Kidney beans vs. Cranberry beans — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison
Summary
Cranberry beans are richer in fiber, magnesium, and folate. Meanwhile, kidney beans are richer in potassium, calcium, vitamin K, and vitamin B6.
Cranberry beans also provide more calories and protein than kidney beans.
Introduction
Cranberry beans and kidney beans belong to the beans family; however, a difference exists between them. This article will discuss the difference between these two beans on nutrition and health impacts.
Nutritional
In this comparison, we are considering 100g of raw beans in both cases.
Macronutrient Comparison
Calories
Cranberry beans provide more calories than kidney beans.
Carbs
Cranberry beans and kidney beans contain almost equal amounts of carbs.
Glycemic index
The glycemic index of kidney beans is lower.
The glycemic index of cranberry beans is equal to 35, while the GI of kidney beans is equal to 22.
Acidity
Kidney beans and cranberry beans have a similar pH value falling in the range of 5 to 6.
Both beans have slightly alkaline PRAL values. Cranberry beans have a PRAL value equal to -0.5, while kidney beans have -0.7. This shows that both beans are considerably acid-producing in the body.
Fibers
Cranberry beans provide more fiber. They have 8.6g of fiber per 100g, while kidney beans have 6.4g.
Nearly 40% of the carbohydrate content of both beans is fiber.
Proteins
Cranberry beans are higher in protein. They have 9.34g, whereas kidney beans have 8.67g of protein per 100g.
Fats
Both beans contain negligible amounts of fats.
Minerals
Cranberry beans are richer in calcium and magnesium. Kidney beans are richer in potassium and phosphorus.
It is important to mention that the RDV% is satisfied for both beans for copper, phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, and iron.
In the diagram below, we can see the mineral distributions.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+16.2%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+19%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+42.9%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+14%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+18.2%
Vitamins
Cranberry beans are richer in folate. Kidney beans are richer in vitamin B6, and K.
In the diagram below, we can see the vitamin distributions.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+12.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+48.1%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+31.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+19%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+59.2%
Health impacts
Although numerous health benefits are shared between cranberry and kidney beans, the main difference in their nutritional content is the vitamin K content of kidney beans. In this section, we will be focusing on the different health impacts rather than the similar ones.
Kidney beans are richer in vitamin K, which provides several positive health impacts.
Kidney bean consumption is linked with lower risks of cancer development and cardiovascular diseases, specifically the calcification of arteries. Kidney beans are also linked with decreased risks of osteoporosis. (1)
Infographic
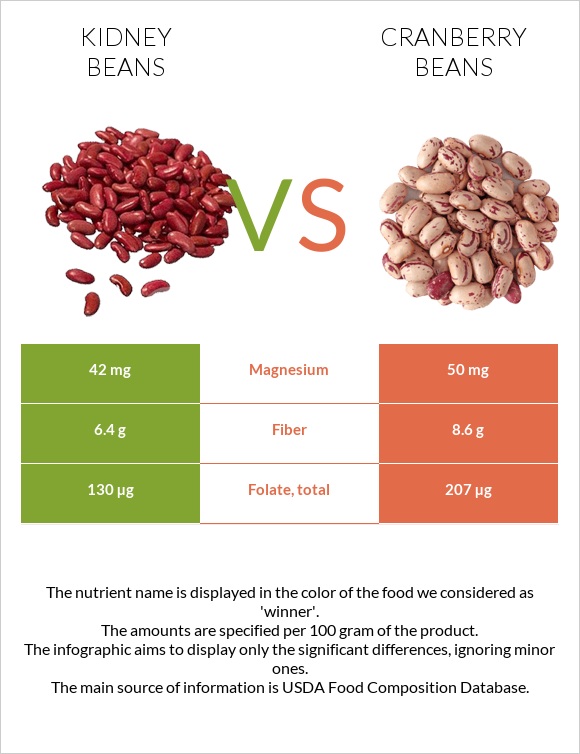
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Folate | 130µg | 207µg | 19% |
| Fiber | 6.4g | 8.6g | 9% |
| Vitamin K | 8.4µg | 7% | |
| Choline | 30.5mg | 6% | |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.16mg | 0.21mg | 4% |
| Manganese | 0.43mg | 0.37mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.12mg | 0.081mg | 3% |
| Magnesium | 42mg | 50mg | 2% |
| Calcium | 35mg | 50mg | 2% |
| Iron | 2.22mg | 2.09mg | 2% |
| Copper | 0.216mg | 0.231mg | 2% |
| Protein | 8.67g | 9.34g | 1% |
| Vitamin C | 1.2mg | 0mg | 1% |
| Carbs | 22.8g | 24.46g | 1% |
| Potassium | 405mg | 387mg | 1% |
| Zinc | 1mg | 1.14mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.058mg | 0.069mg | 1% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.278g | 0.199g | 1% |
| Calories | 127kcal | 136kcal | 0% |
| Fats | 0.5g | 0.46g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 16.4g | 15.86g | N/A |
| Sugar | 0.32g | N/A | |
| Phosphorus | 138mg | 135mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 1mg | 1mg | 0% |
| Vitamin E | 0.03mg | 0% | |
| Selenium | 1.1µg | 1.3µg | 0% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.578mg | 0.515mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.22mg | 0.24mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.073g | 0.119g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.039g | 0.04g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.104mg | 0.111mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.319mg | 0.393mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.41mg | 0.412mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.736mg | 0.746mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.607mg | 0.641mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.113mg | 0.14mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.511mg | 0.505mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.5mg | 0.489mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.238mg | 0.26mg | 0% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -38.7% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +39.7% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Kidney beans - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173740/nutrients
- Cranberry beans - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173736/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






