Ice Cream vs. Custard — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison

Summary
Ice cream contains around 2 times more calories, 4 times more sugar as well as relatively higher fat and carbohydrate content when compared to custard.
In terms of vitamins and minerals, ice cream is relatively richer in vitamin A, while custard is richer in vitamin D, selenium, and phosphorus. They have similar amounts of vitamins B2, B5, and B12, as well as calcium and potassium.
Introduction
Ice cream is one of the most famous refreshing desserts. Its main ingredients are sugar, cream, flavoring, and milk. Ice cream is considered a dairy dessert, mainly because it's made with butterfat, milk/milk fat, or cream.
There are different types of ice cream. It can be sold as light fat, reduced fat, low, and full fat. The lowest fat content of ice cream is light fat which contains 5% milk fat. The upper range of fat content is 10-15%.
There are different ice cream flavors, ranging from fruity flavors like banana, strawberry, and melon to creamy flavors like brownies, vanilla, and chocolate.
Custard is quite similar to ice cream since they share the same essential ingredients of milk, cream, and sugar. However, what sets custard apart is the addition of a key ingredient – egg yolk. Flour or cornstarch can also be added as an ingredient to give it a more solid texture.
Custard is typically available in its two most popular flavors: vanilla and chocolate. While other flavors such as raspberry, strawberry, and mango are also available, they are not as commonly found. These less common flavors are usually offered in the form of powdered custard or synthetic variations.
Varieties
Ice cream has a broader flavor range than custard, resulting in a greater variety in its mineral, vitamin, and micronutrient composition.
Plain vanilla ice cream has a different fat and carbohydrate content, specifically in terms of sugar, compared to strawberry or cheesecake ice cream.
On the other hand, custard can be either homemade or purchased in powder form. The main flavors available are vanilla and chocolate, although additional flavors like strawberry and raspberry can also be found. Generally, there is not much variation in the compositions of different flavors of custard.
Custards, however, can be found in different variations across Europe, ranging from typical desserts to gourmet delicacies. They can be prepared using various methods, such as incorporating caramel, chocolate syrup, or whipped cream, among other ingredients. The nutritional profile of all these variations must be considered while preparing or consuming these types of custards.
We can prepare non-dairy versions of both ice cream and custard by using alternative ingredients instead of milk and eggs. Soy milk and almond milk can be utilized as substitutes for milk. Instead of eggs, bananas or other alternatives can be used. The substitution with bananas significantly alters the nutritional profile of both desserts, resulting in lower amounts of cholesterol and fats, which are major concerns when consuming these foods.
Another important point to note about both ice cream and custard is that during production, some companies may use additives, which can be detrimental to the gut microbiome and potentially cause long-term health issues. It is recommended to avoid ice cream and custards that contain additional additives and preservatives.
Nutritional Content Comparison
In this section, we will compare the nutritional composition of vanilla ice cream and egg custard prepared from the dry mix with whole milk.
The NLEA serving for ice cream has recently increased from ½ of a cup to ⅔ of a cup (1). This is an equivalent of around 85-120g. This recent change has been made to make the serving sizes closer to what people actually consume in their scoop of ice cream or sherbet.
The serving size for custard is similar to ice cream; half a cup serving of custard is around 141 grams.
To make the comparison easier, we will be comparing 100-gram servings of each.
Macronutrients and Calories
As evident from the macronutrient graphs below, ice cream is slightly more nutrient-dense, with a composition of 61% water, whereas custard consists of 73% water. Ice cream also contains more fats and carbs than custard.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+14%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+20.4%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+175%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+34.1%
Calories
For the same amount of serving, custard provides around 2 times lower calories when compared to vanilla ice cream.
Custard has 122 calories per 100g, while ice cream has 207 calories.
Fat
Per 100-gram serving, the fat content of ice cream is 11g, whereas custard contains only 4g of fat. Thus, ice cream has a higher fat content compared to custard.
Ice cream, compared to custard, contains higher amounts of saturated fats and monounsaturated fats. However, custard has a slightly higher cholesterol content, primarily attributed to the presence of additional egg yolk as a key ingredient in its preparation. It contains 51mg of cholesterol, whereas ice cream contains 44mg of cholesterol.
The daily recommended intake of saturated fat is typically less than 20g. In a 100-gram serving, ice cream contains 6.79g of saturated fat, while custard contains 2.03g of saturated fat.
Interestingly, per 100-gram serving, milk contains 2.9g of monounsaturated fat, whereas custard contains 1.1g of monounsaturated fat.
