Kidney Beans vs. Green Beans — Nutrition and Health Differences

Summary
Kidney beans have higher calories and carbs, yet they are richer in fiber, manganese, copper, zinc, potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, iron, vitamin B1, vitamin B6, and folate. In comparison, green beans are richer in vitamins K, C, and A.
Introduction
This article compares two types of beans: kidney beans and green beans. Although they belong to the beans family, they are very different regarding nutritional composition and have several general and health differences.
We will compare them based on their differences regarding their nutritional compositions, health impacts, and general differences.
Nutrition
We will compare 100g of each in cooked forms.
We will compare the differences in their nutrients.
Calories
Kidney beans are higher in calories compared to green beans.
Kidney beans contain 3.6 times more calories than green beans.
Carbohydrates
Kidney beans are much higher in carbs compared to green beans. Kidney beans contain 22.8 grams of carbs, whereas green beans contain 7.9 grams. The difference is nearly 3 times more in kidney beans.
Fiber
When it comes to fiber, kidney beans contain 6.4g of fiber, twice as much as green beans. The difference in fiber is very significant.
Glycemic index
So, regarding the glycemic index, since kidney beans are much higher in carbs, we assume the glycemic index would also be higher. However, they both have low glycemic indices nearly similar to one another.
Kidney beans have a glycemic index of 22, and green beans have a GI equal to 20.
Although kidney beans are higher in carbs, their glycemic index is low.
Fats
Their fat content is negligible.
Protein
Kidney beans are a great source of proteins. They are richer in proteins compared to green beans.
Kidney beans contain 8.7g of protein, whereas green beans contain nearly 2g, which is negligible. Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
WaterWater
+33.3%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+358.7%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+78.6%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+189.3%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+49.3%
Oxalates
Kidney beans contain 40mg of oxalate, which is categorized as low oxalate. In comparison, green beans contain 65mg of oxalate, which is categorized as high.
Minerals
Kidney beans have a richer mineral profile compared to green beans.
Kidney beans are richer in manganese, copper, zinc, potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, and iron. In comparison, green beans are slightly richer in calcium. However, the amount is insignificant.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+25.7%
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+133.3%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+177.4%
Contains
more
IronIron
+241.5%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+278.9%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+300%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+375.9%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+50.9%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+450%
You can read about pintos (pinto beans) vs. black beans in this article.
Vitamins
Kidney beans are richer in vitamin B1 (thiamine), B6, and folate. In comparison, green beans are richer in vitamins K, C, and A.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+708.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+1433.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+67.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+470.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+116.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+197.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+114.3%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+293.9%
Contains
more
CholineCholine
+80.5%
Health Benefits
In this section, we will compare the health impacts of kidney beans and green beans based on their positive impacts on our health.
Weight Loss
Kidney bean extracts are shown to reduce weight and subcutaneous fat levels. However, this mainly focuses on kidney bean extracts (1)(2).
Antioxidant
Kidney beans contain many antioxidants, gallic acid, and tocopherols. These compounds' cumulative effect positively impacts our health (3).
Green beans contain beta-carotene, lutein, zeaxanthin, and phytochemicals. Cooking methods can affect the bioavailability of these compounds. Microwaved heating increases polar polyphenols, but pressure cooking increases the bioavailability of carotenoids. Overall, these compounds positively affect our health system (4).
Diabetes
Kidney beans added to type 2 diabetes diets have positively impacted their overall glycemic control and diabetes management (5).
In addition, since rice is commonly consumed in almost all populations. Associating kidney beans with rice has decreased postprandial blood sugar levels, positively impacting diabetes management (6).
Adding green beans to our diet improves metabolic functioning and reduces the risks of diabetes (7).
You can also read this article's health comparison of pinto beans vs. kidney beans.
Cardiovascular Health
Kidney beans are associated with decreased LDL cholesterol levels and, in addition, decreased risks of cardiovascular diseases (8).
Green beans are associated with decreased risks of heart disease and overall improved cardiovascular functions (7).
The rich profile of kidney beans regarding fiber and potassium can greatly benefit patients with high blood pressure regarding lifestyle and dietary changes (10).
Digestive Health
Kidney beans being richer in fiber improves gastrointestinal health and gut microbiome health. In comparison, green beans are positively associated with these benefits aswell. However, since kidney beans are richer in fiber, they can add to these benefits (7)(9).
You can read about navy beans vs. lima beans in this article.
General Differences
Kidney and green beans have many differences besides nutrition and health impacts.
Green beans are eaten with their pods, whereas kidney beans are eaten as beans.
