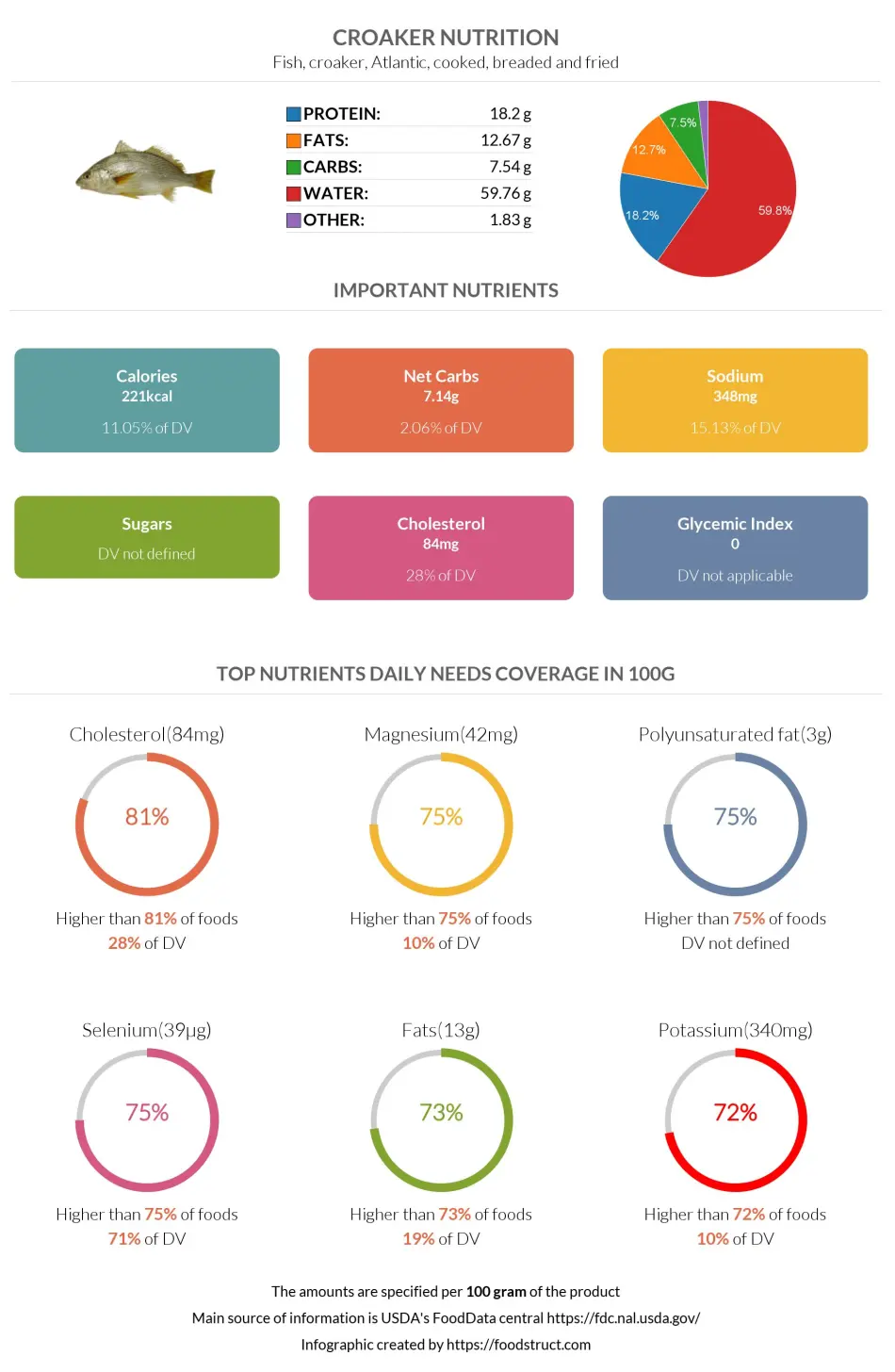
Croaker nutrition facts: calories, protein, carbs, GI, & fats
Fish, croaker, Atlantic, cooked, breaded and fried
*all the values are displayed for the amount of 100 grams
Top nutrition facts for Croaker

| Calories ⓘ Calories for selected serving | 221 kcal |
| Glycemic index ⓘ Croaker can be considered as a 0 glycemic index food as it does not have carbs. Source: https://foodstruct.com/articles/glycemic-index-of-0-no-carb-foods | 0 (low) |
| Net Carbs ⓘ Net Carbs = Total Carbohydrates – Fiber – Sugar Alcohols | 7 grams |
| Default serving size ⓘ Serving sizes are mostly taken from FDA's Reference Amounts Customarily Consumed (RACCs) | 1 fillet (87 grams) |
| Acidity (Based on PRAL) ⓘ PRAL (Potential renal acid load) is calculated using a formula. On the PRAL scale the higher the positive value, the more is the acidifying effect on the body. The lower the negative value, the higher the alkalinity of the food. 0 is neutral. | 8.3 (acidic) |
| Oxalates ⓘ Animal products do not contain oxalate. | 0 mg |
Croaker calories (kcal)
| Calories for different serving sizes of croaker | Calories | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Calories in 100 grams | 221 | |
| Calories in 3 oz | 188 | 85 g |
| Calories in 1 fillet | 192 | 87 g |
| Calories for different varieties of croaker | Calories | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Fish, croaker, Atlantic, cooked, breaded and fried (this food) | 221 | 100 g |
| Croaker raw | 104 | 100 g |
Croaker Glycemic index (GI)
Croaker can be considered as a 0 glycemic index food as it does not have carbs. Source: https://foodstruct.com/articles/glycemic-index-of-0-no-carb-foods
Mineral coverage chart
Mineral chart - relative view
Vitamin coverage chart
Vitamin A:
69µg of 900µg
7.7%
Vitamin E:
0mg of 15mg
0%
Vitamin D:
0µg of 20µg
0%
Vitamin C:
0mg of 90mg
0%
Vitamin B1:
0.27mg of 1mg
23%
Vitamin B2:
0.39mg of 1mg
30%
Vitamin B3:
13mg of 16mg
81%
Vitamin B5:
2.2mg of 5mg
44%
Vitamin B6:
0.78mg of 1mg
60%
Folate:
102µg of 400µg
26%
Vitamin B12:
6.3µg of 2µg
263%
Vitamin K:
0µg of 120µg
0%
Vitamin chart - relative view
Macronutrients chart
Protein:
Daily Value: 36%
18.2 g of 50 g
18.2 g (36% of DV )
Fats:
Daily Value: 19%
12.7 g of 65 g
12.7 g (19% of DV )
Carbs:
Daily Value: 3%
7.5 g of 300 g
7.5 g (3% of DV )
Water:
Daily Value: 3%
59.8 g of 2,000 g
59.8 g (3% of DV )
Other:
1.8 g
1.8 g