Hence, ice cream has a higher fat content, while custard contains higher levels of cholesterol.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-70.1%
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+163.4%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+44.9%
Protein
The protein content of ice cream and custard is almost identical. Ice cream contains 3.5g of protein per 100-gram serving, while custard contains slightly more, with 3.99g of protein.
Carbohydrate
Ice cream has a higher carbohydrate content of 23.6g per 100-gram serving, while custard contains 17.6g of carbohydrates.
Sugars
Ice cream contains 4 times more sugar than custard.
Per 100-gram serving, ice cream contains 21.22g of sugar, whereas custard contains only 4.82g of sugar.
Vitamin Content Comparison
Ice cream and custard have mainly similar vitamin profiles. A single serving of neither ice cream nor custard contains significant amounts of any of the vitamins to be considered a significant source of dietary vitamins. However, ice cream does contain adequate amounts of vitamin B12, vitamin B5, and vitamin B2. On the other hand, custard contains adequate amounts of the same vitamins (B12, B5, B2) along with vitamin D.
The vitamin profile of both ice cream and custard are as follows per 100-gram servings:
- Vitamin B2: Similar in both, with 0.24mg in ice cream and 0.22mg in custard.
- Vitamin B5: Similar in both, with 0.58mg in ice cream and 0.7mg in custard.
- Vitamin B12: Slightly higher in custard, with 0.39µg in ice cream and 0.52µg in custard.
- Vitamin A: Two times higher in ice cream, with 421 IU in ice cream and 182 IU in custard.
- Vitamin D: Six times higher in custard, with 0.2µg in ice cream and1.2µg in custard.
Thus, ice cream is relatively richer in vitamin A, while custard is richer in vitamin D. They have similar amounts of vitamins B2, B5, and B12.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+500%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+48.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+13.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+20.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+33.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin B12Vitamin B12
+33.3%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+80%
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+500%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+126.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+400%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+50%
Mineral Content Comparison
Custard and ice cream have similar mineral profiles; however, their distribution is different. The mineral profile of both ice cream and custard are as follows per 100-gram servings:
- Calcium: Similar in both, with 128mg in ice cream and 139mg in custard.
- Phosphorus: Slightly higher in custard, with 130mg in custard and 105mg in ice cream.
- Selenium: Three times higher in custard, with 6µg in custard and 1.8µg in ice cream.
- Potassium: Similar in both, with 199mg in ice cream and 207mg in custard.
- Zinc: Similar in both, with 0.51mg in ice cream and 0.69mg in custard.
- Sodium: Similar in both, with 80mg in ice cream and 84mg in custard.
Thus, custard is relatively richer in selenium and phosphorus. Ice cream and custard have similar amounts of calcium, potassium, zinc, and sodium.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+14.3%
Contains
more
IronIron
+277.8%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+30.4%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+23.8%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+233.3%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+35.3%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+14.3%
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index is a rating system used for foods containing carbohydrates.
The glycemic index of custard is lower than the glycemic index of ice cream.
Custard is considered a low glycemic food, with a glycemic index of 35. On the other hand, ice cream is considered a medium glycemic index food, with a glycemic index of 62.
Acidity
One way to understand the acidity of foods is through their potential renal acid load (PRAL) value, which shows how much acid or base the given food produces inside the organism.
Based on our calculations, the PRAL value of ice cream is -0.6, which means it has a slightly alkalizing effect on the body. In contrast, the PRAL value for custard is 0.2, which means it has a slightly acidifying effect on the body.
Health Impact
Ice cream exhibits probiotic characteristics that can have an influence on gut bacteria, specifically the normal flora (2).
Acne
The high content of sugars and the high glycemic index of ice cream is related to the increased risk of acne development and severity in teenagers. Ice cream should be consumed in moderation by teenagers or young adults with acne.
Alternatives to ice cream with lower amounts of sugar, like custards, are a better option (3).
Diabetes
For diabetic individuals, it is preferable to consume custard compared to ice cream due to its lower glycemic index. The low glycemic index prevents insulin levels from spiking up (4).
Cardiovascular Health
Consuming custard and ice cream can contribute to metabolic syndrome, which in turn causes obesity, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol. This significantly increases the risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, and cardiovascular disease-related death.
An increased consumption of full-fat dairy products such as custards and ice cream, as determined by food-frequency questionnaires, was associated with a 32% higher risk of mortality due to cardiovascular disease (5).
