 14mg | 6% |
| Vitamin D | 51 IU | 23 IU | 4% |
| Iron | 0.56mg | 0.21mg | 4% |
| Copper | 0.06mg | 0.026mg | 4% |
| Vitamin D | 1.3µg | 0.6µg | 4% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.054mg | 0.023mg | 3% |
| Folate | 3µg | 13µg | 3% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.583g | 0.204g | 3% |
| Potassium | 430mg | 351mg | 2% |
| Zinc | 0.57mg | 0.4mg | 2% |
| Phosphorus | 267mg | 278mg | 2% |
| Vitamin E | 0.28mg | 0.55mg | 2% |
| Choline | 91.6mg | 79.6mg | 2% |
| Calories | 111kcal | 90kcal | 1% |
| Fats | 1.18g | 0.55g | 1% |
| Vitamin B3 | 3.949mg | 4.119mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.432mg | 0.494mg | 1% |
| Vitamin A | 17µg | 21µg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.018mg | 0.013mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.329mg | 0.327mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 0.1µg | 0.1µg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0.005g | N/A | |
| Saturated fat | 0.159g | 0.111g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.134g | 0.074g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.263mg | 0.26mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 1.029mg | 1.015mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 1.082mg | 1.067mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.908mg | 1.882mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 2.157mg | 2.126mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.696mg | 0.686mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.917mg | 0.904mg | 0% |
| Valine | 1.21mg | 1.193mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.691mg | 0.682mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.086g | 0.051g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.423g | 0.109g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.027g | 0.006g | N/A |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.001g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Pollock - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173681/nutrients
- Haddock - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174198/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