Protein quality breakdown
Tryptophan:
624mg of 280mg
223%
Threonine:
2364mg of 1,050mg
225%
Isoleucine:
2541mg of 1,400mg
182%
Leucine:
4440mg of 2,730mg
163%
Lysine:
4713mg of 2,100mg
224%
Methionine:
1575mg of 1,050mg
150%
Phenylalanine:
2226mg of 1,750mg
127%
Valine:
2841mg of 1,820mg
156%
Histidine:
1575mg of 700mg
225%
Fat type information
Saturated fat:
3.5 g
Monounsaturated fat:
5.3 g
Polyunsaturated fat:
2.9 g
Fiber content ratio for Croaker
Sugar:
0 g
Fiber:
0.4 g
Other:
7.1 g
All nutrients for Croaker per 100g
| Nutrient | Value | DV% | In TOP % of foods | Comparison |
| Vitamin A | 23µg | 3% | 42% | |
| Calories | 221kcal | 11% | 43% |
4.7 times more than Orange
|
| Protein | 18g | 43% | 29% |
6.5 times more than Broccoli
|
| Fats | 13g | 19% | 27% |
2.6 times less than Cheese
|
| Vitamin C | 0mg | 0% | 100% |
N/A
|
| Net carbs | 7.1g | N/A | 52% |
7.6 times less than Chocolate
|
| Carbs | 7.5g | 3% | 54% |
3.7 times less than Rice
|
| Cholesterol | 84mg | 28% | 19% |
4.4 times less than Egg
|
| Magnesium | 42mg | 10% | 25% |
3.3 times less than Almonds
|
| Calcium | 32mg | 3% | 43% |
3.9 times less than Milk
|
| Potassium | 340mg | 10% | 28% |
2.3 times more than Cucumber
|
| Iron | 0.86mg | 11% | 65% |
3 times less than Beef broiled
|
| Fiber | 0.4g | 2% | 57% |
6 times less than Orange
|
| Copper | 0.07mg | 7% | 73% |
2.2 times less than Shiitake
|
| Zinc | 0.52mg | 5% | 68% |
12.1 times less than Beef broiled
|
| Phosphorus | 217mg | 31% | 31% |
1.2 times more than Chicken meat
|
| Sodium | 348mg | 15% | 30% |
1.4 times less than White bread
|
| Selenium | 39µg | 71% | 25% | |
| Manganese | 0.08mg | 3% | 62% | |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.09mg | 8% | 52% |
3 times less than Pea raw
|
| Vitamin B2 | 0.13mg | 10% | 62% |
Equal to Avocado
|
| Vitamin B3 | 4.3mg | 27% | 39% |
2.2 times less than Turkey meat
|
| Vitamin B5 | 0.74mg | 15% | 44% |
1.5 times less than Sunflower seeds
|
| Vitamin B6 | 0.26mg | 20% | 44% |
2.2 times more than Oats
|
| Vitamin B12 | 2.1µg | 88% | 30% |
3 times more than Pork
|
| Folate | 34µg | 9% | 40% |
1.8 times less than Brussels sprouts
|
| Saturated fat | 3.5g | 17% | 34% |
1.7 times less than Beef broiled
|
| Monounsaturated fat | 5.3g | N/A | 30% |
1.8 times less than Avocado
|
| Polyunsaturated fat | 2.9g | N/A | 25% |
16.2 times less than Walnut
|
| Tryptophan | 0.21mg | 0% | 64% |
1.5 times less than Chicken meat
|