The American Heart Association advises limiting your daily calorie consumption of saturated fat to 5-6% of total calories. For instance, do not exceed 13 grams of saturated fat daily if your daily caloric intake is 2,000 (6).
References
- https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/food-serving-sizes-have-reality-check
- https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-384947-2.00385-8
- https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-5945-12-13
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31374573/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4006120/
- https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/eat-smart/fats/saturated-fats
Infographic
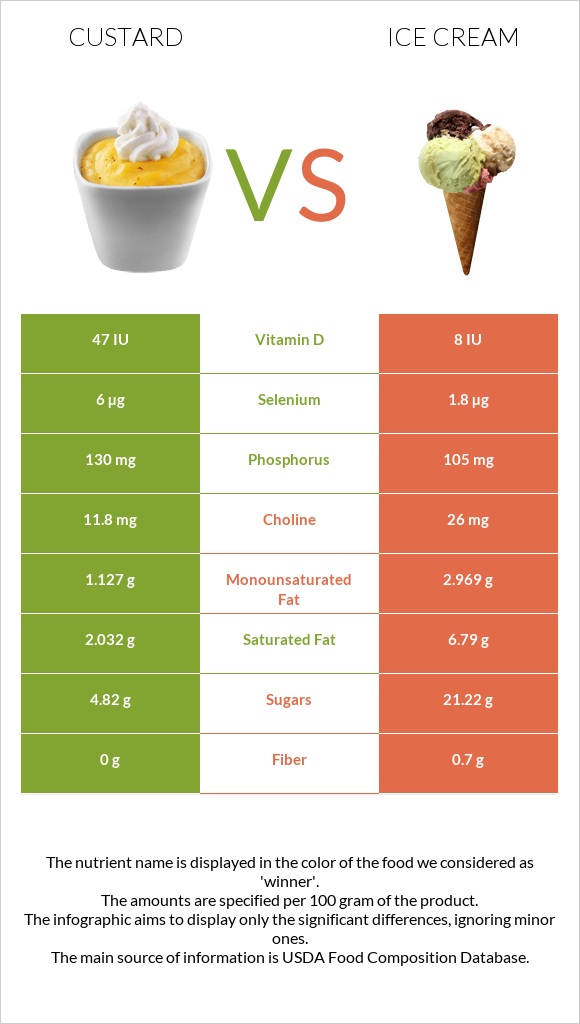
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Saturated fat | 2.032g | 6.79g | 22% |
| Fats | 4g | 11g | 11% |
| Selenium | 6µg | 1.8µg | 8% |
| Vitamin A | 52µg | 118µg | 7% |
| Vitamin D | 47 IU | 8 IU | 5% |
| Vitamin D | 1.2µg | 0.2µg | 5% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.52µg | 0.39µg | 5% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 1.127g | 2.969g | 5% |
| Calories | 122kcal | 207kcal | 4% |
| Phosphorus | 130mg | 105mg | 4% |
| Iron | 0.34mg | 0.09mg | 3% |
| Fiber | 0g | 0.7g | 3% |
| Choline | 11.8mg | 26mg | 3% |
| Carbs | 17.6g | 23.6g | 2% |
| Cholesterol | 51mg | 44mg | 2% |
| Zinc | 0.51mg | 0.69mg | 2% |
| Vitamin E | 0.06mg | 0.3mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.061mg | 0.041mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.22mg | 0.24mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.699mg | 0.581mg | 2% |
| Protein | 3.99g | 3.5g | 1% |
| Vitamin C | 0.1mg | 0.6mg | 1% |
| Calcium | 139mg | 128mg | 1% |
| Copper | 0.03mg | 0.023mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.064mg | 0.048mg | 1% |
| Folate | 9µg | 5µg | 1% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.312g | 0.452g | 1% |
| Net carbs | 17.6g | 22.9g | N/A |
| Magnesium | 16mg | 14mg | 0% |
| Potassium | 207mg | 199mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 4.82g | 21.22g | N/A |
| Sodium | 84mg | 80mg | 0% |
| Manganese | 0.007mg | 0.008mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.132mg | 0.116mg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 0.2µg | 0.3µg | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.082mg | 0.045mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.192mg | 0.146mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.207mg | 0.195mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.337mg | 0.316mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.214mg | 0.258mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.091mg | 0.081mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.173mg | 0.157mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.233mg | 0.217mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.092mg | 0.088mg | 0% |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0g | 0.003g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - DHA | 0.003g | 0g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Custard - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168773/nutrients
- Ice cream - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/167575/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






