Fava beans vs. Lima beans — Health Impact and Nutrition Comparison


Summary
Lima beans are richer in fiber, manganese, potassium, iron, and vitamins B1, B5, and B6. Fava beans are richer in copper, phosphorus, vitamin B2, and folate. Fava beans can be eaten raw, but lima beans should be cooked because they contain cyanotic glycosides, which are toxic.
Introduction
In this article, we will compare two types of legumes; lima beans and fava beans. These beans are commonly used around the world. Noting that lima beans are used more in European and American cuisine. In comparison, fava beans are used more in Middle Eastern and Mediterranean cuisine.
Lima beans are also known as butter beans because of their smooth and creamy texture after cooking. On the other hand, fava beans are known as broad beans.
Taste
Lima beans are smooth and creamy with a nutty flavor after cooking. Fava beans have a sweeter flavor than lima beans. In comparison, fava beans can be eaten raw or cooked, and they have a different flavor profile when it's cooked or not.
Nutritional content comparison
This section will compare 100g of each in cooked forms.
Calories
Lima beans contain 115 b, and fava beans contain 110 calories. They have similar amounts.
Carbs
They have nearly equal amounts of carbs. Approximately 20g for each.
Fiber
They are both excellent sources of fiber.
Lima beans are richer in fiber than fava beans. Lima beans contain 7.4g of fiber, and fava beans contain 5g.
Protein
They have similar amounts of proteins, about 7.7g for each.
Fats
Their fat content is negligible.
Macronutrient Comparison
Contains
more
OtherOther
+42%
To read more about different types of bean comparisons, you can read about navy bean vs. green bean or kidney bean vs. pigeon bean.
Minerals
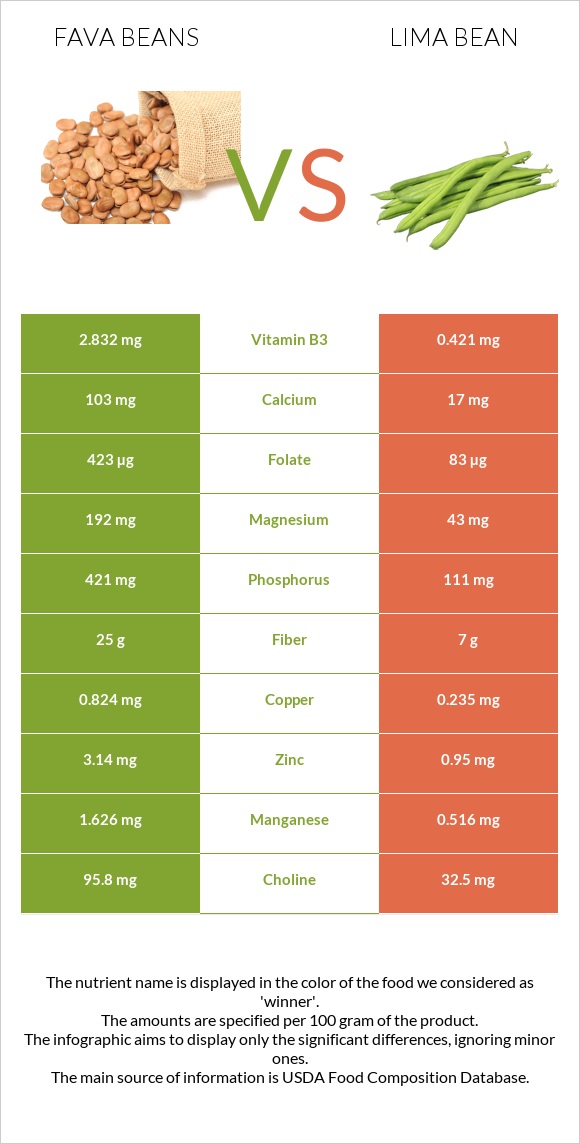
Lima beans are richer in manganese, potassium, and iron. In comparison, fava beans are richer in copper and phosphorus.
Mineral Comparison
Contains
more
CalciumCalcium
+111.8%
Contains
more
PhosphorusPhosphorus
+12.6%
Contains
more
PotassiumPotassium
+89.6%
Contains
more
IronIron
+59.3%
Contains
less
SodiumSodium
-60%
Contains
more
ManganeseManganese
+22.6%
Contains
more
SeleniumSelenium
+73.1%
Vitamins
Lima beans are richer in vitamins B1, B5, and B6. In comparison, fava beans are richer in vitamins B2 and folate.
