Dulce de Leche vs. Caramel — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Dulce de leche is made by heating sugar and milk, whereas caramel is made by heating sugar and water.
Both dulce de leche and caramel are high-calorie and high-carb foods; however, caramel provides more calories, fats, and carbs when compared to dulce de leche.
Dulce de leche contains around 1.6 times more vitamin B2 and 1.3 times more vitamin B5. On the other hand, caramel contains around 6 times more vitamin B1. Dulce de leche is also richer in most minerals, including calcium, phosphorus, zinc, and potassium, while also containing 2 times less sodium than caramel.
Most health benefits found in these foods are associated with choline, while downsides or risks are associated with the high amounts of unhealthy fats and sugar levels.
Introduction
Dulce de leche and caramel are confectionery products made by heating sugar. Dulce de leche is prepared by heating sugar and milk, whereas caramel is prepared by heating sugar (usually white granulated) and water.
Caramel has a darker brown color and denser consistency.
Both dulce de leech and caramel are sweet, tasty, and improve our moods; however, their consumption increase the risk of various chronic diseases.
Use
Dulce de leche is used in a lot of ways. As an ingredient, it’s used in cakes, ice cream, ice cream sandwiches, sundae cups, cheesecakes, brownies, peach pies, caramel or bread puddings, doughnuts, and desserts; it can be used as a topping for waffles or pancakes, sweetens the milk or coffee as well.
Caramel is used in chip pancakes, caramel bacon, brownie bites, popcorn balls, cornbread, cookies, truffles, nuts, eclairs, and marshmallows. It is also used as a filling in chocolate candies, flavoring in puddings and desserts, and toppings for ice cream and cakes. Caramel is used in chai lattes, hot cocoa, and rum too.
Nutrition
The nutritional values are presented for dulce de leche and caramel.
Macronutrients and Calories
One serving of dulce de leche is usually 1 tbsp (19 grams), while one serving of caramel is one piece (10.1 grams).
Dulce de leche consists of 28.7% water, whereas caramel is much denser and consists of 8.5% water. Both are made primarily of carbs.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
ProteinProtein
+48.7%
Contains
more
WaterWater
+237.8%
Contains
more
FatsFats
+10.2%
Contains
more
CarbsCarbs
+39.1%
Calories
Both dulce de leche and caramel are very high in calories. However, caramel provides relatively more calories.
To make the comparison between the two easier, we will be reviewing 100-gram servings of each.
A 100-gram serving of dulce de leche provides 315 calories, whereas a 100-gram serving of caramel provides 382 calories.
Protein and Fats
Dulce de leche contains almost 1.5 times more proteins, whereas caramel contains slightly more fats.
Caramel is slightly richer in fats when compared to dulce de leche. The predominant fats found in caramel are polyunsaturated fatty acids, which are present 1.4 times more when compared to saturated fats.
On the other hand, the predominant fats found in dulce de leche are saturated fatty acids, which are present 12 times more than polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Dulce de leche contains 4 times more cholesterol compared to caramel.
Fat Type Comparison
Contains
more
Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat
+39%
Contains
less
Sat. FatSaturated fat
-45.4%
Contains
more
Poly. FatPolyunsaturated fat
+827.5%
Carbohydrates
Both dulce de leche and caramel are very high in carbs, with caramel containing almost 22g more carbs per 100-gram serving.
A 100g dulce de leche contains 55.35g of carbs, whereas caramel contains 77g. The carbs are mainly sugar (sucrose).
Vitamins
It is important to note that a single serving of neither caramel nor dulce de leche (10-20 grams) provides any significant amounts of vitamins. However, both contain small amounts of various vitamins, which we can compare.
The predominant vitamins found in caramel and dulce de leche are vitamin B2, vitamin B5, and vitamin B12.
Dulce de leche and caramel both contain equal amounts of vitamin B12. Dulce de leche contains around 1.6 times more vitamin B2 and 1.3 times more vitamin B5. On the other hand, caramel contains around 6 times more vitamin B1.
Caramel is absent in vitamin D, while dulce de leche contains small amounts.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+550%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+516.7%
Contains
more
Vitamin DVitamin D
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+58.2%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+41.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+34.7%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+175%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+130%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+543.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+250%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+38.5%
Minerals
Dulce de leche is richer in most of the minerals. It is richer in calcium, phosphorus, zinc, and potassium.
Caramel is also almost two times higher in sodium when compared to dulce de leche.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
MagnesiumMagnesium
+29.4%
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+81.9%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+63.6%
Contains
more
IronIron
+21.4%
Contains
more
ZincZinc
+79.5%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+69.3%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-47.3%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+50%
Contains
more
CopperCopper
+350%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+450%
Glycemic Index
There is no information provided about the glycemic index values of dulce de leche or caramel.
