Croaker vs. Whiting — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Croaker provides more Vitamin B3, B6, B5, B1, magnesium, and iron than Pacific Whiting. Also, it has more sodium.
On the other hand, whiting contains more Vitamin A, D, and calcium. Whiting is lower in saturated fat.
Introduction
We'll discuss the main differences between croaker fish and whiting, focusing on their nutritional content and health impact.
What's The Actual Difference?
Whiting or Pacific whiting belongs to the Merlangius family, while Atlantic croaker belongs to the Sciaenidae family, closely related to the black drum and silver perch.
The Pacific whiting is a silvery fish with black specks on its back that can reach 1.4 pounds and 3 feet in length. Pacific whiting flesh is white, soft and mildly sweet. Atlantic croaker is about 12 inches; it is a lean, full-flavored fish with an almost sweet flavor. The flesh is firm, like that of a black drum.
NUTRITION
The food types discussed in this article are cooked croaker and cooked whiting. To better understand the difference between these two fishes, look at our nutrition infographic at the bottom of the page.
Calories
Both croaker fish and whiting are considered moderate-calories foods.
Croaker has 221 calories per 100g, and Whiting has 116 calories per 100g.
Minerals
Whiting is relatively richer in minerals than croaker. It is richer in calcium, phosphorus, manganese, and potassium and has less sodium.
On the other hand, a croaker contains more magnesium, copper, and iron.
Both fishes contain equal amounts of zinc and selenium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+55.6%
Contains
more
IronIron
+104.8%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+62.5%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+93.8%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+27.6%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+31.3%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-62.1%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+62.5%
Vitamins
Croaker has more vitamins than whiting fish. It provides more Vitamin B1, B5, B2, B3, and folate than whiting fish.
Whiting has more Vitamin A, E, B12, and D.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+32.4%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+116.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+157.5%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+196%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+44.4%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+126.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+65.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+23.8%
Macronutrients
Whiting fish is richer in water. This is why the croaker may seem to have a more solid texture. Croaker is notably richer in fats, while whiting contains more protein. Please check the chart shown below and read about these nutrients in detail in the corresponding sections.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
FatsFats
+649.7%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+∞%
Contains
more
OtherOther
+1425%
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+29%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+25%
Fats
Croaker has 12 times more fat than Whiting. It is significantly richer in all types of fats - saturated and unsaturated.
Cholesterol
Cooked croaker and whiting have equal amounts of cholesterol: both provide 84mg of cholesterol per 100g.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+1095.5%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+396.9%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-88.5%
Protein
Whiting is 5g richer in protein than croaker: croaker contains 18.2 g, and whiting has 23.5g of protein per 100g. Both have essential amino acids, such as lysine, histidine, and phenylalanine.
HEALTH IMPACT
Health Benefits
Croaker fish and whiting both have high omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. These two compounds may benefit cardiovascular, eye, and immune system function [1]. According to research, omega-3 fatty acids may reduce blood clotting, lower blood pressure and the risk of heart failure, and lower triglycerides [2]. Studies show [3] that omega-3-rich fish bioactive proteins, peptides, or protein hydrolysates have immunomodulatory properties.
Whiting fish is higher in selenium. Studies show that selenium may help improve your immune response, and a deficiency may negatively affect immune cells and their function [4].
Infographic
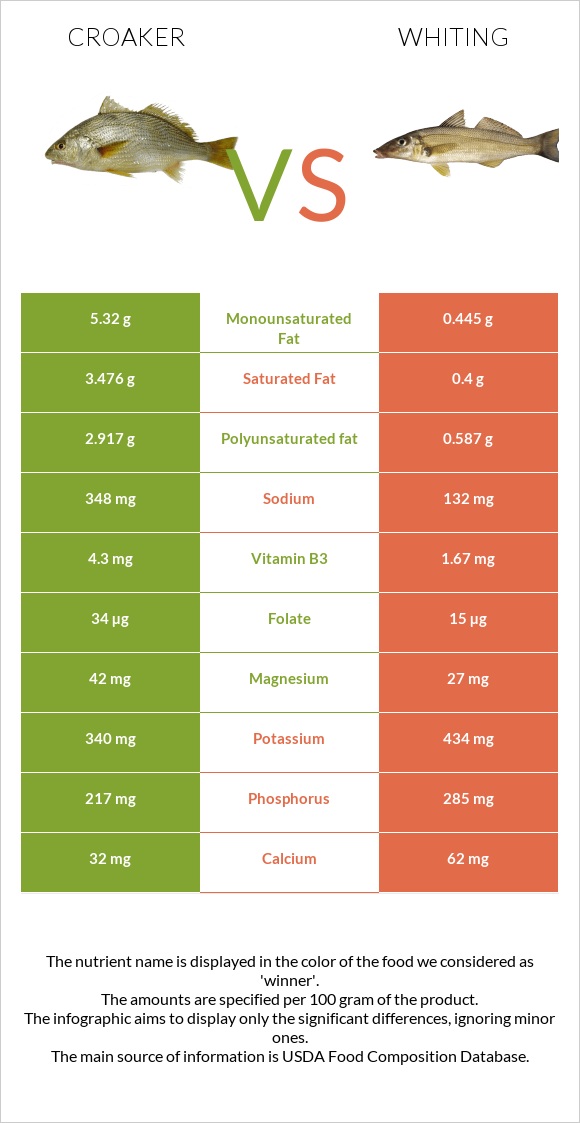
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Vitamin B12 | 2.1µg | 2.6µg | 21% |
| Fats | 12.67g | 1.69g | 17% |
| Vitamin B3 | 4.3mg | 1.67mg | 16% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 2.917g | 0.587g | 16% |
| Choline | 83.3mg | 15% | |
| Saturated fat | 3.476g | 0.4g | 14% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 5.32g | 0.445g | 12% |
| Protein | 18.2g | 23.48g | 11% |
| Phosphorus | 217mg | 285mg | 10% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.74mg | 0.25mg | 10% |
| Vitamin D | 73 IU | 9% | |
| Sodium | 348mg | 132mg | 9% |
| Vitamin D | 1.8µg | 9% | |
| Iron | 0.86mg | 0.42mg | 6% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.26mg | 0.18mg | 6% |
| Calories | 221kcal | 116kcal | 5% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.13mg | 0.06mg | 5% |
| Folate | 34µg | 15µg | 5% |
| Magnesium | 42mg | 27mg | 4% |
| Selenium | 38.8µg | 41.1µg | 4% |
| Carbs | 7.54g | 0g | 3% |
| Calcium | 32mg | 62mg | 3% |
| Potassium | 340mg | 434mg | 3% |
| Copper | 0.065mg | 0.04mg | 3% |
| Vitamin E | 0.38mg | 3% | |
| Fiber | 0.4g | 0g | 2% |
| Vitamin A | 23µg | 38µg | 2% |
| Manganese | 0.08mg | 0.13mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.09mg | 0.068mg | 2% |
| Net carbs | 7.14g | 0g | N/A |
| Cholesterol | 84mg | 84mg | 0% |
| Zinc | 0.52mg | 0.53mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 0.1µg | 0% | |
| Tryptophan | 0.208mg | 0.263mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.788mg | 1.029mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.847mg | 1.082mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 1.48mg | 1.908mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 1.571mg | 2.156mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.525mg | 0.695mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.742mg | 0.917mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.947mg | 1.21mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.525mg | 0.691mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.113g | 0.283g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.089g | 0.235g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.079g | 0.017g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Croaker - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/171957/nutrients
- Whiting - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/175161/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.