Green bean snaps are legumes used in numerous ways in soups and dish recipes.
Vegans and vegetarians can prepare a salad, stews, and casseroles by combining different legumes and pulses, such as green beans, string beans, kidney beans, white beans, green peas, and black-eyed peas.
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32180941/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7063375/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27613272/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28502202/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9667044/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22494488/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7915747/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34835959/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33096647/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32917495/
Infographic
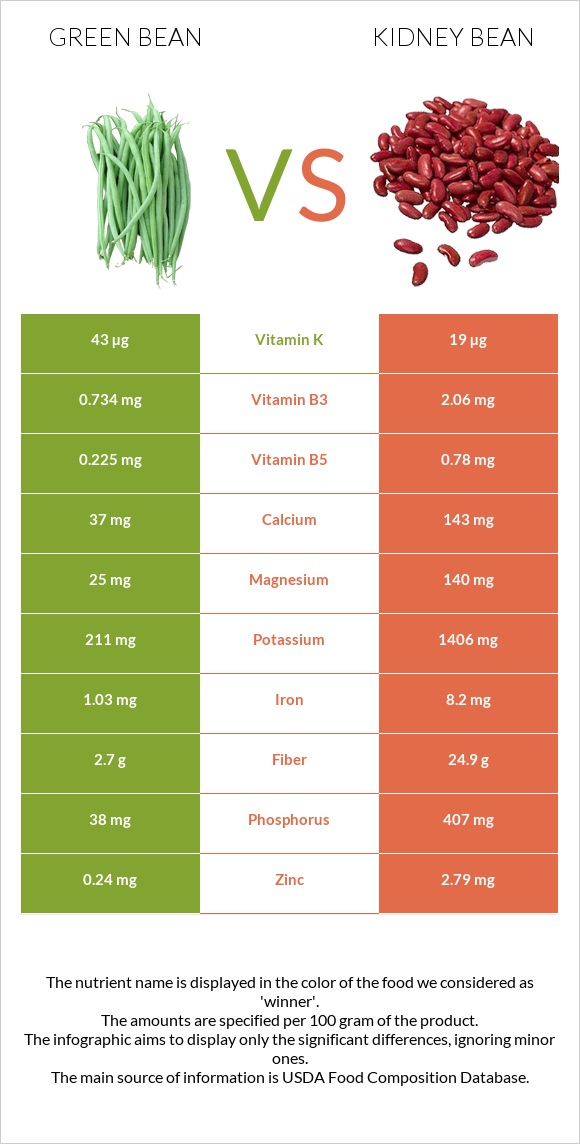
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin K | 47.9µg | 8.4µg | 33% |
| Folate | 33µg | 130µg | 24% |
| Iron | 0.65mg | 2.22mg | 20% |
| Copper | 0.057mg | 0.216mg | 18% |
| Phosphorus | 29mg | 138mg | 16% |
| Protein | 1.89g | 8.67g | 14% |
| Fiber | 3.2g | 6.4g | 13% |
| Vitamin C | 9.7mg | 1.2mg | 9% |
| Potassium | 146mg | 405mg | 8% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.074mg | 0.16mg | 7% |
| Zinc | 0.25mg | 1mg | 7% |
| Magnesium | 18mg | 42mg | 6% |
| Manganese | 0.285mg | 0.43mg | 6% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.056mg | 0.12mg | 5% |
| Calories | 35kcal | 127kcal | 5% |
| Carbs | 7.88g | 22.8g | 5% |
| Vitamin A | 32µg | 0µg | 4% |
| Vitamin E | 0.46mg | 0.03mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.097mg | 0.058mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.074mg | 0.22mg | 3% |
| Choline | 16.9mg | 30.5mg | 2% |
| Selenium | 0.2µg | 1.1µg | 2% |
| Calcium | 44mg | 35mg | 1% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.145g | 0.278g | 1% |
| Fats | 0.28g | 0.5g | 0% |
| Net carbs | 4.68g | 16.4g | N/A |
| Sugar | 3.63g | 0.32g | N/A |
| Sodium | 1mg | 1mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.614mg | 0.578mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.064g | 0.073g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.011g | 0.039g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.02mg | 0.104mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.082mg | 0.319mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.069mg | 0.41mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.116mg | 0.736mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.091mg | 0.607mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.023mg | 0.113mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.069mg | 0.511mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.093mg | 0.5mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.035mg | 0.238mg | 0% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -12.3% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +254.5% |
| Contains more Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat | +91.7% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Green beans - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169141/nutrients
- Kidney beans - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173740/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