Vitamin Comparison
Contains
more
Vitamin CVitamin C
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin AVitamin A
+∞%
Contains
more
Vitamin B2Vitamin B2
+61.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B3Vitamin B3
+68.9%
Contains
more
Vitamin KVitamin K
+45%
Contains
more
FolateFolate
+25.3%
Contains
more
Vitamin EVitamin E
+800%
Contains
more
Vitamin B1Vitamin B1
+66%
Contains
more
Vitamin B5Vitamin B5
+168.8%
Contains
more
Vitamin B6Vitamin B6
+123.6%
Health impacts
Digestion
Both beans are a rich source of fiber; however, since they are richer in fiber, lima beans are ideal legumes to add to our diets. A high-fiber diet decreases the risks of colorectal cancer and diverticular disease and improves gut microbiome and bowel movements. (1)(2)(3)
Unlike lima beans, fava beans are high in FODMAPs, poorly digested carbs that may cause bloating, gases, and abdominal pain. People with IBS or on a low FODMAP diet should avoid fava beans.
G6P deficiency patients
Individuals with G6P deficiency should not consume fava beans since they induce a hemolytic attack. Foods that are often cooked with fava beans should be restricted, falafel is more often done with fava beans, and this should be restricted. (5)
Cyanogenic glycosides
It is important to cook and properly prepare lima beans because they contain toxic cyanogenic glycosides in humans. By thoroughly cooking lima beans, this toxin is eliminated. (6)
Fava beans can be eaten raw; they do not contain cyanogenic glycosides.
Infographic
All nutrients comparison - raw data values
| Nutrient |  |
 |
DV% diff. |
| Iron | 1.5mg | 2.39mg | 11% |
| Potassium | 268mg | 508mg | 7% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.072mg | 0.161mg | 7% |
| Fiber | 5.4g | 7g | 6% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.097mg | 0.161mg | 5% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.157mg | 0.422mg | 5% |
| Folate | 104µg | 83µg | 5% |
| Manganese | 0.421mg | 0.516mg | 4% |
| Copper | 0.259mg | 0.235mg | 3% |
| Selenium | 2.6µg | 4.5µg | 3% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.089mg | 0.055mg | 3% |
| Calcium | 36mg | 17mg | 2% |
| Phosphorus | 125mg | 111mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.711mg | 0.421mg | 2% |
| Zinc | 1.01mg | 0.95mg | 1% |
| Vitamin E | 0.02mg | 0.18mg | 1% |
| Vitamin K | 2.9µg | 2µg | 1% |
| Calories | 110kcal | 115kcal | 0% |
| Protein | 7.6g | 7.8g | 0% |
| Fats | 0.4g | 0.38g | 0% |
| Vitamin C | 0.3mg | 0mg | 0% |
| Net carbs | 14.25g | 13.88g | N/A |
| Carbs | 19.65g | 20.88g | 0% |
| Magnesium | 43mg | 43mg | 0% |
| Sugar | 1.82g | 2.9g | N/A |
| Sodium | 5mg | 2mg | 0% |
| Vitamin A | 1µg | 0µg | 0% |
| Choline | 30.6mg | 32.5mg | 0% |
| Saturated fat | 0.066g | 0.089g | 0% |
| Monounsaturated fat | 0.079g | 0.034g | 0% |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 0.164g | 0.171g | 0% |
| Tryptophan | 0.072mg | 0.092mg | 0% |
| Threonine | 0.27mg | 0.337mg | 0% |
| Isoleucine | 0.306mg | 0.411mg | 0% |
| Leucine | 0.572mg | 0.673mg | 0% |
| Lysine | 0.486mg | 0.523mg | 0% |
| Methionine | 0.062mg | 0.099mg | 0% |
| Phenylalanine | 0.321mg | 0.449mg | 0% |
| Valine | 0.338mg | 0.469mg | 0% |
| Histidine | 0.193mg | 0.238mg | 0% |
Fat Type Comparison
| Contains less Sat. FatSaturated fat | -25.8% |
| Contains more Mono. FatMonounsaturated fat | +132.4% |
People also compare
References
All the values for which the sources are not specified explicitly are taken from FDA’s Food Central. The exact link to the food presented on this page can be found below.
- Fava beans - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173753/nutrients
- Lima beans - https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/174253/nutrients
All the Daily Values are presented for males aged 31-50, for 2000-calorie diets.