Acidity
The PRAL value or potential renal acid load value shows the amount of acid the consumed food produces.
The PRAL values for dulce de leche and caramel are -0.7 and -0.3, respectively. Dulce de leche has a more negative value; therefore, it is more base-producing when compared to caramel.
Weight Loss & Diets
Since both dulce de leche and caramel are high-calorie foods, they are not often included in weight loss diets.
Although they are not suitable for weight-loss diets, dulce de leche would be a better choice for low-carb, low-fat, and low-calorie diets when compared to caramel.
These foods can be used in the third and fourth stages of the Dukan Diet.
They are not a good choice for weight gain diets as well, as they contain too much sugar and lead to unhealthy weight gain.
Health Impact
Health Benefits
Neurological Health
Choline is a micronutrient required for normal brain development and growth. Dulce de leche contains 11 times more choline compared to caramel.
Choline plays an essential role in maintaining the structural and functional integrity of cell membranes; it leads to acetylcholine synthesis, which modulates cholinergic neurotransmission․
Choline improves mood, memory, and cognitive functions as well (1).
Research on mice has shown that choline supplementation during adulthood reveals a beneficial effect on Alzheimer’s disease progression and shows therapeutic effects for patients (2).
Downsides and Risks
Even though caramel and dulce de leche are good sources of nutrients and antioxidants, they mainly have adverse health effects caused by excess carbs and unhealthy fats.
Excess carbs are converted to triglycerides for long-term energy storage. A diet rich in carbs stimulates this process both in the liver and fat tissue leading to elevated postprandial triglycerides, showing adverse effects on health (3, 4).
Studies suggest replacing mentioned fats with polyunsaturated fatty acids, as they are better for health (5).
Cardiovascular Health
If you're comparing the two directly in terms of their impact on CVD, Dulce de Leche might have a slight advantage. This is because dulce de leche is typically made with milk, which provides some essential nutrients like calcium and protein. Caramel, on the other hand, is primarily sugar and doesn't offer much in terms of nutritional value.
Fats mentioned above are another reason for cardiovascular and coronary heart disease risks; fats worsen the progression of the disease and increase all-cause mortality rates.
Unhealthy fats are associated with changes in the heart’s structure and function, predominantly the heart’s left ventricle, leading to its mass and volume gain (6).
High cholesterol impacts cardiac arrhythmias and leads to the development of atherosclerosis (7, 8).
Acrolein is a compound formed during the fat-heating process in caramel and is associated with increased cardiovascular disease risk (9, 10).
Respiratory Health
Diacetyl is a butter flavoring in caramel that may adversely affect the respiratory system. Employees with jobs involving diacetyl exposure or food flavorings containing diacetyl show increased occurrence of airway obstruction, bronchiolitis obliterans, or “popcorn lung,” and other respiratory disorders (11).
Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease & Insulin Resistance
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is the most common liver disease that affects up to a quarter of the population. One of its types is hepatic steatosis or fatty liver.
In most cases, hepatic steatosis is linked to increased fat ingestion. The disease is characterized by increased liver uptake of free fatty acids and de novo lipogenesis (fat synthesis from carbs). On the one hand, insulin resistance plays its role in developing and progressing hepatic steatosis; on the other hand, hepatic steatosis is linked to the secondary development of hepatic insulin resistance (12, 13, 14).
Diabetes
Large amounts or frequent use of dulce de leche and caramel lead to unhealthy weight gain and increase the risk of obesity. Obesity usually goes in parallel with fatty liver, metabolic syndrome, and insulin resistance leading to a high likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes (15, 16, 17).