| Threonine | 0.79mg | 0% | 65% |
1.1 times more than Beef broiled
|
| Isoleucine | 0.85mg | 0% | 65% |
1.1 times less than Salmon raw
|
| Leucine | 1.5mg | 0% | 66% |
1.6 times less than Tuna Bluefin
|
| Lysine | 1.6mg | 0% | 65% |
3.5 times more than Tofu
|
| Methionine | 0.53mg | 0% | 63% |
5.5 times more than Quinoa
|
| Phenylalanine | 0.74mg | 0% | 67% |
1.1 times more than Egg
|
| Valine | 0.95mg | 0% | 65% |
2.1 times less than Soybean raw
|
| Histidine | 0.53mg | 0% | 67% |
1.4 times less than Turkey meat
|
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.11g | N/A | 34% |
6.1 times less than Salmon
|
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.09g | N/A | 35% |
16.4 times less than Salmon
|
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.08g | N/A | 34% |
2.2 times less than Salmon
|
Check out similar food or compare with current
NUTRITION FACTS LABEL
Nutrition Facts
___servings per container
Serving Size ______________
Serving Size ______________
Amount Per 100g
Calories 221
% Daily Value*
19%
Total Fat
13g
16%
Saturated Fat 3.5g
0
Trans Fat
0g
28%
Cholesterol 84mg
15%
Sodium 348mg
2.5%
Total Carbohydrate
7.5g
1.6%
Dietary Fiber
0.4g
Total Sugars 0g
Includes ? g Added Sugars
Protein
18g
Vitamin D
0mcg
0
Calcium
32mg
3.2%
Iron
0.86mg
11%
Potassium
340mg
10%
*
The % Daily Value (DV) tells you how much a nutrient in a serving of food contributes to a daily diet. 2,000 calories a day is used for general nutrition advice.
Health checks
ⓘ
Dietary cholesterol is not associated with an increased risk of coronary heart disease in healthy individuals. However, dietary cholesterol is common in foods that are high in harmful saturated fats.
Source
Low in Cholesterol
ⓘ
Trans fat consumption increases the risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality by negatively affecting blood lipid levels.
Source
No Trans Fats
ⓘ
Saturated fat intake can raise total cholesterol and LDL (low-density lipoprotein) levels, leading to an increased risk of atherosclerosis. Dietary guidelines recommend limiting saturated fats to under 10% of calories a day.
Source
Low in Saturated Fats
ⓘ
While the consumption of moderate amounts of added sugars is not detrimental to health, an excessive intake can increase the risk of obesity, and therefore, diabetes.
Source
Low in Sugars
Croaker nutrition infographic
Infographic link
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.