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31817768/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31298459/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24814684/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1083868/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28645222/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33213727/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20602558/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32645995/
- Ultra-processed food intake and cardiovascular disease risk
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25099132/
- Occupational Exposure to Diacetyl and Food Flavorings Containing Diacetyl
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29936596/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28585211/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15571427/
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1179/acb.2003.58.6.001
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20693348/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31424428/
Infographic
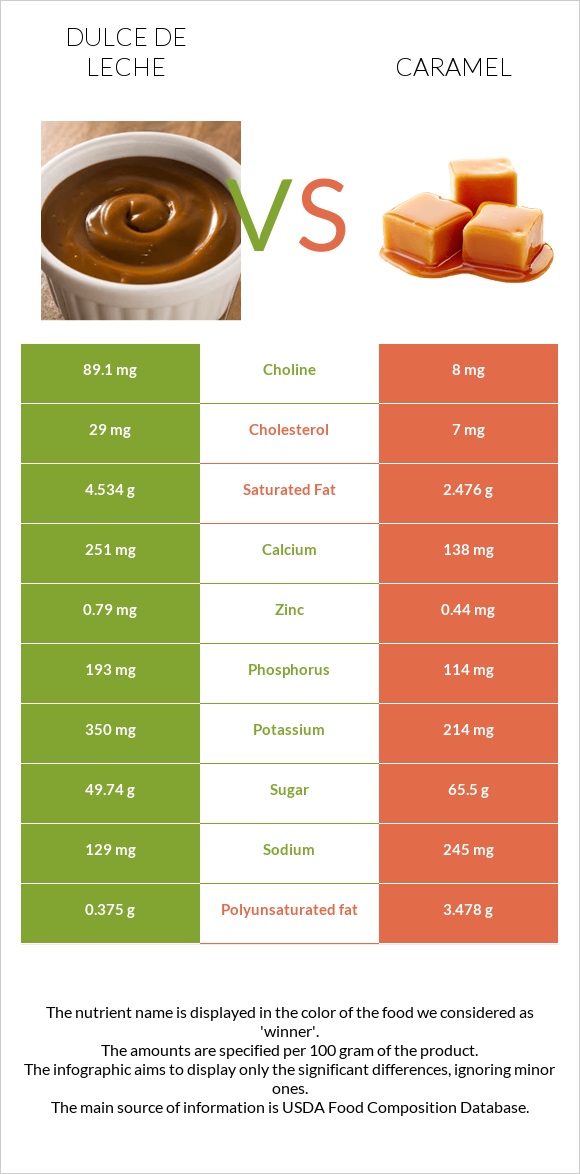
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.375g | 3.478g | 21% |
| Choline | 89.1mg | 8mg | 15% |
| Calcium | 251mg | 138mg | 11% |
| Phosphorus | 193mg | 114mg | 11% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.405mg | 0.256mg | 11% |
| Saturated fat | 4.534g | 2.476g | 9% |
| Carbs | 55.35g | 77g | 7% |
| Cholesterol | 29mg | 7mg | 7% |
| Vitamin A | 74µg | 12µg | 7% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.016mg | 0.103mg | 7% |
| Sodium | 129mg | 245mg | 5% |
| Protein | 6.84g | 4.6g | 4% |
| Potassium | 350mg | 214mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.835mg | 0.62mg | 4% |
| Calories | 315kcal | 382kcal | 3% |
| Zinc | 0.79mg | 0.44mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.016mg | 0.056mg | 3% |
| Vitamin C | 2.6mg | 0.4mg | 2% |
| Copper | 0.004mg | 0.018mg | 2% |
| Vitamin E | 0.2mg | 0.46mg | 2% |
| Selenium | 2.7µg | 1.8µg | 2% |
| Folate | 11µg | 4µg | 2% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 2.143g | 1.542g | 2% |
| Fats | 7.35g | 8.1g | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 6 IU | 0 IU | 1% |
| Magnesium | 22mg | 17mg | 1% |
| Vitamin D | 0.2µg | 0µg | 1% |
| Net carbs | 55.35g | 77g | N/A |
| Iron | 0.17mg | 0.14mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 49.74g | 65.5g | N/A |
| Manganese | 0.002mg | 0.011mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.21mg | 0.148mg | 0% |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.31µg | 0.3µg | 0% |
| Vitamin K | 1.3µg | 1.8µg | 0% |
| Trans fat | 0.364g | N/A | |
| Tryptophan | 0.06mg | 0% | |
| Threonine | 0.192mg | 0% | |
| Isoleucine | 0.258mg | 0% | |
| Leucine | 0.417mg | 0% | |
| Lysine | 0.338mg | 0% | |
| Methionine | 0.107mg | 0% | |
| Phenylalanine | 0.205mg | 0% | |
| Valine | 0.285mg | 0% | |
| Histidine | 0.115mg | 0% | |
| Fructose | 0.32g | 0% | |
| Omega-3 - EPA | 0.004g | 0g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - ALA | 0.05g | N/A | |
| Omega-3 - DPA | 0.009g | 0g | N/A |
| Omega-3 - Eicosatrienoic acid | 0.001g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Gamma-linoleic acid | 0.002g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Dihomo-gamma-linoleic acid | 0.005g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Eicosadienoic acid | 0.001g | N/A | |
| Omega-6 - Linoleic acid | 0.131g | N/A |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Dulce de Leche - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173461/nutrients
- Caramel - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/167974/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.